|
ARA Petrel (Q-16)
ARA ''Petrel'' was a hydrographic survey boat of the Argentine Navy, built in the Cadenazzi Shipyard and based in Buenos Aires. The vessel is named after the petrel, a seabird that inhabits Argentina's littoral, and is the third Argentine naval ship with this name. Design ''Petrel'' was a coastal and fluvial research ship designed by the engineering team at Cadenazzi Shipyard, where it was built. It was powered by two diesel engines driving two propellers. History ''Petrel'' was built in the Cadenazzi Shipyard, in Tigre, Buenos Aires. Commissioned by the Argentine Navy in July 1965, she was assigned to the Argentine Naval Hydrographic Service, Naval Hydrographic Service ( ''Servicio de Hidrografía Naval''). She undertook several campaigns, which included Depth sounding, sounding, current measuring, water sampling and bottom sampling; same as the survey launch ARA Cormorán (Q-15), ''Cormorán''. As of late 2015, ''Petrel'' has been decommissioned. See also * List of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petrel
Petrels are tube-nosed seabirds in the bird order Procellariiformes. Description The common name does not indicate relationship beyond that point, as "petrels" occur in three of the four families within that group (all except the albatross family, Diomedeidae). Having a fossil record that was assumed to extend back at least 60 million years, the Procellariiformes was long considered to be among the older bird groupings, other than the ratites, with presumably distant ties to penguins and loons. However, recent research and fossil finds such as ''Vegavis'' show that the Galliformes (pheasants, grouse and relatives), and Anseriformes (ducks, geese) are still not fully resolved. Known species All the members of the order are exclusively pelagic in distribution—returning to land only to breed. The family Procellariidae is the main radiation of medium-sized true petrels, characterised by united nostrils with medium septum, and a long outer functional primary feather. It is dom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diesel Engines
The diesel engine, named after Rudolf Diesel, is an internal combustion engine in which ignition of the fuel is caused by the elevated temperature of the air in the cylinder due to mechanical compression; thus, the diesel engine is a so-called compression-ignition engine (CI engine). This contrasts with engines using spark plug-ignition of the air-fuel mixture, such as a petrol engine (gasoline engine) or a gas engine (using a gaseous fuel like natural gas or liquefied petroleum gas). Diesel engines work by compressing only air, or air plus residual combustion gases from the exhaust (known as exhaust gas recirculation (EGR)). Air is inducted into the chamber during the intake stroke, and compressed during the compression stroke. This increases the air temperature inside the cylinder to such a high degree that atomised diesel fuel injected into the combustion chamber ignites. With the fuel being injected into the air just before combustion, the dispersion of the fuel is uneven; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ships Built In Argentina
A ship is a large watercraft that travels the world's oceans and other sufficiently deep Sea lane, waterways, carrying cargo or passengers, or in support of specialized missions, such as defense, research, and fishing. Ships are generally distinguished from boats, based on size, shape, load capacity, and purpose. Ships have supported exploration, trade, Naval warfare, warfare, Human migration, migration, colonization, and science. After the 15th century, Columbian Exchange, new crops that had come from and to the Americas via the European seafarers significantly contributed to world population growth. Ship transport is responsible for the largest portion of world commerce. The word ''ship'' has meant, depending on the era and the context, either just a large vessel or specifically a Full-rigged ship, ship-rigged sailing ship with three or more masts, each of which is Square rig, square-rigged. As of 2016, there were more than 49,000 merchant ships, totaling almost 1.8 billion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Research Vessels Of Argentina
Research is " creative and systematic work undertaken to increase the stock of knowledge". It involves the collection, organization and analysis of evidence to increase understanding of a topic, characterized by a particular attentiveness to controlling sources of bias and error. These activities are characterized by accounting and controlling for biases. A research project may be an expansion on past work in the field. To test the validity of instruments, procedures, or experiments, research may replicate elements of prior projects or the project as a whole. The primary purposes of basic research (as opposed to applied research) are documentation, discovery, interpretation, and the research and development (R&D) of methods and systems for the advancement of human knowledge. Approaches to research depend on epistemologies, which vary considerably both within and between humanities and sciences. There are several forms of research: scientific, humanities, artistic, econom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Auxiliary Ships Of The Argentine Navy
This list includes all major auxiliary ships (transports, colliers, tankers, scientific vessels, tugs, among others) in service with the Argentine Navy since being formally established in the 1860s.In 1861 the modern Argentine Republic was born, after the Battle of Pavón. It does not include vessels prior to that date, nor does it include warships which are listed separately. The list is organized by type of ship, by class within each type, and by service entry date within each class. Service entry dates indicate the ship's commissioning into the Argentine Navy, and not the ship's entry in service with another navy unless specifically said. There is a separate list of current ships of the Argentine Navy regardless the type. Naming tradition The current norms establish naming conventions for Argentine Navy ships according to their type; some of these used for auxiliaries are summarized below. ;Avisos, salvage ships, maritime tugs: Mariners or civilians of relevance to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ARA Cormorán (Q-15)
ARA ''Cormorán'' (Q-15) is a hydrographic survey boat of the Argentine Navy, built in the Río Santiago Shipyard and based in Buenos Aires. The vessel is named after the cormorant, a seabird that inhabits Argentina’s littoral, and is the fourth Argentine naval ship with this name. Design ''Cormorán'' is a coastal and fluvial research ship designed by the engineering team at Río Santiago Shipyard, where it was built. Its hull has a metallic structure covered with cedar wooden planks, and its superstructure is made of aluminium. It is powered by two diesel engines driving two propellers, and has a Decca TM 1226 navigation radar. History ''Cormorán'' was built in the Río Santiago Shipyard. Commissioned by the Argentine Navy in February 1964, she was assigned to the Naval Hydrographic Service ( ''Servicio de Hidrografía Naval''). Since then she has undertaken several campaigns, which included depth sounding, current measuring, water sampling and bottom sampling. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Depth Sounding
Depth sounding, often simply called sounding, is measuring the depth of a body of water. Data taken from soundings are used in bathymetry to make maps of the floor of a body of water, such as the seabed topography. Soundings were traditionally shown on nautical charts in fathoms and feet. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA), the agency responsible for bathymetric data in the United States, still uses fathoms and feet on nautical charts. In other countries, the International System of Units (metres) has become the standard for measuring depth. Terminology "Sounding" derives from the Old English ''sund'', meaning "swimming, water, sea"; it is not related to the word ''sound'' in the sense of noise or tones, but to ''sound'', a geographical term. Traditional terms for soundings are a source for common expressions in the English language, notably "deep six" (a sounding of 6 fathoms). On the Mississippi River in the 1850s, the leadsmen also used old-fashione ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argentine Naval Hydrographic Service
