|
AU-rich Element
Adenylate-uridylate-rich elements (AU-rich elements; AREs) are found in the 3' untranslated region (UTR) of many messenger RNAs (mRNAs) that code for proto-oncogenes, nuclear transcription factors, and cytokines. AREs are one of the most common determinants of RNA stability in mammalian cells. AREs are defined as a region with frequent adenine and uridine bases in a mRNA. They usually target the mRNA for rapid degradation. ARE-directed mRNA degradation is influenced by many exogenous factors, including phorbol esters, calcium ionophores, cytokines, and transcription inhibitors. These observations suggest that AREs play a critical role in the regulation of gene transcription during cell growth and differentiation, and the immune response. AREs have been divided into three classes with different sequences. The best characterised adenylate uridylate (AU)-rich Elements have a core sequence of AUUUA within U-rich sequences (for example WWWU(AUUUA)UUUW where W is A or U). This lies wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
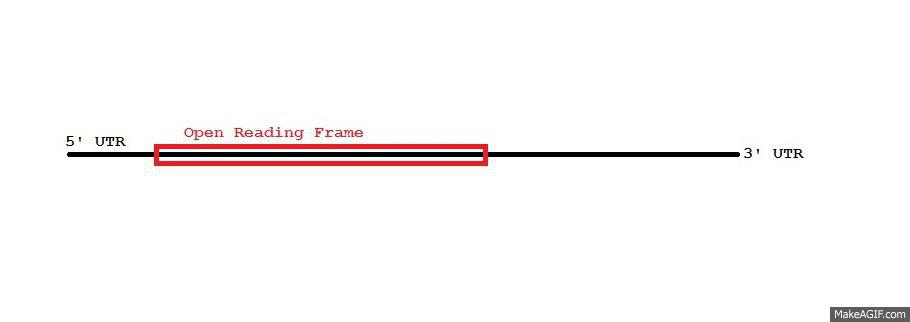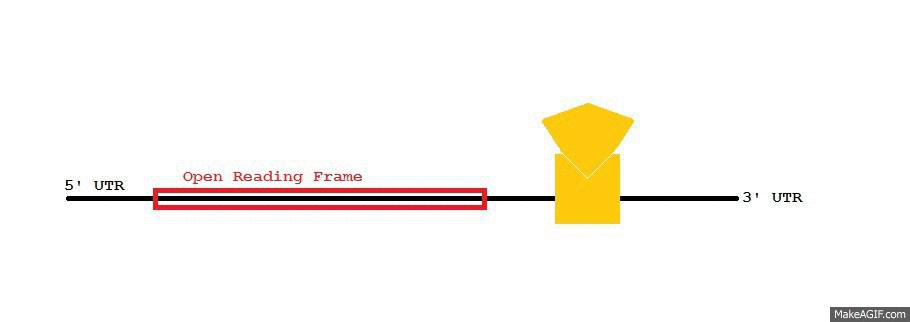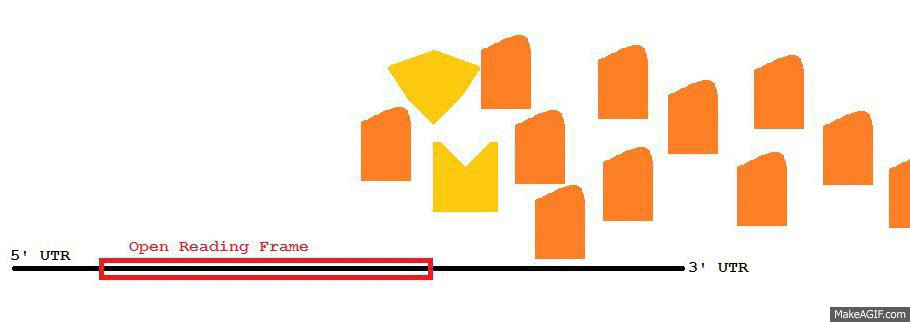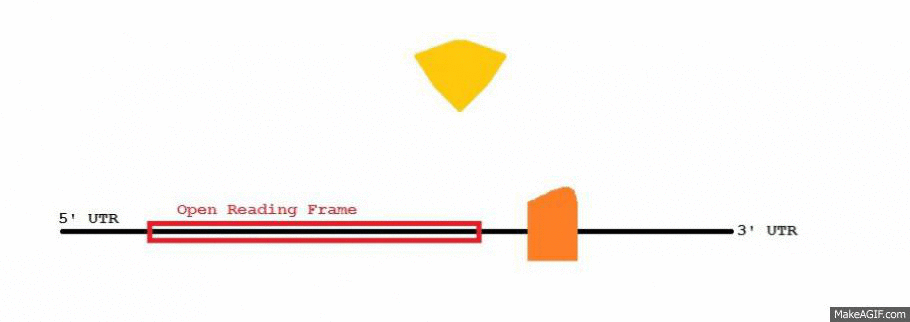
3' Untranslated Region
In molecular genetics, the three prime untranslated region (3′-UTR) is the section of messenger RNA (mRNA) that immediately follows the translation termination codon. The 3′-UTR often contains regulatory regions that post-transcriptionally influence gene expression. During gene expression, an mRNA molecule is transcribed from the DNA sequence and is later translated into a protein. Several regions of the mRNA molecule are not translated into a protein including the 5' cap, 5' untranslated region, 3′ untranslated region and poly(A) tail. Regulatory regions within the 3′-untranslated region can influence polyadenylation, translation efficiency, localization, and stability of the mRNA. The 3′-UTR contains both binding sites for regulatory proteins as well as microRNAs (miRNAs). By binding to specific sites within the 3′-UTR, miRNAs can decrease gene expression of various mRNAs by either inhibiting translation or directly causing degradation of the transcript. The 3� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-fos
Protein c-Fos is a proto-oncogene that is the human homolog of the retroviral oncogene v-fos. It is encoded in humans by the ''FOS'' gene. It was first discovered in rat fibroblasts as the transforming gene of the FBJ MSV (Finkel–Biskis–Jinkins murine osteogenic sarcoma virus) (Curran and Tech, 1982). It is a part of a bigger Fos family of transcription factors which includes c-Fos, FosB, Fra-1 and Fra-2. It has been mapped to chromosome region 14q21→q31. c-Fos encodes a 62 kDa protein, which forms heterodimer with c-jun (part of Jun family of transcription factors), resulting in the formation of AP-1 (Activator Protein-1) complex which binds DNA at AP-1 specific sites at the promoter and enhancer regions of target genes and converts extracellular signals into changes of gene expression. It plays an important role in many cellular functions and has been found to be overexpressed in a variety of cancers. Structure and function c-Fos is a 380 amino acid protein with a basic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CUGBP2
CUGBP, Elav-like family member 2, also known as Etr-3 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''CELF2'' gene. Members of the CELF/BRUNOL protein family are RNA-binding proteins and contain two N-terminal RNA recognition motif (RRM) domains, one C-terminal RRM domain, and a divergent segment of 160-230 aa between the second and third RRM domains. Members of this protein family regulate pre-mRNA alternative splicing and may also be involved in mRNA editing, and translation. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. Interactions CUGBP2 has been shown to interact with A1CF APOBEC1 complementation factor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''A1CF'' gene. Gene Alternative splicing occurs at this locus and three full-length transcript variants, encoding three distinct isoforms, have been described. Additi .... References External links * Further reading * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{gene-10-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostaglandins
The prostaglandins (PG) are a group of physiologically active lipid compounds called eicosanoids having diverse hormone-like effects in animals. Prostaglandins have been found in almost every tissue in humans and other animals. They are derived enzymatically from the fatty acid arachidonic acid. Every prostaglandin contains 20 carbon atoms, including a 5-carbon ring. They are a subclass of eicosanoids and of the prostanoid class of fatty acid derivatives. The structural differences between prostaglandins account for their different biological activities. A given prostaglandin may have different and even opposite effects in different tissues in some cases. The ability of the same prostaglandin to stimulate a reaction in one tissue and inhibit the same reaction in another tissue is determined by the type of receptor to which the prostaglandin binds. They act as autocrine or paracrine factors with their target cells present in the immediate vicinity of the site of their secreti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cox-2
Prostaglandin-endoperoxide synthase 2 (prostaglandin G/H synthase and cyclooxygenase) (The HUGO official symbol is PTGS2; HGNC ID, HGNC:9605), also known as cyclooxygenase-2 or COX-2, is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PTGS2'' gene. In humans it is one of two cyclooxygenases. It is involved in the conversion of arachidonic acid to prostaglandin H2, an important precursor of prostacyclin, which is expressed in inflammation. Function PTGS2 (COX-2), converts arachidonic acid (AA) to prostaglandin endoperoxide H2. PTGSs are targets for NSAIDs and PTGS2 (COX-2) specific inhibitors called coxibs. PTGS-2 is a sequence homodimer. Each monomer of the enzyme has a peroxidase and a PTGS (COX) active site. The PTGS (COX) enzymes catalyze the conversion of arachidonic acid to prostaglandins in two steps. First, hydrogen is abstracted from carbon 13 of arachidonic acid, and then two molecules of oxygen are added by the PTGS2 (COX-2), giving PGG2. Second, PGG2 is reduced to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
C-myc
''Myc'' is a family of regulator genes and proto-oncogenes that code for transcription factors. The ''Myc'' family consists of three related human genes: ''c-myc'' (MYC), ''l-myc'' (MYCL), and ''n-myc'' (MYCN). ''c-myc'' (also sometimes referred to as ''MYC'') was the first gene to be discovered in this family, due to homology with the viral gene ''v-myc''. In cancer, ''c-myc'' is often constitutively (persistently) expressed. This leads to the increased expression of many genes, some of which are involved in cell proliferation, contributing to the formation of cancer. A common human translocation involving ''c-myc'' is critical to the development of most cases of Burkitt lymphoma. Constitutive upregulation of ''Myc'' genes have also been observed in carcinoma of the cervix, colon, breast, lung and stomach. Myc is thus viewed as a promising target for anti-cancer drugs. Unfortunately, Myc possesses several features that render it undruggable such that any anti-cancer drugs f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer Cell
Cancer cells are cells that divide continually, forming solid tumors or flooding the blood with abnormal cells. Cell division is a normal process used by the body for growth and repair. A parent cell divides to form two daughter cells, and these daughter cells are used to build new tissue or to replace cells that have died because of aging or damage. Healthy cells stop dividing when there is no longer a need for more daughter cells, but cancer cells continue to produce copies. They are also able to spread from one part of the body to another in a process known as metastasis. Classification There are different categories of cancer cell, defined according to the cell type from which they originate. * Carcinoma, the majority of cancer cells are epithelial in origin, beginning in a tissue that lines the inner or outer surfaces of the body. * Leukaemia, originate in the tissues responsible for producing new blood cells, most commonly in the bone marrow. * Lymphoma and myeloma, deriv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Virus
A virus is a submicroscopic infectious agent that replicates only inside the living cells of an organism. Viruses infect all life forms, from animals and plants to microorganisms, including bacteria and archaea. Since Dmitri Ivanovsky's 1892 article describing a non-bacterial pathogen infecting tobacco plants and the discovery of the tobacco mosaic virus by Martinus Beijerinck in 1898,Dimmock p. 4 more than 9,000 virus species have been described in detail of the millions of types of viruses in the environment. Viruses are found in almost every ecosystem on Earth and are the most numerous type of biological entity. The study of viruses is known as virology, a subspeciality of microbiology. When infected, a host cell is often forced to rapidly produce thousands of copies of the original virus. When not inside an infected cell or in the process of infecting a cell, viruses exist in the form of independent particles, or ''virions'', consisting of (i) the genetic material, i. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exosome Complex
The exosome complex (or PM/Scl complex, often just called the exosome) is a multi-protein intracellular complex capable of degrading various types of RNA (ribonucleic acid) molecules. Exosome complexes are found in both eukaryotic cells and archaea, while in bacteria a simpler complex called the degradosome carries out similar functions. The core of the exosome contains a six-membered ring structure to which other proteins are attached. In eukaryotic cells, the exosome complex is present in the cytoplasm, nucleus, and especially the nucleolus, although different proteins interact with the exosome complex in these compartments regulating the RNA degradation activity of the complex to substrates specific to these cell compartments. Substrates of the exosome include messenger RNA, ribosomal RNA, and many species of small RNAs. The exosome has an exoribonucleolytic function, meaning it degrades RNA starting at one end (the 3′ end in this case), and in eukaryotes also an endori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RNA Recognition Motif
RNA recognition motif, RNP-1 is a putative RNA-binding domain of about 90 amino acids that are known to bind single-stranded RNAs. It was found in many eukaryotic proteins. The largest group of single strand RNA-binding protein is the eukaryotic RNA recognition motif (RRM) family that contains an eight amino acid RNP-1 consensus sequence. RRM proteins have a variety of RNA binding preferences and functions, and include heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins (hnRNPs), proteins implicated in regulation of alternative splicing (SR, U2AF2, Sxl), protein components of small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (U1 and U2 snRNPs), and proteins that regulate RNA stability and translation ( PABP, La, Hu). The RRM in heterodimeric splicing factor U2 snRNP auxiliary factor appears to have two RRM-like domains with specialised features for protein recognition. The motif also appears in a few single stranded DNA binding proteins. The typical RRM consists of four anti-parallel beta-strands and t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AUF1
The AMX-30 AuF1 is a French self-propelled gun vehicle currently in use by the armies of France and Saudi Arabia. It replaced the former Mk F3 155mm in French Army service. The AuF1 primary advance is that it incorporates full armor and nuclear-biological-chemical (NBC) protection for its crew of four, while the former Mk F3 155mm offered no protection and could carry only two of its four crew members. The AuF1 saw combat with the Iraqi Army in the Iran–Iraq War. History Though the French Mk F3 155mm would remain in production through the 1980s, by the early 1970s the French Army realized there was an urgent need for its replacement. The Mk. 3 155mm lacked a traversable turret and nuclear-biological-chemical (NBC) protection for its crew, and could carry only two of the four crew members needed to operate it (the remaining two having to be transported in support vehicles). Development of the AuF1 began in the late 1960s under the trade name of 155 GCT (155 mm Grande Cadence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |