|
Acrocephalosyndactylia
Acrocephalosyndactyly is a group of autosomal dominant congenital disorders characterized by craniofacial (craniosynostosis) and hand and foot (syndactyly) abnormalities. When polydactyly is present, the classification is acrocephalopolysyndactyly. Acrocephalosyndactyly is mainly diagnosed postnatally, although prenatal diagnosis is possible if the mutation is known to be within the family genome. Treatment often involves surgery in early childhood to correct for craniosynostosis and syndactyly. Characteristics Acrocephalosyndactyly presents in numerous different subtypes, however, considerable overlap in symptoms occurs. Generally, all forms of acrocephalosyndactyly are characterized by craniofacial, hand, and foot abnormalities, such as premature closure of the fibrous joints in between certain bones of the skull, fusion of certain fingers or toes, and/or more than the normal number of digits. Some subtypes also involve structural heart deformations that are present at birth. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pfeiffer Syndrome
Pfeiffer syndrome is a rare genetic disorder characterized by the premature fusion of certain bones of the skull (craniosynostosis) which affects the shape of the head and face. In addition, the syndrome includes abnormalities of the hands (such as wide and deviated thumbs) and feet (such as wide and deviated big toes). Pfeiffer syndrome is caused by mutations in the fibroblast growth factor receptors ''FGFR1'' and ''FGFR2''. The syndrome is grouped into three types, type 1 (classic Pfeiffer syndrome) being milder and caused by mutations in either gene and types 2 and 3 being more severe, often leading to death in infancy, caused by mutations in ''FGFR2''. There is no cure for the syndrome. Treatment is supportive and often involves surgery in the earliest years of life to correct skull deformities and respiratory function. Most individuals with Pfeiffer syndrome type 1 have a normal intelligence and life span, while types 2 and 3 typically result in neurodevelopmental disorde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Medical Genetics
Medical genetics is the branch tics in that human genetics is a field of scientific research that may or may not apply to medicine, while medical genetics refers to the application of genetics to medical care. For example, research on the causes and inheritance of genetic disorders would be considered within both human genetics and medical genetics, while the diagnosis, management, and counselling people with genetic disorders would be considered part of medical genetics. In contrast, the study of typically non-medical phenotypes such as the genetics of eye color would be considered part of human genetics, but not necessarily relevant to medical genetics (except in situations such as albinism). ''Genetic medicine'' is a newer term for medical genetics and incorporates areas such as gene therapy, personalized medicine, and the rapidly emerging new medical specialty, predictive medicine. Scope Medical genetics encompasses many different areas, including clinical practice of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amniocentesis
Amniocentesis is a medical procedure used primarily in the prenatal diagnosis of genetic conditions. It has other uses such as in the assessment of infection and fetal lung maturity. Prenatal diagnostic testing, which includes amniocentesis, is necessary to conclusively diagnose the majority of genetic disorders, with amniocentesis being the gold-standard procedure after 15 weeks' gestation. In this procedure, a thin needle is inserted into the abdomen of the pregnant woman. The needle punctures the amnion, which is the membrane that surrounds the developing fetus. The fluid within the amnion is called amniotic fluid, and because this fluid surrounds the developing fetus, it contains fetal cells. The amniotic fluid is sampled and analyzed via methods such as karyotyping and DNA analysis technology for genetic abnormalities. An amniocentesis is typically performed in the second trimester between the 15th and 20th week of gestation. Women who choose to have this test are prima ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
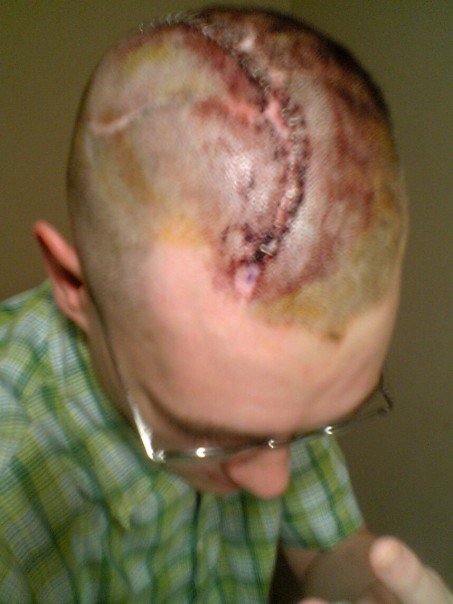
Cranioplasty
Cranioplasty is a surgical operation on the repairing of cranial defects caused by previous injuries or operations, such as decompressive craniectomy. It is performed by filling the defective area with a range of materials, usually a bone piece from the patient or a synthetic material. Cranioplasty is carried out by incision and reflection of the scalp after applying anaesthetics and antibiotics to the patient. The temporalis muscle is reflected, and all surrounding soft tissues are removed, thus completely exposing the cranial defect. The cranioplasty flap is placed and secured on the cranial defect. The wound is then sealed. Cranioplasty was closely related to trephination and the earliest operation is dated to 3000 BC. Currently, the procedure is performed for both cosmetic and functional purposes. Cranioplasty can restore the normal shape of the skull and prevent other complications caused by a sunken scalp, such as the "syndrome of the trephined". Cranioplasty is a risky opera ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brachycephaly
Brachycephaly (derived from the Ancient Greek '' βραχύς'', 'short' and '' κεφαλή'', 'head') is the shape of a skull shorter than typical for its species. It is perceived as a desirable trait in some domesticated dog and cat breeds, notably the pug and Persian, and can be normal or abnormal in other animal species. In humans, the cephalic disorder is known as flat head syndrome, and results from premature fusion of the coronal sutures, or from external deformation. The coronal suture is the fibrous joint that unites the frontal bone with the two parietal bones of the skull. The parietal bones form the top and sides of the skull. This feature can be seen in Down syndrome. In anthropology, human populations have been characterized as either dolichocephalic (long-headed), mesaticephalic (moderate-headed), or brachycephalic (short-headed). The usefulness of the cephalic index was questioned by Giuseppe Sergi, who argued that cranial morphology provided a better mean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sakati–Nyhan–Tisdale Syndrome
Sakati–Nyhan–Tisdale syndrome, is a rare genetic disorder that has been associated with abnormalities in the bones of the legs, congenital heart defects and craniofacial defects. The syndrome belongs to a group of rare genetic disorders known as acrocephalopolysyndactyly or ACPS, for short. Presentation The syndrome was first reported in an eight-year-old boy, but very few cases have been reported since then. The syndrome is detected by abnormalities noted at birth involving the head, limbs, heart, ears, and skin. It is characterized by premature closure of the fibrous joints between certain bones of the skull in a process known as craniosynostosis. As documented in the first case, the victim tends to suffer from cyanosis and other respiratory and breathing infections, all before the age of one. Body development subsequently slows down, but some problems can be fixed under proper guidance, such as learning to walk with special crutches by five years of age. Craniofacial proble ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saethre–Chotzen Syndrome
Saethre–Chotzen syndrome (SCS), also known as acrocephalosyndactyly type III, is a rare congenital disorder associated with craniosynostosis (premature closure of one or more of the sutures between the bones of the skull). This affects the shape of the head and face, resulting in a cone-shaped head and an asymmetrical face. Individuals with SCS also have droopy eyelids ( ptosis), widely spaced eyes (hypertelorism), and minor abnormalities of the hands and feet (syndactyly). Individuals with more severe cases of SCS may have mild to moderate intellectual or learning disabilities. Depending on the level of severity, some individuals with SCS may require some form of medical or surgical intervention. Most individuals with SCS live fairly normal lives, regardless of whether medical treatment is needed or not. Signs and symptoms SCS presents in a variable fashion. The majority of individuals with SCS are moderately affected, with uneven facial features and a relatively flat face due t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orofaciodigital Syndrome
Orofaciodigital syndrome or oral-facial-digital syndrome is a group of at least 13 related conditions that affect the development of the mouth, facial features, and digits in between 1 in 50,000 to 250,000 newborns with the majority of cases being type I (Papillon-League-Psaume syndrome). __TOC__ Type The different types are:s * Type I, Papillon-League-Psaume syndrome * Type II, Mohr syndrome * Type III, Sugarman syndrome * Type IV, Baraitser-Burn syndrome * Type V, Thurston syndrome * Type VI, Varadi-Papp syndrome * Type VII, Whelan syndrome * Type VIII, Oral-facial-digital syndrome, Edwards type (not to be confused with Edwards syndrome) * Type IX, OFD syndrome with retinal abnormalities * Type X, OFD with fibular aplasia The fibula or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. Its upper extremity i ... * Ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crouzon Syndrome
Crouzon syndrome is an autosomal dominant genetic disorder known as a branchial arch syndrome. Specifically, this syndrome affects the first branchial (or pharyngeal) arch, which is the precursor of the maxilla and mandible. Since the branchial arches are important developmental features in a growing embryo, disturbances in their development create lasting and widespread effects. This syndrome is named after Octave Crouzon, a French physician who first described this disorder. First called "craniofacial dysostosis" ("craniofacial" refers to the skull and face, and " dysostosis" refers to malformation of bone), the disorder was characterized by a number of clinical features which can be described by the rudimentary meanings of its former name. This syndrome is caused by a mutation in the fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 (''FGFR2''), located on chromosome 10. The developing fetus's skull and facial bones fuse early or are unable to expand. Thus, normal bone growth cannot occur. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apert Syndrome
Apert syndrome is a form of acrocephalosyndactyly, a congenital disorder characterized by malformations of the skull, face, hands and feet. It is classified as a branchial arch syndrome, affecting the first branchial (or pharyngeal) arch, the precursor of the maxilla and mandible. Disturbances in the development of the branchial arches in fetal development create lasting and widespread effects. In 1906, Eugène Apert, a French physician, described nine people sharing similar attributes and characteristics. Linguistically, in the term "acrocephalosyndactyly", ''acro'' is Greek for "peak", referring to the "peaked" head that is common in the syndrome; ''cephalo'', also from Greek, is a combining form meaning "head"; ''syndactyly'' refers to webbing of fingers and toes. In embryology, the hands and feet have selective cells that die in a process called selective cell death, or apoptosis, causing separation of the digits. In the case of acrocephalosyndactyly, selective cell death ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Testing
Genetic testing, also known as DNA testing, is used to identify changes in DNA sequence or chromosome structure. Genetic testing can also include measuring the results of genetic changes, such as RNA analysis as an output of gene expression, or through biochemical analysis to measure specific protein output. In a medical setting, genetic testing can be used to diagnose or rule out suspected genetic disorders, predict risks for specific conditions, or gain information that can be used to customize medical treatments based on an individual's genetic makeup. Genetic testing can also be used to determine biological relatives, such as a child's biological parentage (genetic mother and father) through DNA paternity testing, or be used to broadly predict an individual's ancestry. Genetic testing of plants and animals can be used for similar reasons as in humans (e.g. to assess relatedness/ancestry or predict/diagnose genetic disorders), to gain information used for selective breeding, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Radiography
Radiography is an imaging technique using X-rays, gamma rays, or similar ionizing radiation and non-ionizing radiation to view the internal form of an object. Applications of radiography include medical radiography ("diagnostic" and "therapeutic") and industrial radiography. Similar techniques are used in airport security (where "body scanners" generally use backscatter X-ray). To create an image in conventional radiography, a beam of X-rays is produced by an X-ray generator and is projected toward the object. A certain amount of the X-rays or other radiation is absorbed by the object, dependent on the object's density and structural composition. The X-rays that pass through the object are captured behind the object by a detector (either photographic film or a digital detector). The generation of flat two dimensional images by this technique is called projectional radiography. In computed tomography (CT scanning) an X-ray source and its associated detectors rotate around the su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)