The Argentine Hydrographic Service ( es, Servicio de Hidrografía Naval, abbreviated SHN) is the branch of the Ministry of Defense responsible for providing hydrographic services. Background Created on January 1, 1879, as ''Oficina Central de Hidrografía'' ( en, Hydrographic Central Office) by decree 11.289 of President Nicolás Avellaneda. It became the current SHN on 1972 by National Law 19.922. Since 2007, it became part of the Ministry of Defense. The main mission of the SHN is to provide safe navigation on national waters. The service do so with the creation and maintenance of nautical charts, coastal marker buoys, and lighthouses. In concordance to the International Maritime Organization regulations, the SHN is also the global coordinator for the NAVAREA VI zone, which covers the South West Atlantic Ocean region being responsible for emitting alerts to ships at sea and coordinating search and rescue operations. The national official time is also a responsibility of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tigre, Buenos Aires
Tigre (, ''Tiger'') is a city in the Buenos Aires Province, Argentina, situated in the north of Greater Buenos Aires, north of Buenos Aires city. Tigre lies on the Paraná Delta and is a tourist and weekend destination, reachable by bus and train services, including the scenic Tren de la Costa. It is the main city and administrative centre of the Tigre Partido. History The area's name derives from the "tigers" or jaguars that were hunted there, on occasions, in its early years. The area was first settled by Europeans who came to farm the land. The city sits on an island created by several small streams and rivers and was founded in 1820, after floods had destroyed other settlements in the area, then known as the ''Partido de las Conchas''. The port developed to serve the delta and to bring fruit and wood from the delta and ports upstream on the Paraná river. Tigre is still an important timber processing port. Transportation Road Tigre is connected to the capital by a spur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Propellers
A propeller (colloquially often called a screw if on a ship or an airscrew if on an aircraft) is a device with a rotating hub and radiating blades that are set at a pitch to form a helical spiral which, when rotated, exerts linear thrust upon a working fluid such as water or air. Propellers are used to pump fluid through a pipe or duct, or to create thrust to propel a boat through water or an aircraft through air. The blades are specially shaped so that their rotational motion through the fluid causes a pressure difference between the two surfaces of the blade by Bernoulli's principle which exerts force on the fluid. Most marine propellers are screw propellers with helical blades rotating on a propeller shaft with an approximately horizontal axis. History Early developments The principle employed in using a screw propeller is derived from sculling. In sculling, a single blade is moved through an arc, from side to side taking care to keep presenting the blade to the water at t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
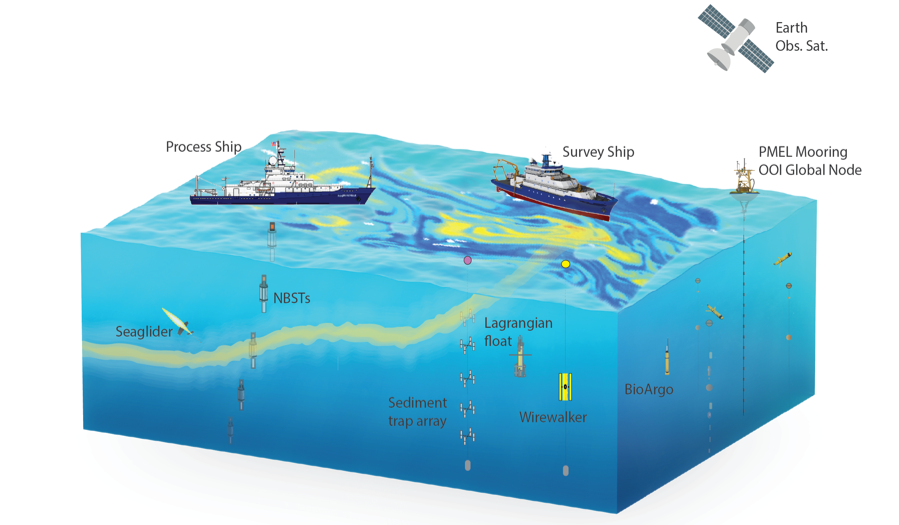
Research Ship
A research vessel (RV or R/V) is a ship or boat designed, modified, or equipped to carry out research at sea. Research vessels carry out a number of roles. Some of these roles can be combined into a single vessel but others require a dedicated vessel. Due to the demanding nature of the work, research vessels may be constructed around an icebreaker hull, allowing them to operate in polar waters. History The research ship had origins in the early voyages of exploration. By the time of James Cook's ''Endeavour'', the essentials of what today we would call a research ship are clearly apparent. In 1766, the Royal Society hired Cook to travel to the Pacific Ocean to observe and record the transit of Venus across the Sun. The ''Endeavour'' was a sturdy vessel, well designed and equipped for the ordeals she would face, and fitted out with facilities for her "research personnel", Joseph Banks. As is common with contemporary research vessels, ''Endeavour'' also carried out more than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |