 |
Abd-Allah Ibn Amir
Abū ʿAbd al-Raḥmān ʿAbd Allāh ibn ʿĀmir ibn Kurayz `Abd Allah ibn `Amir (; 626–678) was a Rashidun Caliphate politician and general. He served as the Governor of Basra from 647 to 656 AD, during the reign of Rashidun Caliph Uthman ibn Affan and was a cousin of the Caliph through his father. He was renowned for his administrative and military skill, particularly for his successful campaigns to reconquer and pacify former territories of the Sasanian Empire (present-day Iran and Afghanistan). Early life Abd Allah ibn Amir was the son of Amir ibn Kurayz ibn Rabi'ah, the brother of Arwa bint Kurayz (mother of Caliph Uthman ibn Affan). Conquests during Caliph Umar's rule Ibn Amir's expeditions were mainly aimed at quelling revolts in former Sasanian Empire territories. Conquest of Sakastan In 650, having secured his position in Kerman, Abd Allah sent an army under Mujashi ibn Mas'ud. After crossing the Dasht-i Lut desert, Mujashi ibn Mas'ud reached Sakastan, but suffe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Mecca
Mecca, officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, is the capital of Mecca Province in the Hejaz region of western Saudi Arabia; it is the Holiest sites in Islam, holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow valley above sea level. Its metropolitan population in 2022 was 2.4million, making it the List of cities in Saudi Arabia by population, third-most populated city in Saudi Arabia after Riyadh and Jeddah. Around 44.5% of the population are Saudis, Saudi citizens and around 55.5% are Muslim world, Muslim foreigners from other countries. Pilgrims more than triple the population number every year during the Pilgrimage#Islam, pilgrimage, observed in the twelfth Islamic calendar, Hijri month of . With over 10.8 million international visitors in 2023, Mecca was one of the ten List of cities by international visitors, most visited cities in the world. Mecca is generally considered "the fountainhead and cradle of Islam". Mecca is revered in Islam as the birthp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Aparviz Of Sakastan
Aparviz was an Iranian aristocrat, who served as the ''marzban'' (general of a frontier province, "margrave") of Sakastan Sistān (), also known as Sakastān (, , current name: Zabol) and Sijistan (), is a historical region in south-eastern Iran and extending across the borders of present-day south-western Afghanistan, and south-western Pakistan. Mostly correspon ... in the 7th century. He is first mentioned in 650/1 during the Arab invasion of Iran, where is mentioned as surrendering to the Rashidun Arabs; when he consulted the Arab military officer Rabi ibn Ziyad Harithi, the latter was using the bodies of two dead soldiers as a chair. This horrified Aparviz, who in order to save the inhabitants of Sakastan, made peace with the Arabs in return for heavy tribute. Two years later, the inhabitants of Sakastan rebelled against the Arabs, however, no mention of Aparviz is made. Sources * * * * Generals of Yazdegerd III Year of birth unknown Year of death unknown Sasania ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Nishapur
Nishapur or Neyshabur (, also ) is a city in the Central District (Nishapur County), Central District of Nishapur County, Razavi Khorasan province, Razavi Khorasan province, Iran, serving as capital of both the county and the district. Nishapur is the second most populous city of the province in the northeast of Iran, situated in a fertile plain at the foot of Binalud Mountains, Binalud Mountain Range. It has been the historic capital of the Western Quarter of Greater Khorasan, the historic Capitals of Persia, capital of the 9th-century Tahirid dynasty, the initial capital of the 11th-century Seljuk Empire, and is currently the capital city of Nishapur County and a historic Silk Road city of Greater Iran, cultural and Economy of Iran, economic importance in Iran and the Greater Khorasan region. Nearby are turquoise mines that have supplied the world with turquoise of the finest and the highest quality for at least two millennia. The city was founded in the 3rd century by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Tabasayn
Tabasayn () was a district in Quhistan in the medieval period. The name, although referring to both cities, was often applied by geographers to either one in isolation. The cities were Tabas al-Tamr ('Tabas of the Dates'), also known as Tabas Gilaki after a famous governor of the city who had pacified the region, and Tabas al-Unnab ('Tabas of the Jujube') or Tabas Masinan. Alternatively, the term might refer to Tabas al-Tamr and the nearby village of Kuri or Kurin, which was fortified and is called "one of the two fortresses of Taban" by the 9th-century geographer al-Baladhuri. The district was strategically important, being located immediately east of the Great Salt Desert; Tabas al-Tamr was called the 'Gate of Khurasan KhorasanDabeersiaghi, Commentary on Safarnâma-e Nâsir Khusraw, 6th Ed. Tehran, Zavvâr: 1375 (Solar Hijri Calendar) 235–236 (; , ) is a historical eastern region in the Iranian Plateau in West Asia, West and Central Asia that encompasses wes ...' by al-Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
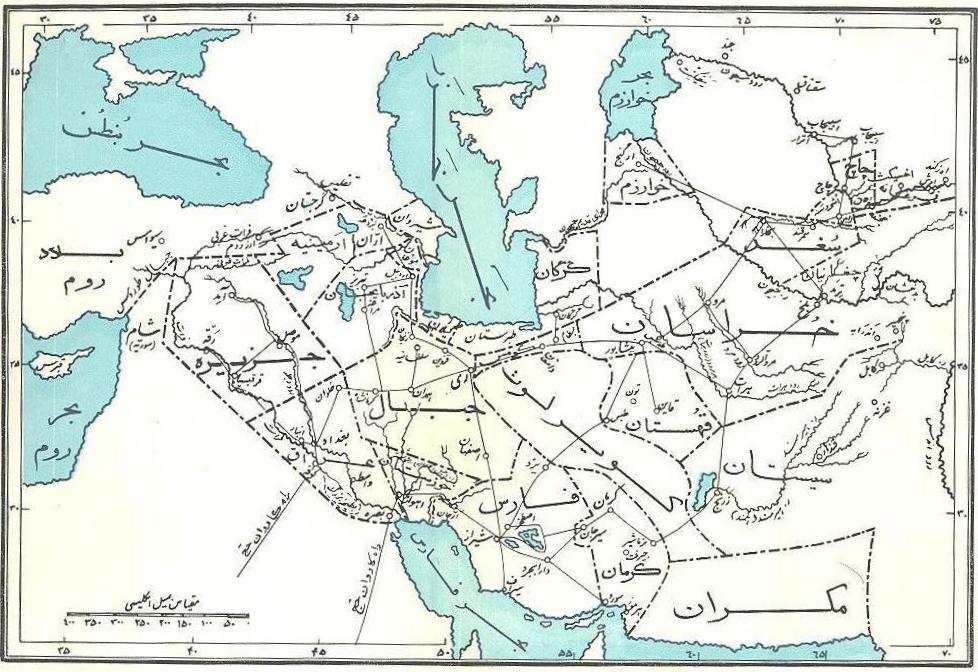 |
Makran
Makran (), also mentioned in some sources as ''Mecran'' and ''Mokrān'', is the southern coastal region of Balochistan. It is a semi-desert coastal strip in the Balochistan province in Pakistan and in Iran, along the coast of the Gulf of Oman. It extends westwards, from the Sonmiani Bay to the northwest of Karachi in the east, to the fringes of the region of Bashkardia/Bāšgerd in the southern part of the Sistan and Baluchestan province of modern Iran. Makrān is thus bisected by the modern political boundary between Pakistan and Iran. In January 2025, a government spokesperson informed that Iran is investigating the possibility of moving its capital to the Makran region. Etymology The southern part of Balochistan is called ''Kech Makran'' on the Pakistani side and Makran on the Iranian side which is also the name of a former Iranian province. The location corresponds to that of the Maka satrapy in Achaemenid times. The Sumerian trading partners of Magan are identified wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Persian Empire
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire, also known as the Persian Empire or First Persian Empire (; , , ), was an Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty in 550 BC. Based in modern-day Iran, it was the largest empire by that point in history, spanning a total of . The empire spanned from the Balkans and Egypt in the west, most of West Asia, the majority of Central Asia to the northeast, and the Indus Valley of South Asia to the southeast. Around the 7th century BC, the region of Persis in the southwestern portion of the Iranian plateau was settled by the Persians. From Persis, Cyrus rose and defeated the Median Empire as well as Lydia and the Neo-Babylonian Empire, marking the establishment of a new imperial polity under the Achaemenid dynasty. In the modern era, the Achaemenid Empire has been recognised for its imposition of a successful model of centralised bureaucratic administration, its multicultural policy, building complex inf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Balkh
Balkh is a town in the Balkh Province of Afghanistan. It is located approximately to the northwest of the provincial capital city Mazar-i-Sharif and approximately to the south of the Amu Darya and the Afghanistan–Uzbekistan border. In 2021–2022, the National Statistics and Information Authority reported that the town had 138,594 residents. Listed as the List of cities in Afghanistan, eighth largest settlement in the country, unofficial 2024 estimates set its population at around 114,883 people. Historically, the site of present-day Balkh was held in considerably high regard due to its religious and political significance in Ariana. A hub of Zoroastrianism and Buddhism, the ancient city was also known to the Ancient Iran, Persians as Zariaspa and to the Ancient Greece, Greeks as Bactra, giving its name to Bactria. As such, it was famously known as the capital of Bactria or Tokharistan. The Italian explorer and writer Marco Polo described Balkh as "a noble city and a great ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Marw Al-Rudh
Marw-Rud (, also ''Marw-Rudh'') or Marw al-Rudh (from ; ), locally used to be known by the older variants Marwarudh () and Marrudh (),"مرورود" in Dehkhoda Dictionary was a medieval settlement in Greater Khurasan, Khurasan. It was also known as Marw-i Kuchik (, ) to distinguish it from the nearby Marw al-Shahijan or Greater Marw. The town was located near the modern Afghanistan, Afghan settlement of Bala Murghab, at the site where the Murghab River leaves the mountains of Gharjistan and enters the steppe of the Karakum Desert. The modern settlement of Maruchak or Marv-i Kuchik, although named after the medieval town, appears to be the site of a former suburb of it, named Qasr-i Ahnaf. The town existed already in pre-Islamic times, its foundation being attributed to the Sasanian king Bahram Gur (reigned 420–438). Its original name in Persian was Marwirōd () or Marvirot (Mrot in Old Armenian, Armenian), which survived in the later Arabic ''nisba (onomastics), nisbas'' of '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Muslim Conquest Of Khorasan
The Muslim conquest of Khorasan, or Arab conquest of Khorasan, was the last phase of the heavy war between the Arab Rashidun caliphate against the Sasanid Empire. Background In 642 the Sasanid Empire was nearly destroyed and almost all parts of Persia were conquered, except parts of Khorasan, which were still held by Sasanids. Khorasan was the second largest province of the Sasanid Empire. It stretched from what is now north-eastern Iran, Afghanistan and Turkmenistan. Its capital was Balkh, in present-day northern Afghanistan. In 651 after Yazdegerd III was murdered by Mahuy Suri, the marzban or administrator of Marw, Tabaristan was afterwards invaded by the Muslim Arabs. During Rashidun and Umayyad era Beginning of conquest The mission of conquering Khurasan was assigned to Ahnaf ibn Qais and Abd Allah ibn Amir, as well as Abu Mansur Muhammad, commander of the cavalry. Abd Alah marched from Fars and took a short and less frequent route via Rayy. Ahnaf then marched ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
 |
Amr Ibn Ma'adi Yakrib
Amr ibn Ma'adi Yakrib al-Zubaīdi al-Madḥ'hijī () (died 642 CE) was an Arabian cavalry commander of the Zubaid clan in Yemen, part of the Madhhij tribe confederation. Amr is considered a legendary warrior, battling against legendary figures like Amir ibn Tufail, Antarah ibn Shaddad and Dorayd bin Al Soma. Amr converted to Islam in the time of the Islamic prophet Muhammad, and became one of the two champions of the Rashidun caliphate, along with Tulayha. Both were said to have the strength of a thousand soldiers. Amr participated in the battle of the Yarmuk and the battle of al-Qadisiyyah against the elephants of the Sassanids. He also led the Rashidun in the battle of Jalula, and served in the Muslim conquest of Khorasan. Amr was killed during the Battle of Nahavand in 642 CE. Amr had several swords that became the subjects of certain legends of later Arabic poetry, particularly during the Abbasid caliphate, such as swords named Dhu al-Nun, al-Qalzam and ash-Shamshara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
Ahnaf Ibn Qais
Abu Bahr Al-Ahnaf ibn Qays () was a Muslim commander who lived during the time of Islamic prophet Muhammad. He hailed from the Arab tribe of Banu Tamim and was born of noble parents. Initially, his father named him ad-Dhahhak, but people called him ''al-Ahnaf'', which meant "the clubfooted" in classical Arabic. Al-Baladhuri, however, noted that he was also identified as Abdallah ibn Khazim. Early life In the early years of Islam, Muhammad sent a missionary to the tribe of Banu Tamim. The tribe members had informed the missionary that no decision could be taken until Al-Ahnaf told them his opinion. Al-Ahnaf listened and questioned the missionary who succeeded in persuading him and his entire tribe to embrace Islam. Al-Ahnaf had never met Muhammad in his lifetime. After Muhammad's death in 632, a number of tribes rebelled for different reasons, al-Ahnaf and his people, however, remained Muslims. When he heard about Musaylimah's claim of prophecy, al-Ahnaf went with his uncle to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
|
 |
Kirman (Sasanian Province)
Kirman (Middle Persian: ''Kirmān'') was a Sasanian province in Late Antiquity, which corresponds to the present-day province of Kerman. The province bordered Pars in the west, Abarshahr and Sakastan in the northeast, Paradan in the east, Spahan in the north, and Mazun in the south. The capital of the province was Shiragan. The province allegedly functioned as some kind of vassal kingdom, being mostly ruled by princes from the royal family, who bore the title of Kirmanshah ("King of Kirman"). The non-royal governors of the province bore the title of ''marzban''. Name The name of the province is derived from Old Persian ''Karmāna''; the etymology of the name is debated, a popular theory is that it is related to Old Iranian ''*kṛma-'' and Middle Persian ''kerm'' ("worm"). History The province was originally part of the Parthian Empire, but was in the early 3rd-century conquered by the first Sasanian king Ardashir I (). According to the medieval Iranian historian al-Tabari, A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |