|
ALTO (XML)
Analyzed Layout and Text Object (ALTO) is an open XML Schema developed by the EU-funded project called METAe. The standard was initially developed for the description of text Optical character recognition, OCR and layout information of pages for digitized material. The goal was to describe the layout and text in a form to be able to reconstruct the original appearance based on the digitized information - similar to the approach of a lossless image saving operation. ALTO is often used in combination with Metadata Encoding and Transmission Standard (METS) for the description of the whole digitized object and creation of references across the ALTO files, e.g. reading sequence description. The standard is hosted by the Library of Congress since 2010 and maintained by the Editorial Board initialized at the same time. In the time from the final version of the ALTO standard in June 2004 (version 1.0) ALTO was maintained by CCCCS Content Conversion Specialists GmbH, Hamburgup to version ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Optical Character Recognition
Optical character recognition or optical character reader (OCR) is the electronics, electronic or machine, mechanical conversion of images of typed, handwritten or printed text into machine-encoded text, whether from a scanned document, a photo of a document, a scene photo (for example the text on signs and billboards in a landscape photo) or from subtitle text superimposed on an image (for example: from a television broadcast). Widely used as a form of data entry from printed paper data recordswhether passport documents, invoices, bank statements, computerized receipts, business cards, mail, printed data, or any suitable documentationit is a common method of digitizing printed texts so that they can be electronically edited, searched, stored more compactly, displayed online, and used in machine processes such as cognitive computing, machine translation, (extracted) text-to-speech, key data and text mining. OCR is a field of research in pattern recognition, artificial intelligen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metadata Encoding And Transmission Standard
The Metadata Encoding and Transmission Standard (METS) is a metadata standards, metadata standard for encoding descriptive, administrative, and structural metadata regarding objects within a digital library, expressed using the XML schema language of the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). The standard is maintained as part of the MARC standards of the Library of Congress, and is being developed as an initiative of the Digital Library Federation (DLF). Overview METS is an XML Schema designed for the purpose of: * Creating XML document instances that express the hierarchical structure of digital library objects. * Recording the names and locations of the files that comprise those objects. * Recording associated metadata. METS can, therefore, be used as a tool for modeling real world objects, such as particular document types. Depending on its use, a METS document could be used in the role of Submission Information Package (SIP), Archival Information Package (AIP), or Dissemination ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metadata
Metadata (or metainformation) is "data that provides information about other data", but not the content of the data itself, such as the text of a message or the image itself. There are many distinct types of metadata, including: * Descriptive metadata – the descriptive information about a resource. It is used for discovery and identification. It includes elements such as title, abstract, author, and keywords. * Structural metadata – metadata about containers of data and indicates how compound objects are put together, for example, how pages are ordered to form chapters. It describes the types, versions, relationships, and other characteristics of digital materials. * Administrative metadata – the information to help manage a resource, like resource type, and permissions, and when and how it was created. * Reference metadata – the information about the contents and quality of Statistical data type, statistical data. * Statistical metadata – also called process data, may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ABBYY FineReader
ABBYY FineReader PDF is an optical character recognition (OCR) application developed by ABBYY. First released in 1993, the program runs on Microsoft Windows (Windows 7 or later) and Apple macOS (10.12 Sierra or later). Since v15, the Windows version can also edit PDF files. Users can use the program to convert image documents (photos, scans, PDF files) and screen captures into editable file formats, including Microsoft Word, Microsoft Excel, Microsoft PowerPoint, Rich Text Format, HTML, PDF/A, searchable PDF, CSV and txt (plain text) files. Since Version 11, files can be saved in the DjVu format. Since Version 15, the program recognizes text in 192 languages and has a built-in spell check for 48 of them. FineReader recognizes new characters in several ways. Users can train the app on characters, adding them to the recognition alphabet. Users can select characters from a list and add them to the alphabet of a selected language (for example, adding certain Icelandic characters ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EScriptorium
eScriptorium is a platform for manual or automated segmentation and text recognition of historical manuscripts and prints. Details The software is an open source software developed at the Paris Sciences et Lettres University as part of the projects ''Scripta'' and ''RESILIENCE'' with contributions from other institutions, partly funded by the EU's Horizon 2020 funding program and a grant from the Andrew W. Mellon Foundation. Scanned pages from manuscripts and prints can be imported into eScriptorium and exported as text in various formats (text, ALTO or PAGE XML, TEI). The text areas with text lines in the images are first recognized manually or automatically (segmentation). The text lines are then transcribed manually or automatically. Both automatic segmentation and text recognition can be trained using manually created or corrected examples (ground truth). The new models created in this way can be shared with others and can therefore be easily reused. eScriptorium is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kitodo
Kitodo (Abbr. of ''key to digital objects'') is an open-source software suite intended to support mass digitization projects for cultural heritage institutions. The software implements international standards such as METS, MODS and other formats maintained by the Library of Congress. Kitodo consists of several independent modules serving different purposes such as controlling the digitization workflow, enriching descriptive and structural metadata, and presenting the results to the public in a modern and convenient way. It is used by archives, libraries, museums, publishers and scanning utilities. Structure Kitodo contains the two main modules ''Kitodo.Presentation'' and ''Kitodo.Production'' and the following properties: * Central management of the digital copies (images) * Central metadata management: it supports cataloguing and integration of metadata from various locations * Controlling mechanisms: they are used to control the progress of work of the partners * Export and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
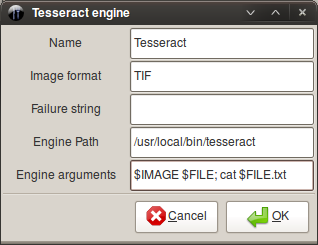
Tesseract (software)
Tesseract is an optical character recognition engine for various operating systems. It is free software, released under the Apache License. Originally developed by Hewlett-Packard as proprietary software in the 1980s, it was released as open source in 2005 and development was sponsored by Google in 2006.Announcing Tesseract OCR - The official Google blog In 2006, Tesseract was considered one of the most accurate open-source OCR engines available. History The Tesseract engine was originally developed as proprietary software at labs in[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transkribus
Transkribus is a platform for the text recognition, image analysis and structure recognition of historical documents. The platform was created in the context of the two EU projects "tranScriptorium" (2013–2015) and "READ" (Recognition and Enrichment of Archival Documents – 2016–2019). It was developed by the University of Innsbruck. Since July 1, 2019 the platform has been directed and further developed by the READ-COOP, a non-profit cooperative. The platform integrates tools developed by research groups throughout Europe, including the ''Pattern Recognition and Human Language Technology'' (PRHLT) group of the Technical University of Valencia and the Computational Intelligence Technology Lab (CITlab) group of University of Rostock. Comparable programs that offer similar functions are eScriptorium eScriptorium is a platform for manual or automated segmentation and text recognition of historical manuscripts and prints. Details The software is an open source sof ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dublin Core
140px, Logo of DCMI, maintenance agency for Dublin Core Terms The Dublin Core vocabulary, also known as the Dublin Core Metadata Terms (DCMT), is a general purpose metadata vocabulary for describing resources of any type. It was first developed for describing web content in the early days of the World Wide Web. The Dublin Core Metadata Initiative (DCMI) is responsible for maintaining the Dublin Core vocabulary. Initially developed as fifteen terms in 1998 the set of elements has grown over time and in 2008 was redefined as a Resource Description Framework (RDF) vocabulary. Designed with minimal constraints, each Dublin Core element is optional and may be repeated. There is no prescribed order in Dublin Core for presenting or using the elements. Milestones * 1995 - In 1995 an invitational meeting hosted by the OCLC Online Computer Library Center and the National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA) takes place at Dublin, Ohio, the headquarters of OCLC. * 1998, Septem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Implementation Strategies
Implementation is the realization of an application, execution of a plan, idea, model, design, specification, standard, algorithm, policy, or the administration or management of a process or objective. Industry-specific definitions Information technology In the information technology industry, implementation refers to the post-sales process of guiding a client from purchase to use of the software or hardware that was purchased. This includes requirements analysis, scope analysis, customizations, systems integrations, user policies, user training and delivery. These steps are often overseen by a project manager using project management methodologies. Software Implementations involve several professionals that are relatively new to the knowledge based economy such as business analysts, software implementation specialists, solutions architects, and project managers. To implement a system successfully, many inter-related tasks need to be carried out in an appropriate sequence. Uti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Open Archives Initiative Protocol For Metadata Harvesting
The Open Archives Initiative Protocol for Metadata Harvesting (OAI-PMH) is a protocol developed for harvesting metadata descriptions of records in an archive so that services can be built using metadata from many archives. An implementation of OAI-PMH must support representing metadata in Dublin Core, but may also support additional representations. The protocol is usually just referred to as the OAI Protocol. OAI-PMH uses XML over HTTP. Version 2.0 of the protocol was released in 2002; the document was last updated in 2015. It has a Creative Commons license BY-SA. History In the late 1990s, Herbert Van de Sompel (Ghent University) was working with researchers and librarians at Los Alamos National Laboratory (US) and called a meeting to address difficulties related to interoperability issues of e-print servers and digital repositories. The meeting was held in Santa Fe, New Mexico, in October 1999. A key development from the meeting was the definition of an interface that perm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
HOCR
hOCR is an open standard of data representation for formatted text obtained from optical character recognition (OCR). The definition encodes text, style, layout information, recognition confidence metrics and other information using Extensible Markup Language (XML) in the form of Hypertext Markup Language (HTML) or XHTML. Software The following OCR software can output the recognition result as hOCR file: * OCRopus * Tesseract * Cuneiform * ghostscript * HebOCR gcv2hocrgImageReader Example The following example is an extract of an hOCR file: ... ... The recognized text is stored in normal text nodes of the HTML file. The distribution into separate lines and words is here given by the surrounding ''span'' tags. Moreover, the usual HTML entities are used, for example the ''p'' tag for a paragraph. Additional information is given in the properties such as: * different layout elements such as "ocr_par", "ocr_line", "ocrx_word" * geometric information for each element with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |