|
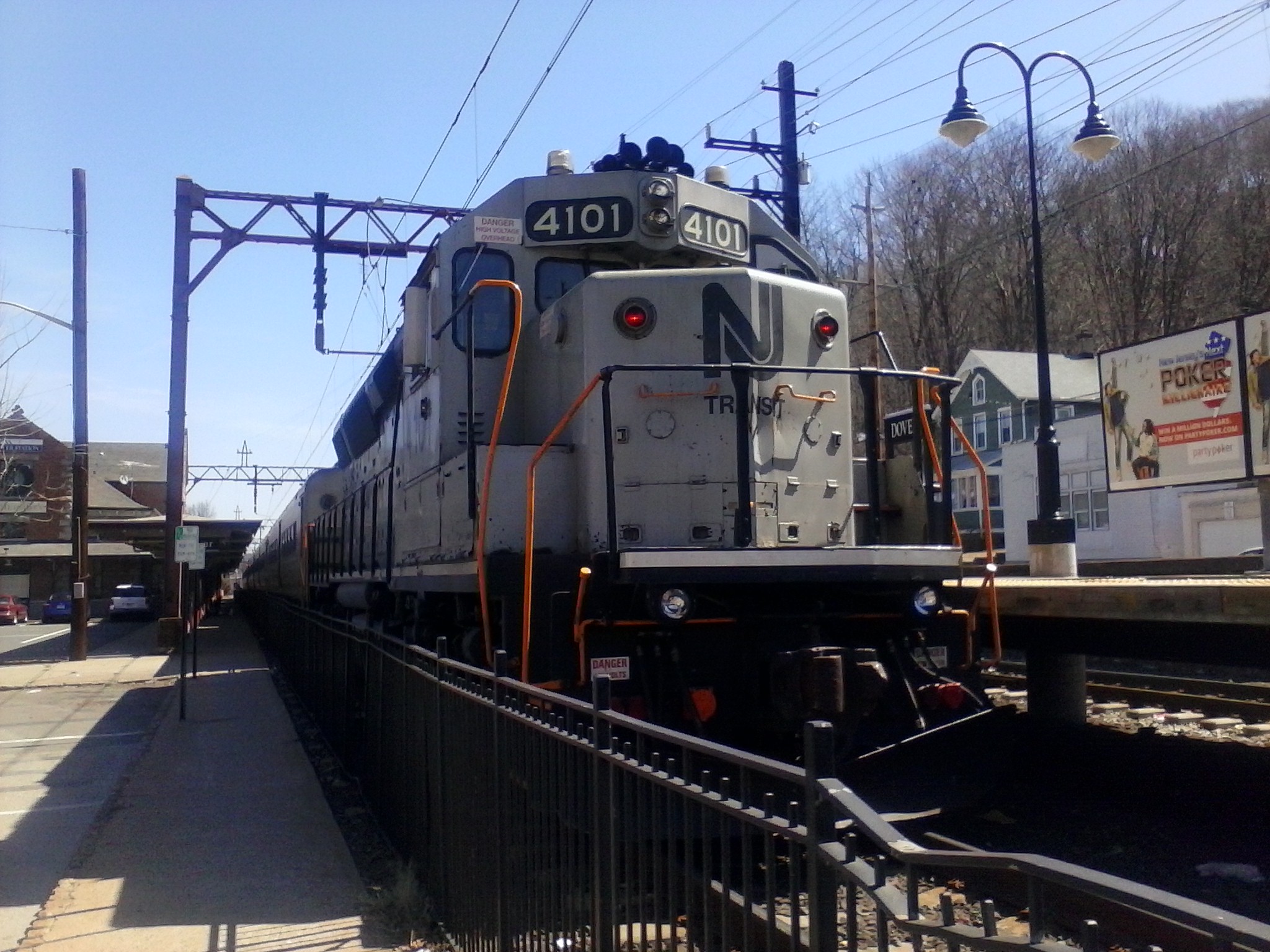
ALP-46
The Bombardier ALP-46 is an electric locomotive built in Germany by Bombardier Transportation, Bombardier between 2001 and 2002 for use in the United States. It is derived from the German DBAG Class 101, Class 101. New Jersey Transit (NJT) is the only railroad to operate this locomotive model, which is used across the electrified NJT system, specifically on the Northeast Corridor Line, Northeast Corridor, North Jersey Coast Line, North Jersey Coast, Morris & Essex Lines, Morris & Essex, and Montclair-Boonton Line, Montclair-Boonton lines. These locomotives replaced the ALP-44 locomotives, which were all retired by 2012. Orders and delivery NJT ordered 29 locomotives: the first 24 ALP-46 locomotives in December 1999 and an additional five locomotives in September 2001. They were built by Bombardier (formerly ADtranz) at their Kassel, Germany plant. The first two locomotives were built as preseries locomotives for testing—4600 was tested on the TTCI test plant in Pueblo, Colorado ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Jersey Transit Rail Operations
NJ Transit Rail Operations is the rail division of NJ Transit. It operates commuter rail service in New Jersey, with most service centered on transportation to and from New York City, Hoboken, and Newark. NJ Transit also operates rail service in Orange and Rockland counties in New York under contract to Metro-North Railroad. The commuter rail lines saw riders in , making it the second-busiest commuter railroad in North America as well as the longest by route length. This does not include NJ Transit's light rail operations. Network and infrastructure The lines operated by NJ Transit were formerly operated by the Pennsylvania Railroad, Central Railroad of New Jersey, New York and Long Branch Railroad and Erie Lackawanna Railroad, most of which date from the mid-19th century. From the 1960s onward, the New Jersey Department of Transportation began subsidizing the commuter lines. By 1976, the lines were all operated by Conrail under contract to NJDOT. The system took its curr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
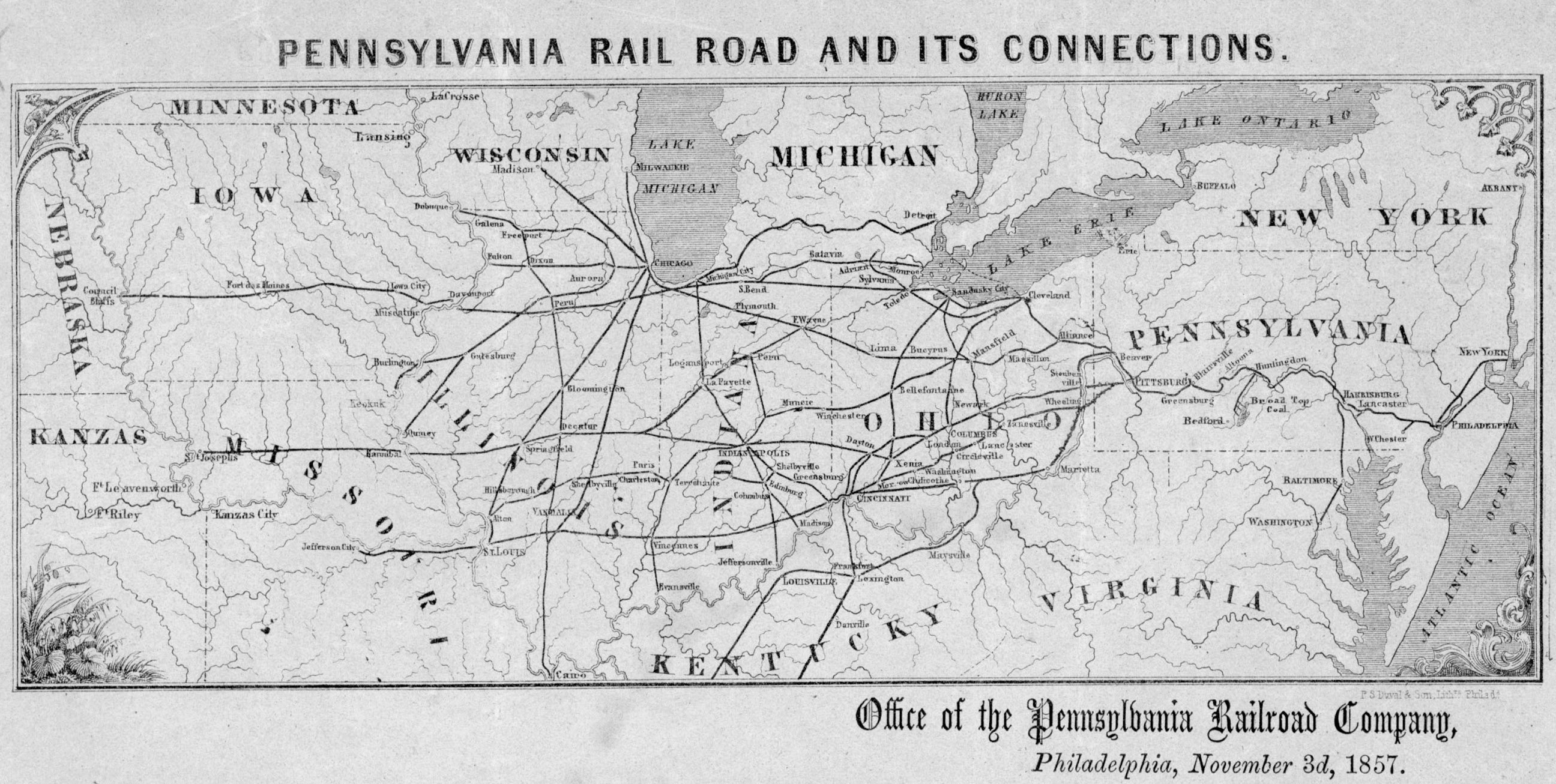
Pennsylvania Railroad
The Pennsylvania Railroad (reporting mark PRR), legal name The Pennsylvania Railroad Company also known as the "Pennsy", was an American Class I railroad that was established in 1846 and headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was named for the commonwealth in which it was established. By 1882, Pennsylvania Railroad had become the largest railroad (by traffic and revenue), the largest transportation enterprise, and the largest corporation in the world. Its budget was second only to the U.S. government. Over the years, it