|
Abu Ahmad Monajjem
Abu Ahmad Yahya ibn Ali ibn Yahya ibn Abi Mansur Aban al-Monajjem ( ar, ōßō®Ŕąōßō≠ŔÖōĮ ŘĆō≠ŘĆŘĆ ōßō®ŔÜ ōĻŔĄŘĆ ōßō®ŔÜ ŘĆō≠ŘĆŘĆ ōßō®ŔÜ ōßō®ŘĆ ŔÖŔÜōĶŔąōĪ ōĘō®ōßŔÜ ōßŔĄŔÖŔÜō¨ŔÖ) (b. 241/855-56, died in 13 Rabi' I 300/29 October 912) was a medieval Persian music theorist, literary historian and poet. He belonged to the family of Banu Munajjem, a family of Iranian descent, associated with the Abbasid court for more than two centuries. His father 'Alńę ibn YaŠł•yńĀ al-Munajjim (died 888) was a student of the renowned musician Ishaq al-Mawsili. He is mainly famous for a treatise on music, ''ResńĀla fi‚Äôl-mŇęsńęqńę'' written for Al-Mu'tadid AbŇę al- ŅAbbńĀs AŠł•mad ibn ŠĻ¨alŠł•a al-Muwaffaq ( ar, ō£ō®Ŕą ōßŔĄōĻō®ōßō≥ ō£ō≠ŔÖōĮ ō®ŔÜ ō∑ŔĄō≠ō© ōßŔĄŔÖŔąŔĀŔā), 853/4 or 860/1 ‚Äď 5 April 902, better known by his regnal name al-Mu ŅtaŠłćid bi-llńĀh ( ar, ōßŔĄŔÖōĻō™ō∂ōĮ ō®ōßŔĄŔĄŔá, link=no, .... His other famous work, of equal importance, is a compilation of biographies with some poetry nam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persian People
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian. The ancient Persians were originally an ancient Iranian people who had migrated to the region of Persis (corresponding to the modern-day Iranian province of Fars) by the 9th century BCE. Together with their compatriot allies, they established and ruled some of the world's most powerful empires that are well-recognized for their massive cultural, political, and social influence, which covered much of the territory and population of the ancient world.. Throughout history, the Persian people have contributed greatly to art and science. Persian literature is one of the world's most prominent literary traditions. In contemporary terminology, people from Afghanistan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan who natively speak the Persian language are know ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banu Munajjem
The Banu al-Munajjim ( ar, ō®ŔÜŔą ōßŔĄŔÖŔÜō¨ŔÖ), was an Iranian family of Abbasid officials attested in the 9th and 10th centuries. They claimed descent from the Sasanian dynasty, and were closely related to the Abbasid caliphs by marriage. History According to Ibn al-Nadim, the Banu al-Munajjim were descended from Mihr-Gushnasp, a son of the last Sasanian king Yazdegerd III (r. 632‚Äď651). The family is first mentioned in the 9th century, when the eponymous ancestor of the family, Abu Mansur al-Munajjim (originally named Aban-Gushnasp), worked at the court of the second Abbasid caliph, al-Mansur (r. 754‚Äď775) as an astrologer (''al-munajjim''). His son, Yahya, worked at the Abbasid court under al-Ma'mun (r. 813‚Äď833), and later converted from Zoroastrianism to Islam. Yahya had four sons named Ali, Sa'id, Abdallah, and Hasan. These four sons would, like their father, work at the Abbasid court. Ali even befriended the caliph al-Mutawakkil (r. 847‚Äď861), and his son Ya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
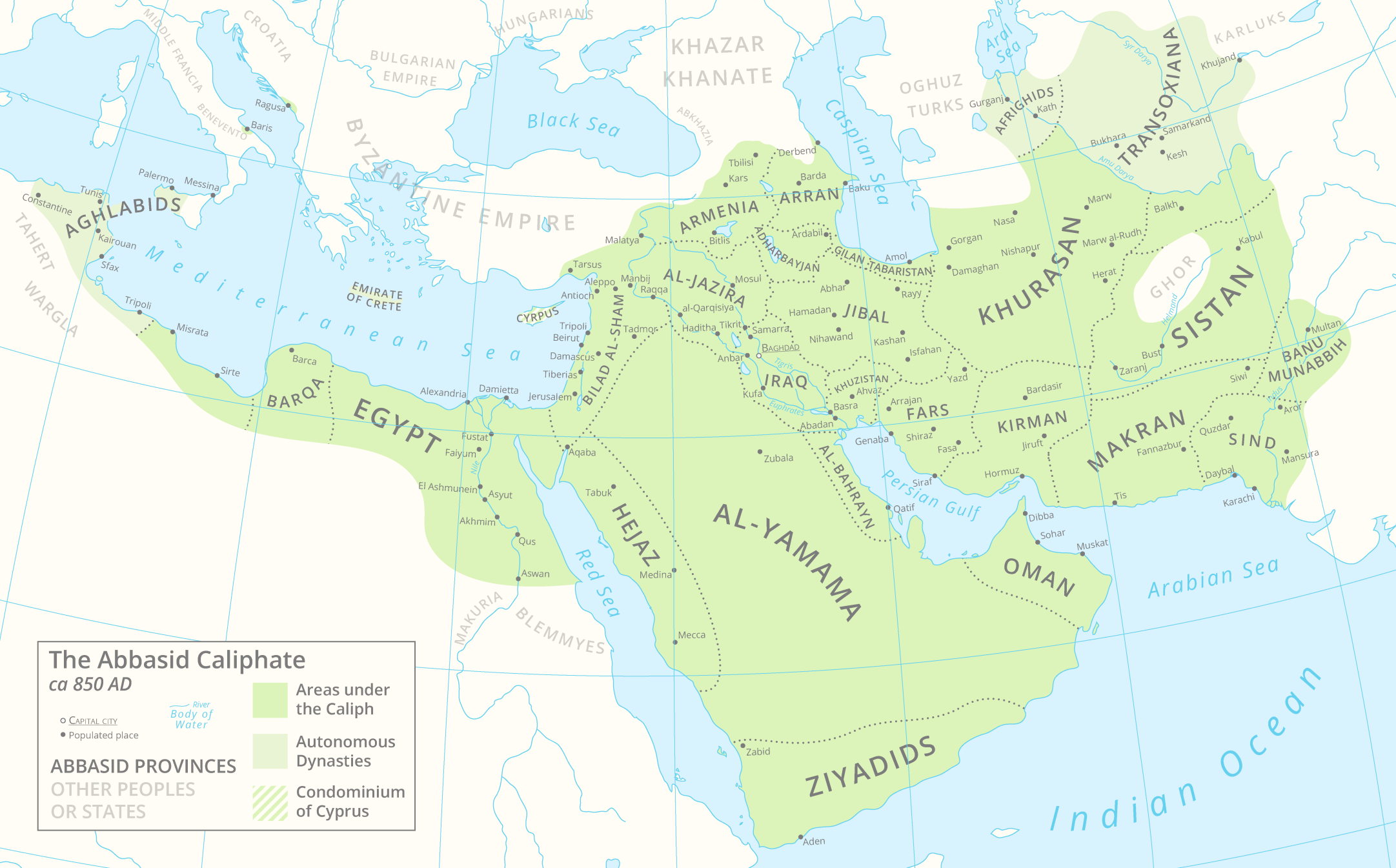
Abbasid Caliphate
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, ōßŔĄŔíōģŔźŔĄŔéōßŔĀŔéō©ŔŹ ōßŔĄŔíōĻŔéō®ŔéŔĎōßō≥ŔźŔäŔéŔĎō©, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib (566‚Äď653 CE), from whom the dynasty takes its name. They ruled as caliphs for most of the caliphate from their capital in Baghdad in modern-day Iraq, after having overthrown the Umayyad Caliphate in the Abbasid Revolution of 750 CE (132 AH). The Abbasid Caliphate first centered its government in Kufa, modern-day Iraq, but in 762 the caliph Al-Mansur founded the city of Baghdad, near the ancient Babylonian capital city of Babylon. Baghdad became the center of science, culture and invention in what became known as the Golden Age of Islam. This, in addition to housing several key academic institutions, including the House of Wisdom, as well as a multiethnic and multi-religious environment, garnered it a worldwide reputation as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ishaq Al-Mawsili
Ishaq al-Mawsili ( ar, ō•ō≥ō≠ōßŔā ōßŔĄŔÖŔąōĶŔĄŔä; 767/772 ‚Äď March 850) was an Arab musician of Persian origin active as a composer, singer, music theorist and writer on music. The leading musician of his time in the Abbasid Caliphate, he served under six successive Abbasid caliphs: Harun al-Rashid, Al-Amin, Al-Ma'mun, Al-Mu'tasim, Al-Wathiq and Al-Mutawakkil. The caliphs and Abbasid court held him in high regard, and his diverse intellect elevated him to a social status that was highly unusual for musicians of the time. Taught by his similarly renowned father Ibrahim al-Mawsili and the noted lutenist Zalzal, he succeeded his father in leading the conservative musical establishment, putting him at odds with progressive musicians such as Ibrahim ibn al-Mahdi and Ziryab. He has appeared in the ''Maqamat'' of Al-Hariri of Basra and ''One Thousand and One Nights''. Life and career Early life Modern sources vary on the exact location and birthdate of Ishaq al-Mawsili. The arabist Ev ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grove Music Online
''The New Grove Dictionary of Music and Musicians'' is an encyclopedic dictionary of music and musicians. Along with the German-language ''Die Musik in Geschichte und Gegenwart'', it is one of the largest reference works on the history and theory of music. Earlier editions were published under the titles ''A Dictionary of Music and Musicians'', and ''Grove's Dictionary of Music and Musicians''; the work has gone through several editions since the 19th century and is widely used. In recent years it has been made available as an electronic resource called ''Grove Music Online'', which is now an important part of ''Oxford Music Online''. ''A Dictionary of Music and Musicians'' ''A Dictionary of Music and Musicians'' was first published in London by Macmillan and Co. in four volumes (1879, 1880, 1883, 1889) edited by George Grove with an Appendix edited by J. A. Fuller Maitland in the fourth volume. An Index edited by Mrs. E. Wodehouse was issued as a separate volume in 1890. In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxford University Press
Oxford University Press (OUP) is the university press of the University of Oxford. It is the largest university press in the world, and its printing history dates back to the 1480s. Having been officially granted the legal right to print books by decree in 1586, it is the second oldest university press after Cambridge University Press. It is a department of the University of Oxford and is governed by a group of 15 academics known as the Delegates of the Press, who are appointed by the vice-chancellor of the University of Oxford. The Delegates of the Press are led by the Secretary to the Delegates, who serves as OUP's chief executive and as its major representative on other university bodies. Oxford University Press has had a similar governance structure since the 17th century. The press is located on Walton Street, Oxford, opposite Somerville College, in the inner suburb of Jericho. For the last 500 years, OUP has primarily focused on the publication of pedagogical texts and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Mu'tadid
AbŇę al- ŅAbbńĀs AŠł•mad ibn ŠĻ¨alŠł•a al-Muwaffaq ( ar, ō£ō®Ŕą ōßŔĄōĻō®ōßō≥ ō£ō≠ŔÖōĮ ō®ŔÜ ō∑ŔĄō≠ō© ōßŔĄŔÖŔąŔĀŔā), 853/4 or 860/1 ‚Äď 5 April 902, better known by his regnal name al-Mu ŅtaŠłćid bi-llńĀh ( ar, ōßŔĄŔÖōĻō™ō∂ōĮ ō®ōßŔĄŔĄŔá, link=no, "Seeking Support in God"), was the caliph of the Abbasid Caliphate from 892 until his death in 902. Al-Mu'tadid was the son of al-Muwaffaq, who was the regent and effective ruler of the Abbasid state during the reign of his brother, Caliph al-Mu'tamid. As a prince, the future al-Mu'tadid served under his father during various military campaigns, most notably in the suppression of the Zanj Rebellion, in which he played a major role. When al-Muwaffaq died in June 891 al-Mu'tadid succeeded him as regent. He quickly sidelined his cousin and heir-apparent al-Mufawwid; when al-Mu'tamid died in October 892, he succeeded to the throne. Like his father, al-Mu'tadid's power depended on his close relations with the army. These were first forged duri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Marzubani
AbŇę 'Abd AllńĀh MuŠł•ammad ibn 'ImrńĀn ibn MŇęsńĀ ibn Sa'ńęd ibn 'Abd AllńĀh al-MarzubńĀnńę () (c. 909 ‚Äď 10 November 994), was a prolific author of adab, akhbar (news), history and Šł•adńęth (traditions). He lived all his life in his native city, Baghdad, although his family came originally from KhurńĀsńĀn. Life Al-MarzubńĀnńę came from a wealthy family connected to the royal court of the AbbńĀsid caliph. Ibn al-JawńĀlńęqńę in his ''KitńĀb al-Mu'arrab'',Sachau. Gawaliqi's Almu'arrab mit Erl√§uterungen herausgegeben. Leipzig, 1867. explains that al-MarzubńĀnńę inherited his Persian epithet "Marzban", which means 'Guardian of the frontier'. The Buyid amir ‚ÄėAŠłćŇęd al-Dawla was known to visit his residence on the east bank of the Tigris, where he would also entertain members of a literary circle dedicated to the conservation and transmission of Arabic philological literature. Fellow authors in his circle were AbŇę Ya'qŇęb al-Najńęramńę (d.1031), AbŇę Sa'ńęd al-SńęrńĀfńę ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Persian Arabic-language Poets
Persian may refer to: * People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language ** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples ** Persian language, an Iranian language of the Indo-European family, native language of ethnic Persians *** Persian alphabet, a writing system based on the Perso-Arabic script * People and things from the historical Persian Empire Other uses * Persian (patience), a card game * Persian (roll), a pastry native to Thunder Bay, Ontario * Persian (wine) * Persian, Indonesia, on the island of Java * Persian cat, a long-haired breed of cat characterized by its round face and shortened muzzle * The Persian, a character from Gaston Leroux's ''The Phantom of the Opera'' * Persian, a generation I Pokémon species * Alpha Indi, star also known as "The Persian" See also * Persian Empire (other) * Persian expedition (other) or Persian campaign * Persian Gulf (other) * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
9th-century Persian-language Poets
The 9th century was a period from 801 ( DCCCI) through 900 ( CM) in accordance with the Julian calendar. The Carolingian Renaissance and the Viking raids occurred within this period. In the Middle East, the House of Wisdom was founded in Abbasid Baghdad, attracting many scholars to the city. The field of algebra was founded by the Muslim polymath al-Khwarizmi. The most famous Islamic Scholar Ahmad ibn Hanbal was tortured and imprisoned by Abbasid official Ahmad ibn Abi Du'ad during the reign of Abbasid caliph al-Mu'tasim and caliph al-Wathiq. In Southeast Asia, the height of the Mataram Kingdom happened in this century, while Burma would see the establishment of the major kingdom of Pagan. Tang China started the century with the effective rule under Emperor Xianzong and ended the century with the Huang Chao rebellions. While the Maya experienced widespread political collapse in the central Maya region, resulting in internecine warfare, the abandonment of cities, and a northward ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10th-century Persian-language Poets
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number representing a single or the only entity. 1 is also a numerical digit and represents a single unit of counting or measurement. For example, a line segment of ''unit length'' is a line segment of length 1. In conventions of sign where zero is considered neither positive nor negative, 1 is the first and smallest positive integer. It is also sometimes considered the first of the infinite sequence of natural numbers, followed by 2, although by other definitions 1 is the second natural number, following 0. The fundamental mathematical property of 1 is to be a multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. Most if not all properties of 1 can be deduced from this. In advanced mathematics, a multiplicative identity is often denoted 1, even if it is not a number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number; this was not universally accepted until the mid-20th century. Additionally, 1 is the s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
9th-century Persian-language Writers
The 9th century was a period from 801 (Roman numerals, DCCCI) through 900 (Roman numerals, CM) in accordance with the Julian calendar. The Carolingian Renaissance and the Viking raids occurred within this period. In the Middle East, the House of Wisdom was founded in Abbasid Caliphate, Abbasid Baghdad, attracting many scholars to the city. The field of algebra was founded by the Muslim polymath al-Khwarizmi. The most famous Islamic Scholar Ahmad ibn Hanbal was tortured and Imprisonment, imprisoned by Abbasid official Ahmad ibn Abi Du'ad during the reign of Abbasid caliph al-Mu'tasim and caliph al-Wathiq. In Southeast Asia, the height of the Mataram Kingdom happened in this century, while Burma would see the establishment of the major kingdom of Pagan Kingdom, Pagan. Tang china, Tang China started the century with the effective rule under Emperor Xianzong of Tang, Emperor Xianzong and ended the century with the Huang Chao#Rebellions, Huang Chao rebellions. While the Maya civilizati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)
.jpg)


