|
Aavani Kanavukal
''Aavani Kanavukal'' (1997) is a Malayalam studio album by Bombay Ravi Ravi Shankar Sharma (3 March 1926 – 7 March 2012), often referred to mononymously as Ravi, was an Indian music director, who had composed music for several Hindi and Malayalam films. After a successful career in Hindi cinema, he took a brea .... The lyrics for this album was penned by Yusuf Ali Kecheri. Track list References External links {{Authority control 1997 albums ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bombay Ravi
Ravi Shankar Sharma (3 March 1926 – 7 March 2012), often referred to mononymously as Ravi, was an Indian music director, who had composed music for several Hindi and Malayalam films. After a successful career in Hindi cinema, he took a break from the 1970s to 1984, and made a successful comeback in the Malayalam music scene under the stage name Bombay Ravi. Biography Ravi was born in Delhi on 3 March 1926. He had no formal training in classical music; instead he learned music by listening to his father sing bhajans. He taught himself to play harmonium and other classical instruments and worked as an electrician to support his family. In 1950 he decided to shift to Bombay and become a professional singer. At first Ravi was homeless, living on the streets and sleeping on Malad railway station at night. In 1952, Ravi was discovered by Hemant Kumar who hired him to sing backing vocals in ''Vande Mataram'' from the film ''Anand Math''. Ravi gave several hit songs and received ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malayalam
Malayalam (; , ) is a Dravidian language spoken in the Indian state of Kerala and the union territories of Lakshadweep and Puducherry (Mahé district) by the Malayali people. It is one of 22 scheduled languages of India. Malayalam was designated a "Classical Language of India" in 2013. Malayalam has official language status in Kerala, and Puducherry ( Mahé), and is also the primary spoken language of Lakshadweep, and is spoken by 34 million people in India. Malayalam is also spoken by linguistic minorities in the neighbouring states; with significant number of speakers in the Kodagu and Dakshina Kannada districts of Karnataka, and Kanyakumari, district of Tamil Nadu. It is also spoken by the Malayali Diaspora worldwide, especially in the Persian Gulf countries, due to large populations of Malayali expatriates there. There are significant population in each cities in India including Mumbai, Bengaluru, Delhi, Kolkata, Pune etc. The origin of Malayalam remains a matter of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yusuf Ali Kecheri
Yusufali Kechery (Yūsaphali Kēccēri; യൂസഫലി കേച്ചേരി 16 May 1934 – 21 March 2015) was a poet, film lyricist, film producer and director from Kerala, India. He wrote during the modern era of Malayalam poetry and won the Odakkuzhal Award, the Kerala Sahitya Academy Award and the Vallathol Award. Career K. P. Narayana Pisharody was Kechery's Sanskrit teacher and taught him free of cost for four years. Kechery's poetry works include ''Sainaba'', ''Aayiram Navulla Mounam'', ''Anchu Kanyakakal'', ''Nadabhramam'', ''Amrithu'', ''Kecheri Puzha'', ''Anuragagaanam Pole'', ''Aalila'', ''Kadhaye Premicha Kavitha'', ''Perariyatha Nombaram'' and ''Ahaindavam''. He also directed the films ''Vanadevatha'' (1977) and '' Neelathamara'' (1979). He wrote the lyrics for the songs in the film ''Dhwani'', which were composed by musician Naushad. In 2000 he was awarded a National Award for a Sanskrit song written for the Malayalam film ''Mazha'' (''Rain''). Kechery ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madhyamavathi
Madhyamavati (madhyamāvati) is a rāga in Carnatic music (musical scale of South Indian classical music). It is an ''audava'' rāga (or ''owdava'' rāga, meaning pentatonic scale), as it does not have all the seven musical notes (''swaras''). It is a ''janya'' rāga (derived scale). The equivalent of ''Madhyamavati'' in Hindustani music is ''Madhumad Sarang''.''Raganidhi'' by P. Subba Rao, Pub. 1964, The Music Academy of Madras It also has other equivalents in Hindustani music such as ragas Megh and Megh Malhar. It is considered a very auspicious rāgam and every Carnatic music concert ends with either a song in ''Madhyamavati'' or the ending of the last song is sung in this rāgam.''Ragas in Carnatic music'' by Dr. S. Bhagyalekshmy, Pub. 1990, CBH Publications It is very suitable for elaboration and exploration due to even spacing of notes. The scale uses the first three notes of the cycle of fifths ''S, P and R2'' and fourths ''S, M1 and N2''. Structure and Lakshana ''Madh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Unni Menon
Unni Menon (born 2 December 1955) is an Indian film playback singer. He has recorded over 4000 songs in many Indian languages including Malayalam, Tamil, Telugu and Kannada.S.S.KavutaA melodious journey The Hindu. Retrieved 29 November 2008 In the early part of his career, he spent many years as a low-profile playback singer. The turning point in his career came with the song "Pudhu Vellai Mazhai" from Mani Ratnam's award-winning 1992 Tamil film ''Roja'', composed by A. R. Rahman. He has frequently associated with A. R. Rahman, lending his voice to nearly 27 popular songs from films like ''Karuththamma'' (1994) and ''Minsaara Kanavu'' (1997). Early life Menon was born in Valanchery in the Malappuram district of Kerala to V.K.S Menon and Malathy. His father was an officer in Tamil Nadu police and a native of Guruvayoor in Thrissur district. He did his schooling at Basel Evangelical Mission Higher Secondary School, Palakkad. Later, he attended the Government Victoria College, P ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sindhu Bhairavi (raga)
Sindhu Bhairavi is a raga in Hindustani classical music, Hindustani and Carnatic classical music, Carnatic Indian classical music, classical music, belonging to the Asavari thaat. In Carnatic music it is a Janya, Janya raga of the 8th Melakarta, melakartha raga Hanumatodi. The raga brings Viraham (separation), Shokam (sorrow), Karunam (compassion) and Bhakthi (devotion) Rasa (aesthetics), rasas. In Carnatic music it is a ''Bhashangaraga'', in which all the 12 notes are applicable. Sindhu Bhairavi is not to be confused with other similarly named ragas such as Sindhi Bhairavi, Sindh (raga), Sindh, Sindhura and Sindhura Bhairavi. Theory Arohana: Avarohana: Vadi (music), Vadi: Samavadi: Popular compositions Popular carnatic compositions in the raga are: * ''Vinnum mannum'' - Subramania Bharati * ''Venkatachala Nilayam, Tamboori meetidava, Vrindavanave Mandira, Tirupati Venkataramana, Harihara ninnanu, Elliruvano Ranga'', ''Kai Meeri Hoda Matige'' By Purandara Dasa * ''Naras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ranjani
Ranjani is a Carnatic raga, which is also sometimes written as ''Ranjini''. This raga is a ''janya'' of the 59th ''Melakarta'' raga Dharmavati.''Raganidhi'' by P. Subba Rao, Pub. 1964, The Music Academy of Madras''Ragas in Carnatic music'' by Dr. S. Bhagyalekshmy, Pub. 1990, CBH Publications It is an asymmetric pentatonic scale, which is pleasing and has been more popular in last 50 years. It figures in ''ragamalikas'', ''slokams'', ''vrittams'' and light popular songs, as it is a pleasing scale. Structure and Lakshana This ragam is an asymmetric scale and is classified as an ''audava-audava'' ragam (five notes in the ascending and descending scale). * : * : The notes in this scale are ''chathushruthi rishabham, sadharana gandharam, prati madhyamam, chathusruthi dhaivatam'' in ''arohana'' and additional ''kakli nishadham'' in ''avarohanam'', in place of ''sadharna rishabham'' (see pictures). From ''Dharmavati'' scale (59th melakarta), the panchamam is removed in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hamsadhwani
Hamsadhvani (meaning "the cry of the swan"), is a rāga in Carnatic music (musical scale of Carnatic tradition of Indian classical music). It is an ''audava'' rāgam (or ''owdava'' rāga, meaning pentatonic scale). It is a ''janya'' rāga of the Melakartha raga, Sankarabharanam (29th) but according to Hamsadhvani's prayoga or the way it is sung it is said to be the janya of Kalyani (65th). ''Hamsadhvani'' is also extensively used in Hindustani music and said to be borrowed into it from Carnatic music.''Raganidhi'' by P. Subba Rao, Pub. 1964, The Music Academy of Madras It was created by the Carnatic composer Ramaswami Dikshitar (1735–1817), father of Muthuswami Dikshitar (one of the musical trinity of Carnatic music), and brought into Hindustani music by Aman Ali Khan of the Bhendibazaar gharana. It has become popular due to Amir Khan. Structure and lakshana ''Hamsadhvani'' does not contain ''madhyamam'' or ''dhaivatham''. It is a pentatonic scale (''audava-audava'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mohanam
Mohanam is a rāga in Carnatic music (musical scale of South Indian classical music). It is an ''audava'' rāga (or ''owdava'' rāga, meaning pentatonic scale). It is usually described as a ''janya'' rāga of Harikamboji (28th Melakartha Raga). However, alternate opinions suggest that ''Mechakalyani'' may be a more appropriate classification based on the lakshana of the raga. The equivalent of ''Mohanam'' in Hindustani music is '' Bhoop''''Ragas in Carnatic music'' by Dr. S. Bhagyalekshmy, Pub. 1990, CBH Publications (or ''Bhopali''''Raganidhi'' by P. Subba Rao, Pub. 1964, The Music Academy of Madras). It is one of the most common pentatonic scales across the world and is very popular in East Asian and Southeast Asian music, including China and Japan. Structure and Lakshana ''Mohanam'' is a symmetric rāga that does not contain ''madhyamam'' and ''nishādham''. It is a symmetric pentatonic scale (''audava-audava'' raga in Carnatic music classification - ''audava'' meaning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
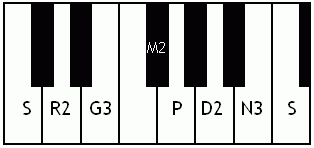
Kalyani (rāga)
Kalyani is a melakarta raga (parent musical scale) in the Carnatic music. It was called Kalyan but is now more popularly called Yaman in Hindustani Music. Its Western equivalent is the Lydian mode. Kalyani in Carnatic music In South Indian weddings it is a very prominently played raga. The word ''Kalyani'' means ''she who causes auspicious things''. It is the 65th melakarta raga under the Katapayadi sankhya. It is also called ''Mechakalyani''. The notes for Kalyani are S R2 G3 M2 P D2 N3. Kalyani is the first Prathi Madhyama raga that was ever discovered. It was obtained by the process of Graha Bhedam or modal shift of tonic of the ancient Shadja Grama. Specifics on this raga Kalyani has scope for elaborate alapana. One should not remain too long on panchamam (pa) or alternate between shadjamam and panchamam too frequently. Kalyani is prominently known among the public. It is often performed at the beginning of concerts because it is considered auspicious. Structure and l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)