acquired, merged with, or owned part of at least 800 other rail lines and companies. At the end of 1926, it operated of rail line;This mileage includes companies independently operated. PRR miles of all tracks, which includes first (or main), second, third, fourth, and sidings, totalled 28,040.49 at the end of 1926. in the 1920s, it carried nearly three times the traffic as other railroads of comparable length, such as the Union Pacific and Atchison, T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ALP-44
The ABB ALP-44 was an electric locomotive which was built by Asea Brown Boveri of Sweden between 1989 and 1997 for the New Jersey Transit and SEPTA railway lines. Service New Jersey Transit New Jersey Transit acquired 32 ALP-44s for use on its electric railway lines. The first fifteen, numbered 4400–4414 and designated ALP-44O (Original), were delivered in 1990 (prototypes 4400 and 4401 in late 1989). Five additional units, numbered 4415–4419 and designated ALP-44E (Extended), were delivered in 1995. The final 12 locomotives, numbered 4420–4431 and designated ALP-44M (Microprocessor), were delivered in 1996 for the new Midtown Direct service. NJT's ALP-44s were to be overhauled for a cost of $2 million during a two-year period by Philadelphia-based Interfleet Technology. A car builder had not yet been selected to carry out the overhaul. However, by June 2009, NJT decided that it would be more efficient (economically and physically) to replace the ALP-44s rather than overh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northeast Corridor Line
The Northeast Corridor Line is a commuter rail service operated by NJ Transit between the Trenton Transit Center and New York Penn Station on Amtrak's Northeast Corridor in the United States. The service is the successor to Pennsylvania Railroad commuter trains between Trenton and New York, and is NJ Transit's busiest commuter rail service. After arrival at New York Penn Station, some trains load passengers and return to New Jersey, while others continue east to Sunnyside Yard for storage. Most servicing is done at the Morrisville Yard, at the west end of the line. The Northeast Corridor Line is colored red on NJ Transit system maps and its symbol is the State House. The Princeton Branch is a shuttle service connecting to the line. Connecting SEPTA Trenton Line service between Philadelphia and Trenton is listed in the timetable. History Early history Service on what is now the Northeast Corridor dates to the 1830s, with trains originating and terminating at the PRR's terminal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clocker (Amtrak)
