|
ACEGES
The ACEGES model (Agent-based Computational Economics of the Global Energy System) is a decision support tool for energy policy by means of controlled computational experiments. The ACEGES tool is designed to be the foundation for large custom-purpose simulations of the global energy system. The ACEGES methodological framework, developed by Voudouris (2011) by extending Voudouris (2010), is based on the agent-based computational economics (ACE) paradigm. ACE is the computational study of economies modeled as evolving systems of autonomous interacting agents.Tesfatsion, L and Judd, K. (2006), Handbook of Computational Economics, Volume 2: Agent-Based Computational Economics, North Holland The ACEGES tool is written in Java and runs on Windows, Mac OS and Linux platforms. The ACEGES tool is based on: * ThMASONlibrarya discrete-event multiagent simulation library * The R Project for statistical computing * ThGAMLSS framework It is important to clarify that although the ACEGES model ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
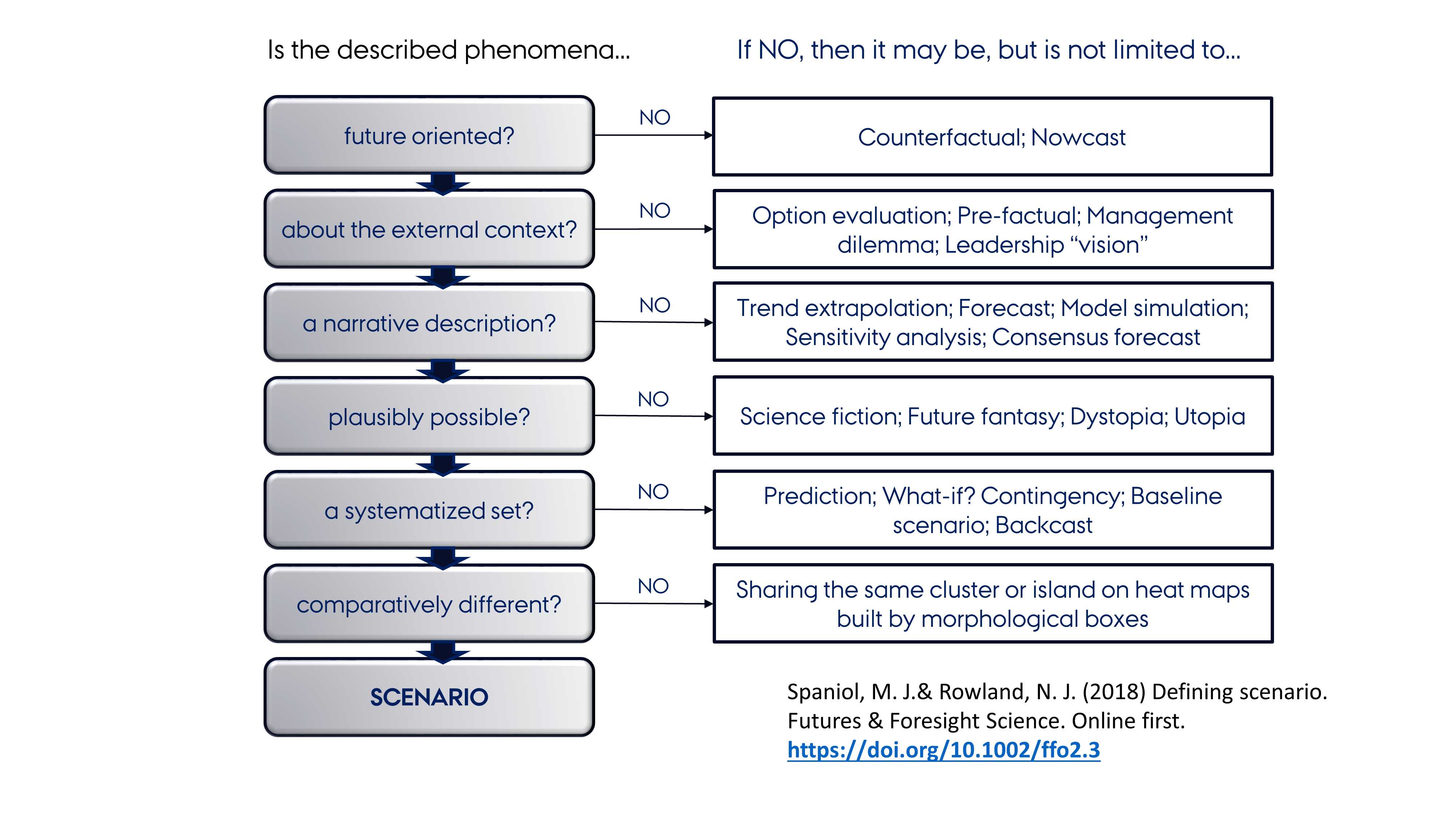
Scenario Analysis
Scenario planning, scenario thinking, scenario analysis, scenario prediction and the scenario method all describe a strategic planning method that some organizations use to make flexible long-term plans. It is in large part an adaptation and generalization of classic methods used by military intelligence. In the most common application of the method, analysts generate simulation games for policy makers. The method combines known facts, such as demographics, geography and mineral reserves, with military, political, and industrial information, and key driving forces identified by considering social, technical, economic, environmental, and political ("STEEP") trends. In business applications, the emphasis on understanding the behavior of opponents has been reduced while more attention is now paid to changes in the natural environment. At Royal Dutch Shell for example, scenario planning has been described as changing mindsets about the exogenous part of the world prior to formulating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agent-based Computational Economics
Agent-based computational economics (ACE) is the area of computational economics that studies economic processes, including whole economies, as dynamic systems of interacting agents. As such, it falls in the paradigm of complex adaptive systems. In corresponding agent-based models, the " agents" are "computational objects modeled as interacting according to rules" over space and time, not real people. The rules are formulated to model behavior and social interactions based on incentives and information. Such rules could also be the result of optimization, realized through use of AI methods (such as Q-learning and other reinforcement learning techniques). The theoretical assumption of mathematical optimization by agents in equilibrium is replaced by the less restrictive postulate of agents with bounded rationality ''adapting'' to market forces. ACE models apply numerical methods of analysis to computer-based simulations of complex dynamic problems for which more conventional meth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peak Oil
Peak oil is the hypothetical point in time when the maximum rate of global oil production is reached, after which it is argued that production will begin an irreversible decline. It is related to the distinct concept of oil depletion; while global petroleum reserves are finite, the limiting factor is not whether the oil exists but whether it can be extracted economically at a given price. A secular decline in oil extraction could be caused both by depletion of accessible reserves and by reductions in demand that reduce the price relative to the cost of extraction, as might be induced to reduce carbon emissions. Numerous predictions of the timing of peak oil have been made over the past century before being falsified by subsequent growth in the rate of petroleum extraction.David White, "The unmined supply of petroleum in the United States," ''Transactions of the Society of Automotive Engineers'', 1919, v.14, part 1, p.227.Daniel Yergin“There will be oil,”Wall Street Jou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of London
The University of London (UoL; abbreviated as Lond or more rarely Londin in post-nominals) is a federal public research university located in London, England, United Kingdom. The university was established by royal charter in 1836 as a degree-awarding examination board for students holding certificates from University College London and King's College London and "other such other Institutions, corporate or unincorporated, as shall be established for the purpose of Education, whether within the Metropolis or elsewhere within our United Kingdom". This fact allows it to be one of three institutions to claim the title of the third-oldest university in England, and moved to a federal structure in 1900. It is now incorporated by its fourth (1863) royal charter and governed by the University of London Act 2018. It was the first university in the United Kingdom to introduce examinations for women in 1869 and, a decade later, the first to admit women to degrees. In 1913, it appointe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Energy Economics
Energy economics is a broad scientific subject area which includes topics related to supply and use of energy in societies. Considering the cost of energy services and associated value gives economic meaning to the efficiency at which energy can be produced. Energy services can be defined as functions that generate and provide energy to the “desired end services or states”. The efficiency of energy services is dependent on the engineered technology used to produce and supply energy. The goal is to minimise energy input required (e.g. kWh, mJ, see Units of Energy) to produce the energy service, such as lighting ( lumens), heating (temperature) and fuel (natural gas). The main sectors considered in energy economics are transportation and building, although it is relevant to a broad scale of human activities, including households and businesses at a microeconomic level and resource management and environmental impacts at a macroeconomic level. Due to diversity of issues a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decision Support Systems
A decision support system (DSS) is an information system that supports business or organizational decision-making activities. DSSs serve the management, operations and planning levels of an organization (usually mid and higher management) and help people make decisions about problems that may be rapidly changing and not easily specified in advance—i.e. unstructured and semi-structured decision problems. Decision support systems can be either fully computerized or human-powered, or a combination of both. While academics have perceived DSS as a tool to support decision making processes, DSS users see DSS as a tool to facilitate organizational processes. Some authors have extended the definition of DSS to include any system that might support decision making and some DSS include a decision-making software component; Sprague (1980)Sprague, R;(1980).A Framework for the Development of Decision Support Systems" MIS Quarterly. Vol. 4, No. 4, pp.1-25. defines a properly termed DSS as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Computational Economics
Computational Economics is an interdisciplinary research discipline that involves computer science, economics, and management science.''Computational Economics''."About This Journal"an"Aims and Scope" This subject encompasses computational modeling of economic systems. Some of these areas are unique, while others established areas of economics by allowing robust data analytics and solutions of problems that would be arduous to research without computers and associated numerical methods.• Hans M. Amman, David A. Kendrick, and John Rust, ed., 1996. ''Handbook of Computational Economics'', v. 1, ElsevierDescription & chapter-previelinks. • Kenneth L. Judd, 1998. ''Numerical Methods in Economics'', MIT Press. Links tdescription anchapter previews Computational methods have been applied in various fields of economics research, including but not limiting to: Econometrics: Non-parametric approaches, Semi-parametric approaches, and Machine Learning. Dynamic Syste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UK Parliament
The Parliament of the United Kingdom is the supreme legislative body of the United Kingdom, the Crown Dependencies and the British Overseas Territories. It meets at the Palace of Westminster, London. It alone possesses legislative supremacy and thereby ultimate power over all other political bodies in the UK and the overseas territories. Parliament is bicameral but has three parts, consisting of the sovereign ( King-in-Parliament), the House of Lords, and the House of Commons (the primary chamber). In theory, power is officially vested in the King-in-Parliament. However, the Crown normally acts on the advice of the prime minister, and the powers of the House of Lords are limited to only delaying legislation; thus power is ''de facto'' vested in the House of Commons. The House of Commons is an elected chamber with elections to 650 single-member constituencies held at least every five years under the first-past-the-post system. By constitutional convention, all governmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Select Committee (United Kingdom)
In British politics, parliamentary select committees can be appointed from the House of Commons, like the Foreign Affairs Select Committee; from the House of Lords, like the Delegated Powers and Regulatory Reform Committee; or as a joint committee of Parliament drawn from both, such as the Joint Committee on Human Rights. Committees may exist as "sessional" committees – i.e. be near-permanent – or as "ad-hoc" committees with a specific deadline by which to complete their work, after which they cease to exist, such as the Lords Committee on Public Service and Demographic Change. The Commons select committees are generally responsible for overseeing the work of government departments and agencies, whereas those of the Lords look at general issues, such as the constitution, considered by the Constitution Committee, or the economy, considered by the Economic Affairs Committee. Both houses have their own committees to review drafts of European Union directives: the Eur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intelligent Energy Europe
The Competitiveness and Innovation Framework Programme (CIP) of the European Commission is meant to improve the competitiveness of European companies facing the challenges of globalization. The programme is mainly aimed at small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), which will receive support for innovation activities, better access to finance and business support services. It will run from 2007 to 2013. The programme wants to encourage the usage of information and communications technologies (ICT), renewable energies and to promote energy efficiency. History The CIP is based on Decision No 1639/2006/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council of 24 October 2006 establishing a ''Competitiveness and Innovation Framework Programme'' (2007 to 2013). CIP is complementary to the 7th Framework Programme (FP7) and is supposed to be "mutually-reinforcing . each designed to contribute to the success of the other." The program COSME followed up CIP and runs 2014 to 2020. Operational p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London School Of Economics
, mottoeng = To understand the causes of things , established = , type = Public research university , endowment = £240.8 million (2021) , budget = £391.1 million (2020–21) , chair = Susan Liautaud , chancellor = The Princess Royal(as Chancellor of the University of London) , director = The Baroness Shafik , head_label = Visitor , head = Penny Mordaunt(as Lord President of the Council '' ex officio'') , students = () , undergrad = () , postgrad = () , city = London , country = United Kingdom , coor = , campus = Urban , free_label = Newspaper , free = '' The Beaver'' , free_label2 = Printing house , free2 = LSE Press , co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |