|
Abipón
The Abipones ( es, Abipones, singular ) were an indigenous people of Argentina's Gran Chaco region, speakers of one of the Guaicuruan languages. They ceased to exist as an independent ethnic group in the early 19th century. A small number of survivors assimilated into Argentine society. History The Abipones originally occupied the Gran Chaco of Argentina, in the lower portions of the Bermejo River. They were originally a seasonally mobile people of hunters, gatherers, fishers and to a limited extent farmers. By 1641, the Abipones had already obtained the horse from the Spanish settlers and abandoned farming for cattle and horse raiding. By that time they still lived north of the Bermejo River They became feared by their neighbours and the Spanish farmers, and even threatened major cities. It is likely they were driven south of their original range by the Spaniards and other native tribes, such as the Tobas. They were finally concentrated in the Argentinian territory lying betwe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abipón Language
The Abipón language was a native American language of the Guaicuruan group of the Guaicuruan languages, Guaycurú-Charruan languages, Charruan family that was at one time spoken in Argentina by the Abipón people. Its last speaker is thought to have died in the 19th century. John Mackenzie (ed.), ''Peoples, Nations and Cultures''. Phonology Consonants Vowels Bibliography Cited in the Catholic EncyclopediaAdolph Francis Bandelier (1907)Catholic Encyclopedia article on the Abipones Accessed on 2009-08-08. * Lorenzo Hervás, Hervas (1785), Origine, Formazione, Mecanismo, ed Armonia degli Idiomi (Cesena) * Hervas (1787), Vocabulario poliglotto * Hervas (1787), Saggio practico delle Lingue ... * Adrian Balbi (1826), Atlas ethnographique du globe (Paris) * Alcide d'Orbigny (1839), L'Homme americain (Paris) * Daniel Brinton, The American Race. UPSID References External links *Abipón basic lexicon at the Global Lexicostatistical Database* World Atlas of Language Structures i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guaycuru Peoples
Guaycuru or Guaykuru is a generic term for several ethnic groups Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous to the Gran Chaco region of South America, speaking related Guaicuruan languages. In the 16th century, the time of first contact with Spanish Empire, Spanish explorers and colonists, the Guaycuru people lived in the present-day countries of Argentina (north of Santa Fe Province), Paraguay, Bolivia, and Brazil (south of Corumbá). The name is written ''guaycurú'' or ''guaicurú'' in Spanish language, Spanish (plural ''guaycurúes'' or ''guaicurúes''), and ''guaicuru'' in Portuguese language, Portuguese (plural ''guaicurus''). It was originally an offensive epithet given to the Mbayá people, Mbayá people of Paraguay by the Guarani people, Guarani, meaning "savage" or "barbarian", which later was extended to the whole group. It has also been used in the past to include other peoples of the Chaco region, but is now restricted to those speaking a Guaicuruan language. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guaicuruan Languages
Guaicuruan (Guaykuruan, Waikurúan, Guaycuruano, Guaikurú, Guaicuru, Guaycuruana) is a language family spoken in northern Argentina, western Paraguay, and Brazil (Mato Grosso do Sul). The speakers of the languages are often collectively called the Guaycuru peoples. For the most part, the Guaycuruans lived in the Gran Chaco and were nomadic and warlike, until finally subdued by the various countries of the region in the 19th century. Genetic relations Jorge A. Suárez includes Guaicuruan with Charruan in a hypothetical ''Waikuru-Charrúa'' stock. Morris Swadesh includes Guaicuruan along with Matacoan, Charruan, and Mascoian within his '' Macro-Mapuche'' stock. Both proposals appear to be obsolete. Family division There is a clear binary split between Northern Guaicuruan (Kadiwéu) and Southern Guaicuruan according to Nikulin (2019).Nikulin, Andrey V. 2019. The classification of the languages of the South American Lowlands: State-of-the-art and challenges / Классифи ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
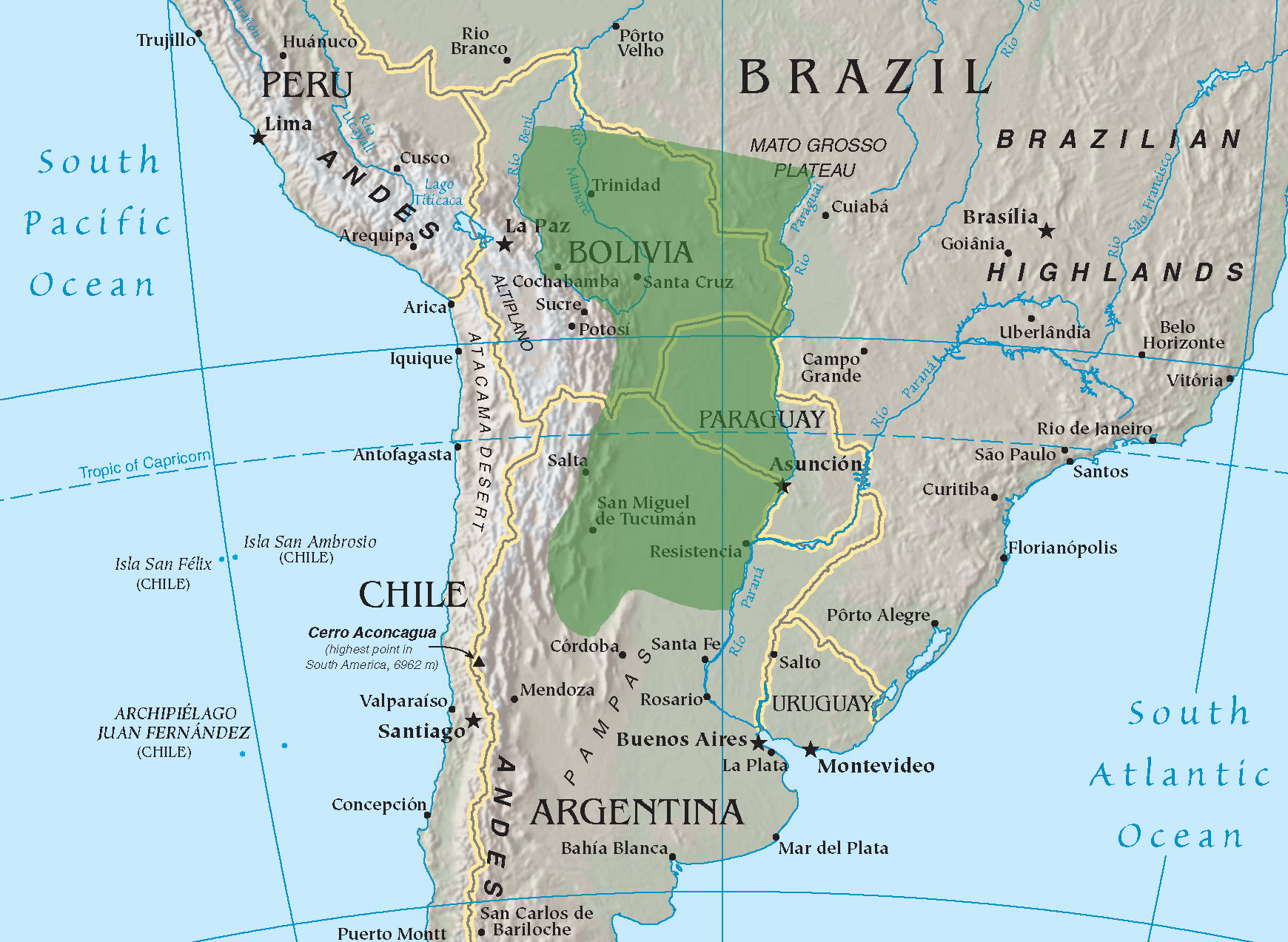
Gran Chaco
The Gran Chaco or Dry Chaco is a sparsely populated, hot and semiarid lowland natural region of the Río de la Plata basin, divided among eastern Bolivia, western Paraguay, northern Argentina, and a portion of the Brazilian states of Mato Grosso and Mato Grosso do Sul, where it is connected with the Pantanal region. This land is sometimes called the Chaco Plain. Toponymy The name Chaco comes from a word in Quechua, an indigenous language from the Andes and highlands of South America. The Quechua word ''chaqu'' meaning "hunting land" comes probably from the rich variety of animal life present throughout the entire region. Geography The Gran Chaco is about 647,500 km² (250,000 sq mi) in size, though estimates differ. It is located west of the Paraguay River and east of the Andes, and is mostly an alluvial sedimentary plain shared among Paraguay, Bolivia, and Argentina. It stretches from about 17 to 33°S latitude and between 65 and 60°W longitude, though estimate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toba People
The Toba people, also known as the Qom people, are one of the largest indigenous groups in Argentina who historically inhabited the region known today as the Pampas of the Central Chaco. During the 16th century, the Qom inhabited a large part of what is today northern Argentina, in the current provinces of Salta, Chaco, Santiago del Estero, Formosa and the province of Gran Chaco in the southeast of the Department of Tarija in Bolivia (which the Qom have inhabited since the 20th century). Currently, many Toba, due to persecution in their rural ancestral regions, live in the suburbs of San Ramón de la Nueva Orán, Salta, Tartagal, Resistencia, Charata, Formosa, Rosario and Santa Fe and in Greater Buenos Aires. Nearly 130,000 people currently identify themselves as Toba or Qom. With more than 120,000 Qom living in Argentina, the Qom community is one of the largest indigenous communities in the country. Like most indigenous groups in South America, the Qom have a long history o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toba (tribe)
The Toba people, also known as the Qom people, are one of the largest indigenous groups in Argentina who historically inhabited the region known today as the Pampas of the Central Chaco. During the 16th century, the Qom inhabited a large part of what is today northern Argentina, in the current provinces of Salta, Chaco, Santiago del Estero, Formosa and the province of Gran Chaco in the southeast of the Department of Tarija in Bolivia (which the Qom have inhabited since the 20th century). Currently, many Toba, due to persecution in their rural ancestral regions, live in the suburbs of San Ramón de la Nueva Orán, Salta, Tartagal, Resistencia, Charata, Formosa, Rosario and Santa Fe and in Greater Buenos Aires. Nearly 130,000 people currently identify themselves as Toba or Qom. With more than 120,000 Qom living in Argentina, the Qom community is one of the largest indigenous communities in the country. Like most indigenous groups in South America, the Qom have a long hist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Corrientes
Corrientes (; Guaraní language, Guaraní: Taragüí, literally: "Currents") is the capital city of the Provinces of Argentina, province of Corrientes Province, Corrientes, Argentina, located on the eastern shore of the Paraná River, about from Buenos Aires and from Posadas, Misiones, Posadas, on National Route 12 (Argentina), National Route 12. It has a population of 346,334 according to the INDEC, 2010 Census. It lies opposite its twin city, Resistencia, Chaco, Resistencia, Chaco Province, Chaco. Corrientes has a mix of colonial and modern architecture, several churches and a number of lapacho, Erythrina crista-galli, ceibo, jacaranda and orange trees. It is also home to one of the biggest carnival and chamamé celebrations in the country. The annual average temperature is . The annual rainfall is around . Transportation Located in the Argentine Littoral, near the Argentina–Paraguay border, the General Belgrano Bridge crosses the Paraná River which serves as the natu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jesuit
, image = Ihs-logo.svg , image_size = 175px , caption = ChristogramOfficial seal of the Jesuits , abbreviation = SJ , nickname = Jesuits , formation = , founders = , founding_location = , type = Order of clerics regular of pontifical right (for men) , headquarters = Generalate:Borgo S. Spirito 4, 00195 Roma-Prati, Italy , coords = , region_served = Worldwide , num_members = 14,839 members (includes 10,721 priests) as of 2020 , leader_title = Motto , leader_name = la, Ad Majorem Dei GloriamEnglish: ''For the Greater Glory of God'' , leader_title2 = Superior General , leader_name2 = Fr. Arturo Sosa, SJ , leader_title3 = Patron saints , leader_name3 = , leader_title4 = Ministry , leader_name4 = Missionary, educational, literary works , main_organ = La Civiltà Cattolica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Martin Dobrizhoffer
Martin Dobrizhoffer (7 September 1717 – 17 July 1791) was an Austrian Roman Catholic missionary and writer. Biography Dobrizhoffer was born in Frymburk (Friedberg), Bohemia. He joined the Society of Jesus in 1736, and in 1749 proceeded to Paraguay, where for eighteen years he worked devotedly first among the Guaranis, and then among the Abipones. Returning to Europe, on the expulsion of the Jesuits from South America, he settled at Vienna, obtained the friendship of Maria Theresa, survived the suppression of his order, and wrote the history of his mission. He died in Vienna in 1791. Book The book on which his claim to fame rests, "An Account of the Abipones, an Equestrian People of Paraguay" was found in Vienna in 1784 in the author's own Latin, and in a German translation by Professor Kreil of the University of Pest. Of its contents some idea may be obtained from its extended title: :''Historia de Abiponibus, equestri bellicosaque Paraquariae natione, locupletata copiosi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animism
Animism (from Latin: ' meaning 'breath, Soul, spirit, life') is the belief that objects, places, and creatures all possess a distinct Spirituality, spiritual essence. Potentially, animism perceives all things—Animal, animals, Plant, plants, Rock (geology), rocks, River, rivers, Weather, weather systems, human handiwork, and perhaps even Word, words—as animated and alive. Animism is used in the anthropology of religion, as a term for the Belief, belief system of many Indigenous peoples, especially in contrast to the relatively more recent development of organized religions. Animism focuses on the Metaphysics, metaphysical universe, with a specific focus on the concept of the immaterial soul. Although each culture has its own mythologies and rituals, animism is said to describe the most common, foundational thread of indigenous peoples' "spiritual" or "supernatural" perspectives. The animistic perspective is so widely held and inherent to most indigenous peoples, that they ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mocoví
The Mocoví ( Mocoví: ''moqoit'') are an indigenous people of the Gran Chaco region of South America. They speak the Mocoví language and are one of the ethnic groups belonging to the Guaycuru peoples. In the 2010 Argentine census, 22,439 people self-identified as Mocoví. Not much is known about them before the Spanish arrived. They were nomadic and lived off of their fishing, hunting and gathering. They hunted deer and rhea and slept on animal skins and flimsy shelters. They did not farm because the soil conditions were poor where they roamed and there was flooding. Trade routes were discovered in the Chaco forest, indicating trading and it was assumed they traded skins and feathers for gold, silver and copper objects. When the Jesuits arrived, they taught the Mocoví to farm with cattle and they became sedentary. In 1924, at least 200 Mocoví and Toba people The Toba people, also known as the Qom people, are one of the largest indigenous groups in Argentina who historicall ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)