The ''Clocker'' was a passenger train service between Philadelphia and New York City on the Northeast Corridor at first by the Pennsylvania Railroad and later by Amtrak. The service was nicknamed the ''Clocker'' by riders as trains were scheduled to leave each terminal at the top of the hour. The name was eventually adopted into official use by Amtrak in 1981. The service was briefly renamed ''Acela Commuter'' in 1999 before the name reverted to ''Clocker'' in 2003. Amtrak discontinued the service on October 28, 2005, and it was partially replaced by New Jersey Transit express trains between Trenton, NJ and New York City at times approximating the ''Clocker'' schedule. History Pennsylvania Railroad The ''Clocker'' was originally a Pennsylvania Railroad express train service between New York and Broad Street Station in Philadelphia;; 15 the name was unofficial, and PRR timetables didn't use it. Soon after New York Penn Station opened in 1910, the express trains began de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North Jersey Coast Line
The North Jersey Coast Line is a commuter rail Commuter rail, or suburban rail, is a passenger rail transport service that primarily operates within a metropolitan area, connecting commuters to a central city from adjacent suburbs or commuter towns. Generally commuter rail systems are con ... line running from Rahway, New Jersey, Rahway to Bay Head, New Jersey, traversing through the Jersey Shore region. Operated by New Jersey Transit, the line is electrified as far south as Long Branch, New Jersey, Long Branch. On rail system maps it is colored light blue, and its symbol is a sailboat. The line runs along the former New York & Long Branch Railroad, which was co-owned by the Central Railroad of New Jersey and the Pennsylvania Railroad. Most Trains that are on the line run between Pennsylvania Station (New York City) and Long Branch, New Jersey. Some Weekday Rush Hour Trains run between New York and Bay Head, New Jersey. Select trains will also run between New York and Sou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bombardier MultiLevel Coach
The Bombardier MultiLevel Coach is a bi-level passenger rail car manufactured by Bombardier for use on commuter rail lines. The first units were delivered in 2006 and deliveries (in various orders) continued to 2014. Overview There are 643 of these coaches in service as of 2015 on NJ Transit, Exo, and MARC. NJ Transit received 429 cars, including 62 cab cars, while Exo's predecessor, Agence métropolitaine de transport (AMT), received 160 cars, including 26 cab cars. The MARC order consists of 39 trailers and 15 cab cars for a total of 54 cars. The coaches were based on the Comet V and have a two-by-two seating arrangement and more knee and leg room than single-level coaches. The seats are also bigger and it has 15-30% more seating than on single-level coaches. The intermediate levels have 5 inward-facing seats on each side which flip up for wheelchairs or bicycles. On cab cars, a large equipment locker behind the cab replaces one row of seats. There are single-width side do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bombardier Transportation
Bombardier Transportation was a Canadian-German rolling stock and rail transport manufacturer, headquartered in Berlin, Germany. It was one of the world's largest companies in the rail vehicle and equipment manufacturing and servicing industry. Bombardier Transportation had many regional offices, production and development facilities worldwide. It produced a wide range of products including passenger rail vehicles, locomotives, bogies, propulsion and controls. In February 2020, the company had 36,000 employees, and 63 manufacturing and engineering locations around the world. Formerly a subsidiary and rail equipment division of Bombardier Inc., the company was acquired by French manufacturer Alstom on 29 January 2021. History 20th century 1970s: Formation and first orders Canadian company Bombardier Inc. entered the rail market in 1970 when it purchased Lohnerwerke GmbH of Austria. Bombardier Transportation's first order for mass transit rolling stock was in 1974 for the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DBAG Class 101
The DB Class 101 is a class of three-phase electric locomotives built by Adtranz and operated by DB Fernverkehr in Germany. 145 locomotives were built between 1996 and 1999 to replace the 30-year-old and aging DB Class 103, Class 103 as the flagship of the Deutsche Bahn, primarily hauling Intercity (Deutsche Bahn), Intercity services. This class encompasses the latest generation of locomotives of the Deutsche Bahn. In the United States, the Bombardier ALP-46 is derived from the DB Class 101. The Bombardier Traxx shares a common heritage. Background Around 1990, it became apparent that the current electric locomotives serving the heavy and fast (speeds over ) Intercity (Deutsche Bahn), Intercity services, the DB Class 103, Class 103, were wearing out. Their annual mileage of up to , and the faster and heavier trains, for which these units had not been designed, meant increasing wear damage to the control units, traction motors, and bogie frames. In addition, as part of the Pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electric Locomotive
An electric locomotive is a locomotive powered by electricity from overhead lines, a third rail or on-board energy storage such as a battery or a supercapacitor. Locomotives with on-board fuelled prime movers, such as diesel engines or gas turbines, are classed as diesel-electric or gas turbine-electric and not as electric locomotives, because the electric generator/motor combination serves only as a power transmission system. Electric locomotives benefit from the high efficiency of electric motors, often above 90% (not including the inefficiency of generating the electricity). Additional efficiency can be gained from regenerative braking, which allows kinetic energy to be recovered during braking to put power back on the line. Newer electric locomotives use AC motor-inverter drive systems that provide for regenerative braking. Electric locomotives are quiet compared to diesel locomotives since there is no engine and exhaust noise and less mechanical noise. The lack of re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Montclair-Boonton Line
The Montclair-Boonton Line is a commuter rail line of New Jersey Transit Rail Operations in the United States. It is part of the Hoboken Division. The line is a consolidation of three individual lines: the former Delaware, Lackawanna & Western Railroad's Montclair Branch, which ran from Hoboken Terminal to Bay Street, Montclair; the Erie Railroad's Greenwood Lake Division (segment from Montclair to Mountain View-Wayne), which originally ran from the Erie's Jersey City Terminal to Greenwood Lake, NY; and the former Lackawanna Boonton Line, which ran from Hoboken to Hackettstown, New Jersey. The Montclair-Boonton line was formed when the Montclair Connection opened on September 30, 2002. The line serves 28 active rail stations in New Jersey along with New York Pennsylvania Station. It crosses through six counties, serving six stations in the township of Montclair, two in the town of Bloomfield, and one in the city of Newark. Trains along the Montclair-Boonton Line heading eastw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maurice River Township, New Jersey
Maurice River Township () is the easternmost township in Cumberland County, New Jersey, United States. It is part of the Vineland- Millville- Bridgeton Primary Metropolitan Statistical Area for statistical purposes. As of the 2010 United States census, the township's population was 7,976, reflecting an increase of 1,048 (+15.1%) from the 6,928 counted in the 2000 Census, which had in turn increased by 280 (+4.2%) from the 6,648 counted in the 1990 Census. Maurice River Township was first formed as a precinct on January 19, 1748, and was incorporated by an act of the New Jersey Legislature on February 21, 1798, as one of New Jersey's initial group of 104 townships. Portions of the township were taken to form Millville on March 1, 1866.Snyder, John P''The Story of New Jersey's Civil Boundaries: 1606-1968'' Bureau of Geology and Topography; Trenton, New Jersey; 1969. p. 121. Accessed October 23, 2012. The township derives its name from Maurice, Prince of Orange. It is a dry tow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |