|
Abderus
In Greek mythology, Abderus or Abderos (Ancient Greek: Ἄβδηρος) was a divine hero, reputed by some to be one of Heracles' lovers (eromenoi), and reputedly a son of Hermes by some accounts, and eponym of Abdera, Thrace. Pseudo-Scymnos, ''Circuit de la terre'' 646 ff. Family The paternity of Abderus differs according to the sources. Some say he was the son of the god Hermes and a native of Opus in Locris, but according to other writers, he was the son of Thromius the Locrian. Photius writes that he was brother of Patroclus. Pindar makes Abderus a son of Poseidon and Thronia. Mythology Abderus was mostly known for his tragic role in Heracles' Eighth Labor. Along with others, he helped Heracles capture the four savage mares of Diomedes the king of the Thracian Bistones. Heracles overpowered the grooms and drove the Mares of Diomedes into the sea and left them in the care of Abderus. However, while Heracles was away, the horses devoured Abderus. In revenge, Heracles fed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mares Of Diomedes
The Mares of Diomedes ( grc-gre, Διομήδους ἵπποι), also called the Mares of Thrace, were a herd of man-eating horses in Greek mythology. Magnificent, wild, and uncontrollable, they belonged to Diomedes of Thrace (not to be confused with Diomedes, son of Tydeus), king of Thrace, son of Ares and Cyrene who lived on the shores of the Black Sea. Bucephalus, Alexander the Great's horse, was said to be descended from these mares. Mythology As the eighth of his Twelve Labours, also categorised as the second of the Non-Peloponnesian labours, Heracles was sent by King Eurystheus to steal the Mares from Diomedes. The mares’ madness was attributed to their unnatural diet which consisted of the flesh of unsuspecting guests or strangers to the island. Some versions of the myth say that the mares also expelled fire when they breathed. The Mares, which were the terror of Thrace, were kept tethered by iron chains to a bronze manger in the now vanished city of Tirida and wer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thronia
In Greek mythology, the name Thronia (Ancient Greek: Θρωνία) or Thronie (Θρωνίη) may refer to: * Thronia, daughter of King Belus of Egypt and possibly of either Achiroe or Side. She was the mother of Arabus, the eponym of Arabia, by Hermes. * Thronia, a Naiad nymph, mother of Abderus by Poseidon and the eponym of the city Thronion in Opuntian Locris.Scholia on Homer, ''Iliad'' 2.533 Notes References * Apollodorus, ''The Library'' with an English Translation by Sir James George Frazer, F.B.A., F.R.S. in 2 Volumes, Cambridge, MA, Harvard University Press; London, William Heinemann Ltd. 1921. Online version at the Perseus Digital Library. * |
Hermes
Hermes (; grc-gre, Ἑρμῆς) is an Olympian deity in ancient Greek religion and mythology. Hermes is considered the herald of the gods. He is also considered the protector of human heralds, travellers, thieves, merchants, and orators. He is able to move quickly and freely between the worlds of the mortal and the divine, aided by his winged sandals. Hermes plays the role of the psychopomp or "soul guide"—a conductor of souls into the afterlife. In myth, Hermes functions as the emissary and messenger of the gods, and is often presented as the son of Zeus and Maia, the Pleiad. Hermes is regarded as "the divine trickster," about which the '' Homeric Hymn to Hermes'' offers the most well-known account. His attributes and symbols include the herma, the rooster, the tortoise, satchel or pouch, talaria (winged sandals), and winged helmet or simple petasos, as well as the palm tree, goat, the number four, several kinds of fish, and incense. However, his main symbol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mares Of Diomedes
The Mares of Diomedes ( grc-gre, Διομήδους ἵπποι), also called the Mares of Thrace, were a herd of man-eating horses in Greek mythology. Magnificent, wild, and uncontrollable, they belonged to Diomedes of Thrace (not to be confused with Diomedes, son of Tydeus), king of Thrace, son of Ares and Cyrene who lived on the shores of the Black Sea. Bucephalus, Alexander the Great's horse, was said to be descended from these mares. Mythology As the eighth of his Twelve Labours, also categorised as the second of the Non-Peloponnesian labours, Heracles was sent by King Eurystheus to steal the Mares from Diomedes. The mares’ madness was attributed to their unnatural diet which consisted of the flesh of unsuspecting guests or strangers to the island. Some versions of the myth say that the mares also expelled fire when they breathed. The Mares, which were the terror of Thrace, were kept tethered by iron chains to a bronze manger in the now vanished city of Tirida and were ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heracles
Heracles ( ; grc-gre, Ἡρακλῆς, , glory/fame of Hera), born Alcaeus (, ''Alkaios'') or Alcides (, ''Alkeidēs''), was a divine hero in Greek mythology, the son of Zeus and Alcmene, and the foster son of Amphitryon.By his adoptive descent through Amphitryon, Heracles receives the epithet Alcides, as "of the line of Alcaeus", father of Amphitryon. Amphitryon's own, mortal son was Iphicles. He was a great-grandson and half-brother (as they are both sired by the god Zeus) of Perseus, and similarly a half-brother of Dionysus. He was the greatest of the Greek heroes, the ancestor of royal clans who claimed to be Heracleidae (), and a champion of the Olympian order against chthonic monsters. In Rome and the modern West, he is known as Hercules, with whom the later Roman emperors, in particular Commodus and Maximian, often identified themselves. The Romans adopted the Greek version of his life and works essentially unchanged, but added anecdotal detail of their own, so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
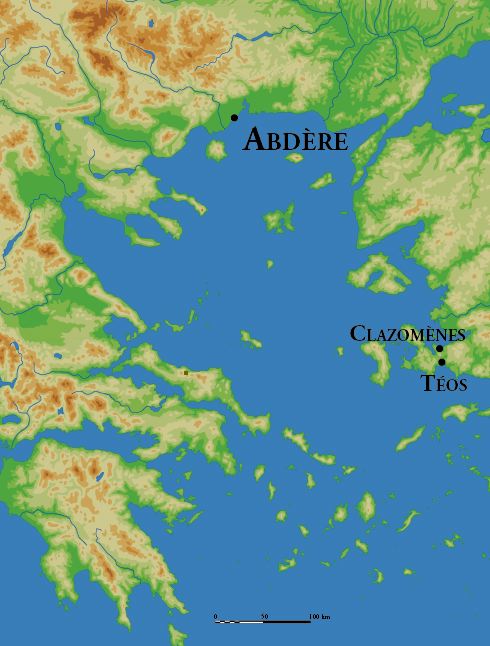
Abdera, Thrace
Abdera () is a municipality in the Xanthi regional unit of Thrace, Greece. In classical antiquity, it was a major Greek ''polis'' on the Thracian coast. The ancient polis is to be distinguished from the municipality, which was named in its honor. The polis lay 17 km east-northeast of the mouth of the Nestos River, almost directly opposite the island of Thasos. It was a colony placed in previously unsettled Thracian territory, not then a part of Hellas, during the age of Greek colonization. The city that developed from it became of major importance in ancient Greece. After the 4th centuryAD it declined, contracted to its acropolis, and was abandoned, never to be reoccupied except by archaeologists. Meanwhile, life went on as the changing population settled in other communities in the region. One named Polystylus changed its name to Abdera. In 2011 the municipality of Abdera was synoecized from three previous municipalities comprising a number of modern settlements. The ancie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Mythology
A major branch of classical mythology, Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, and a genre of Ancient Greek folklore. These stories concern the Cosmogony, origin and Cosmology#Metaphysical cosmology, nature of the world, the lives and activities of List of Greek mythological figures, deities, Greek hero cult, heroes, and List of Greek mythological creatures, mythological creatures, and the origins and significance of the ancient Greeks' own cult (religious practice), cult and ritual practices. Modern scholars study the myths to shed light on the religious and political institutions of ancient Greece, and to better understand the nature of myth-making itself. The Greek myths were initially propagated in an oral tradition, oral-poetic tradition most likely by Minoan civilization, Minoan and Mycenaean Greece, Mycenaean singers starting in the 18th century BC; eventually the myths of the heroes of the Trojan War and its after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paean
A paean () is a song or lyric poem expressing triumph or thanksgiving. In classical antiquity, it is usually performed by a chorus, but some examples seem intended for an individual voice (monody). It comes from the Greek παιάν (also παιήων or παιών), "song of triumph, any solemn song or chant". "Paeon" was also the name of a divine physician and an epithet ("byname") of Apollo. Etymology The basis of the word παιάν is *παιάϝων." Its ultimate etymology is unclear. R. S. P. Beekes has suggested the meaning "who heals illnesses through magic", from *παῖϝα/*παϝία "blow", related to παίω "beat" (from Proto-Indo-European ''*ph2u-ie/o-'') or παύω "withhold" (of uncertain etymology). He alternatively suggested that ''paian'' "may well be Pre-Greek". R. S. P. Beekes, ''Etymological Dictionary of Greek'', Brill, 2009, p. 1142 (see also pp. 1144 and 1159). Ancient Greek paean In Homer, PaeonMycenaean Greek , ''pa-ja-wo-ne'' /pajāwonei/ ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diomedes (Thracian King)
In Greek mythology, King Diomedes of Thrace (Ancient Greek: Διομήδης) was the son of Ares and Cyrene. He lived on the shores of the Black Sea ruling the warlike tribe of Bistones. He is known for his man-eating horses, which Heracles stole in order to complete the eighth of his Twelve Labours, slaying Diomedes in the process. Mythology Heracles encounters King Diomedes through performing his eighth labour. Eurystheus, King of Tiryns and Heracles' cousin, had sent Heracles to capture the Mares of Diomedes after he had completed his seventh labour, capturing the Cretan Bull. Heracles travelled to the shores of the Black Sea to meet King Diomedes. He was said to have been the son of the god Ares and Cyrene, who is said to be the daughter of Hypseus, King of the Lapiths. King Diomedes was a savage; he enjoyed feeding strangers and prisoners to his mares. They did not like the taste of oats and grain; instead they feasted on human flesh, which their master gave them will ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bistoni
Bistones ( el, "Βίστονες") is the name of a Thracian people who dwelt between Mount Rhodopé and the Aegean Sea, beside Lake Bistonis, near Abdera "extending westward as far as the river Nestus". It was through the land of the Bistones that " Xerxes marched on his invasion of Greece (480 BC)". "The Bistones continued to exist at the time when the Romans were masters of Thrace". "Roman poets sometimes use the names of the Bistones for that of the Thracians in general." "Pliny mentions one town as belonging to the Bistones: Tirida; the other towns on their coast, Dicaea, Ismaron, Parthenion, Phalesina and Maronea, were Greek colonies." Mythology The Bistones were militant people who worshiped Ares, Dionysus or Bacchus, Minerva, and Bellona. In the play Alcestis by Euripides, the mythical Heracles is on his way "to the land of the Bistones" in his "labour for Tirynthian Eurystheus" "to fetch the chariot-steeds of Thracian Diomedes." The Thracian Diomedes "was king o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imagines (work By Philostratus)
''Imagines'' ( grc-gre, Εἰκόνες) are two works in Ancient Greek by two authors, both known as Philostratus, describing and explaining various artworks. The first of these two works called ''Imagines'', consists of two books (one consisting of an introduction and 31 chapters and the other of 34 chapters) are generally attributed to Philostratus of Lemnos, or possibly to his more famous father-in-law Philostratus of Athens. ''Imagines'' ostensibly describes 65 works of art seen by Philostratus in Naples. The entire work is framed in terms of explaining art, its symbols and meaning, to a young audience. The author of the work in the introduction states that the ten-year-old son of his host was the immediate cause of the composition of this work and that the author will structure the book and each of its chapters as if this boy is being addressed. The second ''Imagines'' (consisting of 17 chapters) is by the grandson of Philostratus of Lemnos, known as Philostratus the Younger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philostratus Of Lemnos
Philostratus of Lemnos ( grc-gre, Φιλόστρατος ὁ Λήμνιος; c. 190 – c. 230 AD), also known as Philostratus the Elder to distinguish him from Philostratus the Younger who was also from Lemnos, was a Greek sophist of the Roman imperial period. He was probably a nephew of the sophist Philostratus of Athens, and is credited with two books formerly attributed to his uncle. Works '' Eikones'' (, ''Images'' or ''Imagines'') is ostensibly a description of 64 pictures in a Neapolitan gallery. Goethe, Welcker, Brunn, E. Bertrand and Helbig, among others, have held that the descriptions are of actually existing works of art, while Heyne and Friederichs deny this. In any case they are interesting as showing the way in which ancient artists treated mythological and other subjects, and are written with artistic knowledge and in attractive language. A second series of ''Imagines'' was produced by his grandson. Philostratus the Younger certainly wrote the 2nd series of '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |