|
ARX (Algorithmic Research Ltd.)
ARX (Algorithmic Research Ltd.) is a digital security company headquartered in San Francisco, CA, with offices in the UK, the Netherlands, Australia and Israel. It is the creator of CoSign by ARX, a digital signature technology, along with related digital signature security technology products. ARX was acquired by DocuSign in May 2015. The acquisition builds on a three-year business partnership between DocuSign and ARX, bringing together ARX's CoSign digital signature technology with DocuSign's Digital Transaction Management (DTM) platform and broadens The DocuSign Global Trust Network. The ARX digital signature products are based on public key infrastructure (PKI) technology, with the digital signatures resulting from a cryptographic operation that creates a ‘fingerprint’ unique to both the signer and the content, so that they cannot be copied, forged or tampered with. This process provides proof of signer identity, data integrity and the non-repudiation of signed documents ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CoSign Single Sign On
Cosign is an open-source project originally designed by the Research Systems Unix Group to provide the University of Michigan with a secure single sign-on web authentication system. Cosign authenticates a user on the web server and then provides an environment variable for the user's name. When the user accesses a part of the site that requires authentication, the presence of that variable allows access without having to sign on again. Cosign is part of the National Science Foundation Middleware Initiative (NMI) EDIT software release. See also * Central Authentication Service * Pubcookie Stanford WebAuth* Shibboleth (Internet2) Shibboleth is a single sign-on log-in system for computer networks and the Internet. It allows people to sign in using just one identity to various systems run by federations of different organizations or institutions. The federations are often un ... External links cosign homepagecosign Wiki Computer security software Federated identity ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CAdES (computing)
CAdES (''CMS Advanced Electronic Signatures'') is a set of extensions to Cryptographic Message Syntax (CMS) signed data making it suitable for advanced electronic signatures. Description CMS is a general framework for electronic signatures for various kinds of transactions like purchase requisition, contracts or invoices. CAdES specifies precise profiles of CMS signed data making it compliant with the European eIDAS regulation (Regulation on electronic identification and trust services for electronic transactions in the internal market). The eIDAS regulation enhances and repeals the Electronic Signatures Directive 1999/93/EC. EIDAS is legally binding in all EU member states since July 2014. An electronic signature that has been created in compliance with eIDAS has the same legal value as a handwritten signature. An electronic signature, technically implemented based on CAdES has the status of an advanced electronic signature. This means that * it is uniquely linked to the signato ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amos Fiat
Amos Fiat (born December 1, 1956) is an Israeli computer scientist, a professor of computer science at Tel Aviv University. He is known for his work in cryptography, online algorithms, and algorithmic game theory. Biography Fiat earned his Ph.D. in 1987 from the Weizmann Institute of Science under the supervision of Adi Shamir. After postdoctoral studies with Richard Karp and Manuel Blum at the University of California, Berkeley, he returned to Israel, taking a faculty position at Tel Aviv University. Research Many of Fiat's most highly cited publications concern cryptography, including his work with Adi Shamir on digital signatures (leading to the Fiat–Shamir heuristic for turning interactive identification protocols into signature schemes) and his work with David Chaum and Moni Naor on electronic money, used as the basis for the ecash system. With Shamir and Uriel Feige in 1988, Fiat invented the Feige–Fiat–Shamir identification scheme, a method for using public- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
USDA
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) is the federal executive department responsible for developing and executing federal laws related to farming, forestry, rural economic development, and food. It aims to meet the needs of commercial farming and livestock food production, promotes agricultural trade and production, works to assure food safety, protects natural resources, fosters rural communities and works to end hunger in the United States and internationally. It is headed by the Secretary of Agriculture, who reports directly to the President of the United States and is a member of the president's Cabinet. The current secretary is Tom Vilsack, who has served since February 24, 2021. Approximately 80% of the USDA's $141 billion budget goes to the Food and Nutrition Service (FNS) program. The largest component of the FNS budget is the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (formerly known as the Food Stamp program), which is the cornerstone of USDA's ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
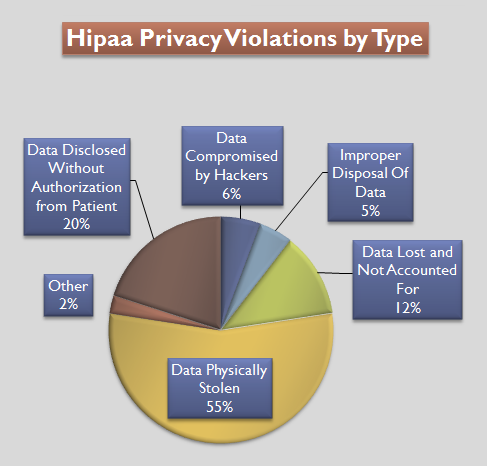
HIPAA
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA or the Kennedy– Kassebaum Act) is a United States Act of Congress enacted by the 104th United States Congress and signed into law by President Bill Clinton on August 21, 1996. It modernized the flow of healthcare information, stipulates how personally identifiable information maintained by the healthcare and healthcare insurance industries should be protected from fraud and theft, and addressed some limitations on healthcare insurance coverage. It generally prohibits healthcare providers and healthcare businesses, called ''covered entities'', from disclosing protected information to anyone other than a patient and the patient's authorized representatives without their consent. With limited exceptions, it does not restrict patients from receiving information about themselves. It does not prohibit patients from voluntarily sharing their health information however they choose, nor does it require confidentialit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarbanes–Oxley Act
The Sarbanes–Oxley Act of 2002 is a United States federal law that mandates certain practices in financial record keeping and reporting for corporations. The act, (), also known as the "Public Company Accounting Reform and Investor Protection Act" (in the Senate) and "Corporate and Auditing Accountability, Responsibility, and Transparency Act" (in the House) and more commonly called Sarbanes–Oxley, SOX or Sarbox, contains eleven sections that place requirements on all U.S. public company boards of directors and management and public accounting firms. A number of provisions of the Act also apply to privately held companies, such as the willful destruction of evidence to impede a federal investigation. The law was enacted as a reaction to a number of major corporate and accounting scandals, including Enron and WorldCom. The sections of the bill cover responsibilities of a public corporation's board of directors, add criminal penalties for certain misconduct, and require t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Title 21 CFR Part 11
Title 21 CFR Part 11 is the part of Title 21 of the Code of Federal Regulations that establishes the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulations on electronic records and electronic signatures (ERES). Part 11, as it is commonly called, defines the criteria under which electronic records and electronic signatures are considered trustworthy, reliable, and equivalent to paper records (Title 21 CFR Part 11 Section 11.1 (a)). Coverage Practically speaking, Part 11 applies to drug makers, medical device manufacturers, biotech companies, biologics developers, CROs, and other FDA-regulated industries, with some specific exceptions. It requires that they implement controls, including audits, system validations, audit trails, electronic signatures, and documentation for software and systems involved in processing the electronic data that FDA predicate rules require them to maintain. A predicate rule is any requirement set forth in the Federal Food, Drug and Cosmetic Act, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UETA
Ueta (written: or ) is a Japanese surname. Notable people with the surname include: *, Japanese murderer *, Japanese volleyball player *, Japanese triple jumper See also *1619 Ueta, a main-belt asteroid *Ueta Station, a railway station in Toyohashi, Aichi Prefecture, Japan *Uniform Electronic Transactions Act *Ueda (other) {{surname Japanese-language surnames ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Signatures In Global And National Commerce Act
The Electronic Signatures in Global and National Commerce Act (ESIGN, , ) is a United States federal law passed by the U.S. Congress to facilitate the use of electronic records and electronic signatures in interstate and foreign commerce by ensuring the validity and legal effect of contracts entered into electronically. Although every state has at least one law pertaining to electronic signatures, it is the federal law that lays out the guidelines for interstate commerce. The general intent of the ESIGN Act is spelled out in the first section (101.a), that a contract or signature “may not be denied legal effect, validity, or enforceability solely because it is in electronic form”. This simple statement provides that electronic signatures and records are just as good as their paper equivalents, and therefore subject to the same legal scrutiny of authenticity that applies to paper documents. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reuters
Reuters ( ) is a news agency owned by Thomson Reuters Corporation. It employs around 2,500 journalists and 600 photojournalists in about 200 locations worldwide. Reuters is one of the largest news agencies in the world. The agency was established in London in 1851 by the German-born Paul Reuter. It was acquired by the Thomson Corporation of Canada in 2008 and now makes up the media division of Thomson Reuters. History 19th century Paul Reuter worked at a book-publishing firm in Berlin and was involved in distributing radical pamphlets at the beginning of the Revolutions in 1848. These publications brought much attention to Reuter, who in 1850 developed a prototype news service in Aachen using homing pigeons and electric telegraphy from 1851 on, in order to transmit messages between Brussels and Aachen, in what today is Aachen's Reuters House. Reuter moved to London in 1851 and established a news wire agency at the London Royal Exchange. Headquartered in London, Reuter' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EAL4+
The Evaluation Assurance Level (EAL1 through EAL7) of an IT product or system is a numerical grade assigned following the completion of a Common Criteria security evaluation, an international standard in effect since 1999. The increasing assurance levels reflect added assurance requirements that must be met to achieve Common Criteria certification. The intent of the higher levels is to provide higher confidence that the system's principal security features are reliably implemented. The EAL level does not measure the security of the system itself, it simply states at what level the system was tested. To achieve a particular EAL, the computer system must meet specific ''assurance requirements''. Most of these requirements involve design documentation, design analysis, functional testing, or penetration testing. The higher EALs involve more detailed documentation, analysis, and testing than the lower ones. Achieving a higher EAL certification generally costs more money and takes more ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Criteria
The Common Criteria for Information Technology Security Evaluation (referred to as Common Criteria or CC) is an international standard (ISO/IEC 15408) for computer security certification. It is currently in version 3.1 revision 5. Common Criteria is a framework in which computer system users can ''specify'' their security ''functional'' and ''assurance'' requirements (SFRs and SARs respectively) in a Security Target (ST), and may be taken from Protection Profiles (PPs). Vendors can then ''implement '' or make claims about the security attributes of their products, and testing laboratories can ''evaluate'' the products to determine if they actually meet the claims. In other words, Common Criteria provides assurance that the process of specification, implementation and evaluation of a computer security product has been conducted in a rigorous and standard and repeatable manner at a level that is commensurate with the target environment for use. Common Criteria maintains a list of ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |