|
Abraham Portal
Abraham Portal (baptised 1726 – 1809) was an English goldsmith and dramatist. Life He was the son of a clergyman, Peter William Portal, of Huguenot origin. He started in life as a goldsmith and jeweller on Ludgate Hill, but lost money both in this trade and as a bookseller, and finished his career as a box-keeper at Drury Lane Theatre. It appears from his ''Poems'' that Portal was a close friend of John Langhorne. Other friends were Edmund Cartwright and John Scott of Amwell. His brother was the Rev. Andrew Portal, headmaster and usher of Abingdon School. In the spring of 1796 Portal seems to have been living in Castle Street, Holborn. Works Portal's writings include: * ''Olindo and Sophronia: a Tragedy'', the story taken from Torquato Tasso, two editions, 1758, London. * ''The Indiscreet Lover: a Comedy'', performed at the Haymarket for the benefit of the British Lying-In Hospital in Brownlow Street; dedicated to the Duke of Portland; two editions, London, 1768. To the pri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Huguenot
The Huguenots ( , also , ) were a religious group of French Protestants who held to the Reformed, or Calvinist, tradition of Protestantism. The term, which may be derived from the name of a Swiss political leader, the Genevan burgomaster Bezanson Hugues (1491–1532?), was in common use by the mid-16th century. ''Huguenot'' was frequently used in reference to those of the Reformed Church of France from the time of the Protestant Reformation. By contrast, the Protestant populations of eastern France, in Alsace, Moselle, and Montbéliard, were mainly Lutherans. In his ''Encyclopedia of Protestantism'', Hans Hillerbrand wrote that on the eve of the St. Bartholomew's Day massacre in 1572, the Huguenot community made up as much as 10% of the French population. By 1600, it had declined to 7–8%, and was reduced further late in the century after the return of persecution under Louis XIV, who instituted the '' dragonnades'' to forcibly convert Protestants, and then finally revoke ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Brinsley Sheridan
Richard Brinsley Butler Sheridan (30 October 17517 July 1816) was an Irish satirist, a politician, a playwright, poet, and long-term owner of the London Theatre Royal, Drury Lane. He is known for his plays such as ''The Rivals'', ''The School for Scandal'', ''The Duenna'' and ''A Trip to Scarborough''. He was also a Whig MP for 32 years in the British House of Commons for Stafford (1780–1806), Westminster (1806–1807), and Ilchester (1807–1812). He is buried at Poets' Corner in Westminster Abbey. His plays remain a central part of the canon and are regularly performed worldwide. Early life Sheridan was born in 1751 in Dublin, Ireland, where his family had a house on then fashionable Dorset Street. His mother, Frances Sheridan, was a playwright and novelist. She had two plays produced in London in the early 1760s, though she is best known for her novel ''The Memoirs of Miss Sidney Biddulph'' (1761). His father, Thomas Sheridan, was for a while an actor-manager at ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
English Goldsmiths
English usually refers to: * English language * English people English may also refer to: Peoples, culture, and language * ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England ** English national identity, an identity and common culture ** English language in England, a variant of the English language spoken in England * English languages (other) * English studies, the study of English language and literature * ''English'', an Amish term for non-Amish, regardless of ethnicity Individuals * English (surname), a list of notable people with the surname ''English'' * People with the given name ** English McConnell (1882–1928), Irish footballer ** English Fisher (1928–2011), American boxing coach ** English Gardner (b. 1992), American track and field sprinter Places United States * English, Indiana, a town * English, Kentucky, an unincorporated community * English, Brazoria County, Texas, an unincorporated community * Engli ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1809 Deaths
Eighteen or 18 may refer to: * 18 (number), the natural number following 17 and preceding 19 * one of the years 18 BC, AD 18, 1918, 2018 Film, television and entertainment * ''18'' (film), a 1993 Taiwanese experimental film based on the short story ''God's Dice'' * ''Eighteen'' (film), a 2005 Canadian dramatic feature film * 18 (British Board of Film Classification), a film rating in the United Kingdom, also used in Ireland by the Irish Film Classification Office * 18 (''Dragon Ball''), a character in the ''Dragon Ball'' franchise * "Eighteen", a 2006 episode of the animated television series ''12 oz. Mouse'' Music Albums * ''18'' (Moby album), 2002 * ''18'' (Nana Kitade album), 2005 * '' 18...'', 2009 debut album by G.E.M. Songs * "18" (5 Seconds of Summer song), from their 2014 eponymous debut album * "18" (One Direction song), from their 2014 studio album ''Four'' * "18", by Anarbor from their 2013 studio album '' Burnout'' * "I'm Eighteen", by Alice Cooper commonly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1726 Births
Seventeen or 17 may refer to: *17 (number), the natural number following 16 and preceding 18 * one of the years 17 BC, AD 17, 1917, 2017 Literature Magazines * ''Seventeen'' (American magazine), an American magazine * ''Seventeen'' (Japanese magazine), a Japanese magazine Novels * ''Seventeen'' (Tarkington novel), a 1916 novel by Booth Tarkington *''Seventeen'' (''Sebuntiin''), a 1961 novel by Kenzaburō Ōe * ''Seventeen'' (Serafin novel), a 2004 novel by Shan Serafin Stage and screen Film * ''Seventeen'' (1916 film), an American silent comedy film *''Number Seventeen'', a 1932 film directed by Alfred Hitchcock * ''Seventeen'' (1940 film), an American comedy film *''Eric Soya's '17''' (Danish: ''Sytten''), a 1965 Danish comedy film * ''Seventeen'' (1985 film), a documentary film * ''17 Again'' (film), a 2009 film whose working title was ''17'' * ''Seventeen'' (2019 film), a Spanish drama film Television * ''Seventeen'' (TV drama), a 1994 UK dramatic short starring Christ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Edward John Littleton, 1st Baron Hatherton
Edward John Littleton, 1st Baron Hatherton PC, FRS (18 March 17914 May 1863), was a British politician from the extended Littleton/Lyttelton family, of first the Canningite Tories and later the Whigs. He had a long political career, active in each of the Houses of Parliament in turn over a period of forty years. He was closely involved in a number of major reforms, particularly Catholic Emancipation, the Truck Act of 1831, the Parliamentary Boundaries Act 1832 and the Municipal Corporations Act 1835. Throughout his career he was actively concerned with the Irish question and he was Chief Secretary for Ireland between 1833 and 1834. Hatherton was also a major Staffordshire landowner, farmer and businessman. As heir to two family fortunes, he had large holdings in agricultural and residential property, coal mines, quarries and brick works, mainly concentrated around Penkridge, Cannock and Walsall. Background and education Littleton was born Edward Walhouse, and was educated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
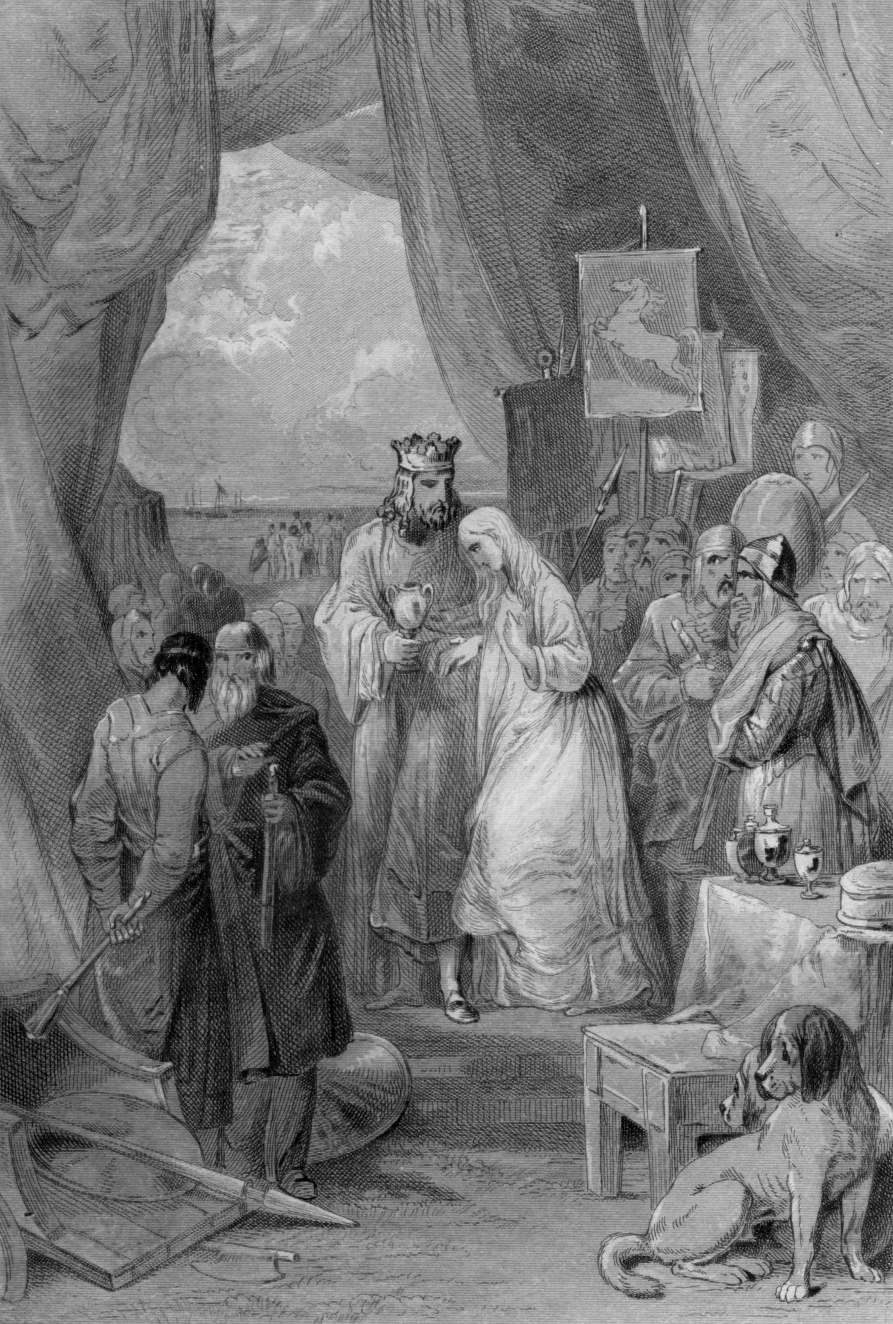
Vortigern And Rowena
''Vortigern and Rowena'', or ''Vortigern, an Historical Play'', is a play that was touted as a newly discovered work by William Shakespeare when it first appeared in 1796. It was eventually revealed to be a Shakespeare hoax, the product of prominent forger William Henry Ireland. Its first performance was on 2 April 1796, when it was ridiculed by the audience. Its titular protagonists, Vortigern and Rowena, are figures from Britain's traditional history. History Ireland had produced several earlier documents he claimed represented the writings of Shakespeare, but ''Vortigern and Rowena'' was the first play he attempted. He shortly followed it with a forged ''Henry II''. He had announced his "discovery" of the lost play as early as 26 December 1794 but did not show his father a manuscript until March 1795. He also provided a purported correspondence between Shakespeare and a printer explaining why the play was unpublished, as well as a deed accounting for how it came to be in han ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Samuel Ireland
Samuel Ireland (21 May 1744 – July 1800), English author and engraver, is best remembered today as the chief victim of the Ireland Shakespeare forgeries created by his son, William Henry Ireland. Early life He began life as a weaver in Spitalfields, London, but soon took to dealing in prints and drawings and devoted his spare time to teaching himself drawing, etching, and engraving. He made sufficient progress to obtain a medal from the Society of Arts in 1760. In 1784 he appears as an exhibitor for the first and apparently only time at the Royal Academy, sending a view of Oxford. Between 1780 and 1785 he etched many plates after John Hamilton Mortimer and Hogarth. Etched portraits by him of General Oglethorpe (1785) and Thomas Inglefield, an armless artist (1787), are in the print room of the British Museum, together with etchings after Ruisdael (1786) and Teniers (1787) and other masters, and some architectural drawings in water-colour. Meanwhile, Ireland's taste for coll ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vortigern
Vortigern (; owl, Guorthigirn, ; cy, Gwrtheyrn; ang, Wyrtgeorn; Old Breton: ''Gurdiern'', ''Gurthiern''; gle, Foirtchern; la, Vortigernus, , , etc.), also spelled Vortiger, Vortigan, Voertigern and Vortigen, was a 5th-century warlord in Britain, known perhaps as a king of the Britons or at least connoted as such in the writings of Bede and Gildas. His existence is contested by scholars and information about him is obscure. He may have been the "superbus tyrannus" said to have invited Hengist and Horsa to aid him in fighting the Picts and the Scots, whereupon they revolted, killing his son in the process and forming the Kingdom of Kent. It is said that he took refuge in North Wales, and that his grave was in Dyfed or the Llŷn Peninsula. Gildas later denigrated Vortigern for his misjudgement and also blamed him for the loss of Britain. He is cited at the beginning of the genealogy of the early Kings of Powys. Medieval accounts Gildas The 6th-century cleric and historia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Linley The Elder
Thomas Linley (17 January 1733 – 19 November 1795) was an English bass and musician active in Bath, Somerset. Born in Badminton, Gloucestershire, Linley began his musical career after he moved to Bath at age 11 and became apprentice to the organist Thomas Chilcot. After his marriage to Mary Johnson in 1752, Linley at first supported his wife and growing family predominantly as a music teacher. As his children grew and he developed their musical talent, he drew an increasing amount of income from their concerts while also managing the assembly rooms in Bath. When the new Bath Assembly Rooms opened in 1771, Linley became musical director and continued to promote his children's careers. He was eventually able to move to London with the thousands of pounds which he had amassed from their concerts. Among Linley's students were his eight children ( Elizabeth Ann, Thomas, Mary, Samuel, Maria, Ozias, William, and Jane), as well as tenor Charles Dignum, singer and actress Anna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
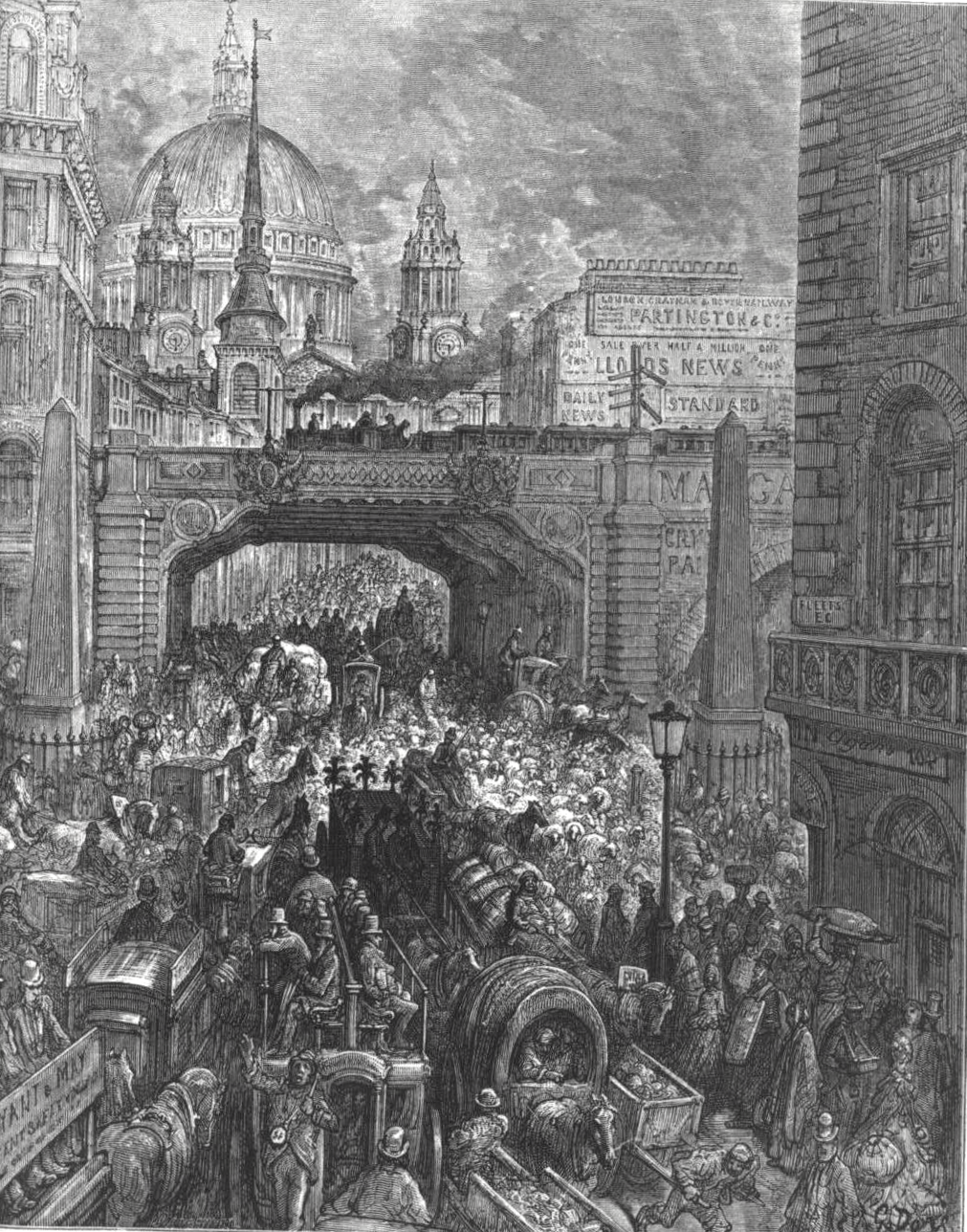
Ludgate Hill
Ludgate Hill is a street and surrounding area, on a small hill in the City of London. The street passes through the former site of Ludgate, a city gate that was demolished – along with a gaol attached to it – in 1760. The area includes St Paul's Cathedral. The modern cathedral, it has been claimed, was built on a site that – during the Roman British era of the early first millennium – was occupied by a major Roman temple, dedicated to the goddess Diana. Ludgate Hill itself is traditionally regarded as one of a trio of hills in Central London, the others being Tower Hill and Cornhill. The highest point is just north of St Paul's, at above sea level. The modern street named Ludgate Hill, which was previously a much narrower thoroughfare named Ludgate Street, runs between St Paul's Churchyard and Ludgate Circus (built in 1864), at which point it becomes Fleet Street. Description Many small alleys on Ludgate Hill were swept away in the mid 1860s to build Ludgate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Lying-In Hospital
The British Lying-In Hospital was a maternity hospital established in London in 1749, the second such foundation in the capital. Background The impetus for the creation of a dedicated maternity hospital was dissatisfaction on the part of the governors of the Middlesex Hospital with its maternity facilities. A new hospital with 20 beds was established in 1749 in Brownlow Street, Long Acre, Holborn, under the presidency of the 2nd Duke of Portland, and initially called the Lying-In Hospital for Married Women. ("Lying-in" is an archaic term for childbirth, referring to the long bedrest prescribed for new mothers in their postpartum confinement.) Consequent on the establishment of the City of London Lying-In Hospital for Married Women in 1750, and the General Lying-In Hospital (later renamed the Queen Charlotte's Hospital) in 1752, the Holborn hospital changed its name to the British Lying-In Hospital for Married Women in 1856. Early years The hospital was funded by voluntary su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |