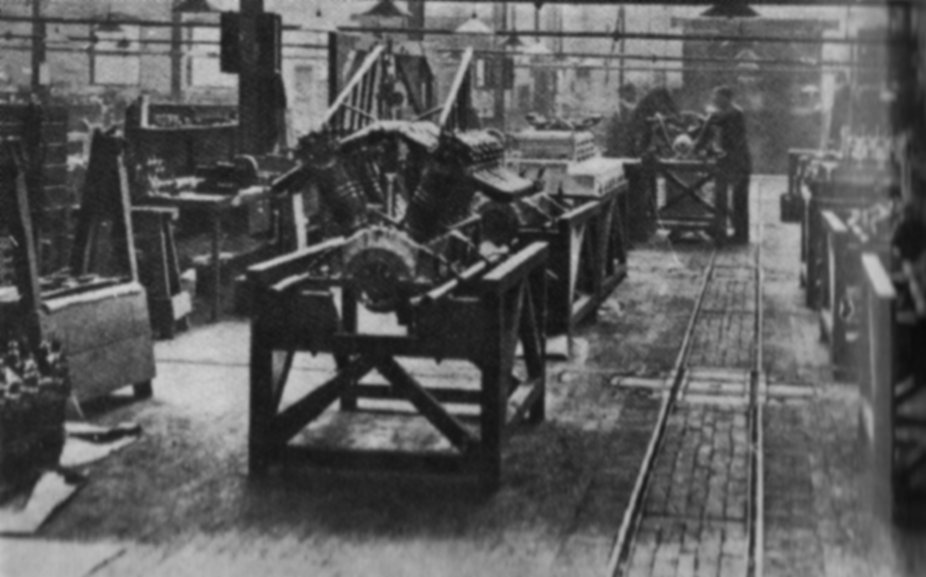
|
ABC Dragonfly I
The ABC Dragonfly was a British radial engine developed towards the end of the First World War. It was expected to deliver excellent performance for the time and was ordered in very large numbers. It proved, however, to be extremely unreliable and was abandoned when its faults were unable to be corrected. Design and development ABC Motors was founded in 1911 by Granville Bradshaw, who was also the company's chief designer. In 1917, after initial promising tests of the ABC Wasp air-cooled radial, Bradshaw produced a design for a larger and more powerful engine, the nine-cylinder Dragonfly. The engine was simple and easy to produce, and was predicted to give 340 hp (254 kW) for a weight of 600 lb (273 kg). One distinctive feature was the use of copper-plated cooling fins, which were claimed by Bradshaw to be so effective that water would not boil on the surface of the radiators.Bruce 1974, p.292 On the basis of the promised performance, Sir William Weir, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
WikiProject Aircraft
A WikiProject, or Wikiproject, is a Wikimedia movement affinity group for contributors with shared goals. WikiProjects are prevalent within the largest wiki, Wikipedia, and exist to varying degrees within sister projects such as Wiktionary, Wikiquote, Wikidata, and Wikisource. They also exist in different languages, and translation of articles is a form of their collaboration. During the COVID-19 pandemic, CBS News noted the role of Wikipedia's WikiProject Medicine in maintaining the accuracy of articles related to the disease. Another WikiProject that has drawn attention is WikiProject Women Scientists, which was profiled by '' Smithsonian'' for its efforts to improve coverage of women scientists which the profile noted had "helped increase the number of female scientists on Wikipedia from around 1,600 to over 5,000". On Wikipedia Some Wikipedia WikiProjects are substantial enough to engage in cooperative activities with outside organizations relevant to the field at issue. For e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bill Gunston
Bill Gunston (1 March 1927 – 1 June 2013) was a British aviation and military author. He flew with Britain's Royal Air Force from 1945 to 1948, and after pilot training became a flying instructor. He spent most of his adult life doing research and writing on aircraft and aviation. He was the author of over 350 books and articles. His work included many books published by Salamander Books. Early life Born William Tudor Gunston in London on 1 March 1927,"William Tudor Gunston." ''Contemporary Authors Online.'' Detroit: Gale, 2001. ''Biography in Context''. Web. 21 February 2013. Gunston was educated at Pinner County Grammar School. In his spare time, he was Flight Sergeant in the school Air Training Corps squadron and, for several months, the London Philharmonic Orchestra's librarian. Royal Air Force Gunston joined the Royal Air Force in 1945 and went to University College, Durham on an RAF cadetship. In 1946 he moved to No 4 Flying Training School in Bulawayo, Southern Rhodesi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sopwith Bulldog
The Sopwith 2FR.2 Bulldog was a prototype British two-seat fighter of the First World War. A single-engined biplane, the Bulldog was a fighter/reconnaissance aircraft intended to replace the Bristol F.2 Fighter, but was unsuccessful, with no replacement for the Bristol Fighter being purchased. Development and design In August 1917, the Sopwith Aviation Company started design of a two-seat fighter reconnaissance aircraft intended to replace the Bristol F.2 Fighter, and received permission to build prototypes of the Sopwith FR.2. It was intended to power the FR.2 with a 200 hp (149 kW) Hispano-Suiza 8 water-cooled V-8 engine, but the Hispano was in great demand, and it was decided to switch to the new Clerget 11, an eleven-cylinder rotary engine, a change which led to the prospective design being redesignated 2FR.2.Mason 1992, p.131. The Bulldog was a compact single-bay biplane resembling the first prototype Sopwith Snipe single-seat fighter. The pilot sat under the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nieuport London
The Nieuport London was a British night bomber aircraft designed in the First World War. A twin-engined triplane, the London was dogged by the unavailability and unreliability of its engines, and did not fly until 1920. Only two were built. Development and design In 1918, Henry Folland, chief designer of the Nieuport (England) Ltd (later to become the Nieuport & General Aircraft Co Ltd.), formerly of the Royal Aircraft Factory and designer of the S.E.5, designed the Nieuport London to meet the RAF Type VII specification for a night bomber, an order for six Londons was placed in July 1918.Mason 1994, p.124. The London was a twin-engined triplane with equal span, two-bay wings, powered by the new ABC Dragonfly radial engine. It was designed for ease of production, and was built of wood with use of metal fittings minimised. The angular fuselage was covered by ¼ inch (6 mm) thick wooden boarding joined by Tongue and groove joints, techniques more usually found in furn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bristol Badger
The Bristol Badger was designed to meet a British need for a two-seat fighter-reconnaissance aeroplane at the end of the First World War. Three Badgers were delivered to the Air Board to develop air-cooled radial engines, particularly that which became the Bristol Jupiter; two other Badgers were also built. Development The Bristol Badger had its roots in the Type 22 F.2C, a proposed upgrade of the Bristol F.2B using a 200 hp (150 kW) Salmson radial (Type 22), a 300 hp (220 kW) ABC Dragonfly radial (Type 22A), or a 230 hp (170 kW) Bentley B.R.2 rotary (Type 22B). The Type 23 Badger was a new design using the Dragonfly engine, drawn up at the end of 1917 to meet a two-seat fighter-reconnaissance role and owing a good deal to the Bristol Scout F. It was a single-bay biplane with strongly staggered, unswept and unequal-span wings. The pilot and observer sat in tandem, the pilot in front under the upper-wing trailing edge and the observer behind w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Boulton Paul Bourges
The Boulton & Paul P.7 Bourges was a prototype British twin-engined biplane day bomber built by Boulton & Paul to replace the Airco DH.10 Amiens. Despite demonstrating excellent performance and manoeuvrability, only three prototypes were built, post World War I cost cutting leading to the DH.10 not being replaced. Development and design In 1918, the British Air Ministry drew up specification A.2 (B) for the replacement of the Airco DH.10 Amiens medium bomber, despite the fact that the Amiens had not yet entered service. In response, J.D North, chief designer of Boulton & Paul's aircraft department designed a twin-engined aircraft, the P.7 Bourges, powered, like most of the types designed to replace the DH.10, by two of the new ABC Dragonfly radial engines. The ABC was ordered off the drawing board by the Ministry and high hopes were held for it. The Bourges was a three-seat, three bay biplane with unstaggered wings of all-wooden construction. The armament was two Lewis guns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BAT Basilisk
The BAT F.K.25 Basilisk was a prototype British fighter aircraft of the First World War. A single engined biplane intended to meet a requirement to replace the Sopwith Snipe, the Basilisk was unsuccessful, only three being built. Development and design In 1918, the British Air Ministry issued the RAF Type 1 specification for a single-seat fighter, powered by the new (and untried) ABC Dragonfly air cooled radial engine to replace the Sopwith Snipe. To meet this requirement, Frederick Koolhoven, (formerly of Armstrong Whitworth Aircraft and before that Deperdussin) chief designer of the British Aerial Transport Company of London, designed the F.K. 25 Basilisk.Lewis 1979, pp.128, 130. Like Koolhovens earlier F.K.23 Bantam, the Basilisk was a two-bay biplane with a wooden monocoque fuselage, but was larger and heavier to accommodate the larger engine and the equipment required by the Specification. Armament was two Vickers machine guns mounted ahead of the pilot, and enclosed in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Avro 533 Manchester
The Avro 533 Manchester was a First World War-era twin-engine biplane photo-reconnaissance and bomber aircraft designed and manufactured by Avro. Design and development Designed as a twin-engine bomber and photo-reconnaissance aircraft, the Avro 533 was a development of the earlier 523 and 529A. Originally designated the Avro 529B, the new 320 hp (240 kW) ABC Dragonfly I nine-cylinder engine was specified, but with a redesign in July 1918, the type number was subsequently changed to Avro 533. When the original engines were not available, the 300 hp (220 kW) Siddeley Puma engine was substituted on the second prototype in November 1918, this acquiring a new designation, the Avro 533A Manchester Mk II, and first flying in December that year. An American 400 hp (300 kW) Liberty engine was also proposed as an alternate engine.Harlan and Jenks 1973, p. 61. Operational history The Avro 533A Manchester Mk II flew for the first time in December 1918 with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Austin Greyhound
The Austin Greyhound was a British two-seat biplane fighter aircraft of World War I built by car manufacturer Austin. Owing to the end of the War and an unreliable engine, it was unsuccessful, only three being built. Development and design In 1918, Britain's Royal Air Force issued the Type III specification for a replacement for the Bristol F.2 Fighter to be powered by the new ABC Dragonfly radial engine. The Austin Motor Company, who had produced large numbers of aircraft, including 800 Royal Aircraft Factory S.E.5s, submitted a design by J Kenworthy, formerly of the Royal Aircraft Factory, which was named the Austin Greyhound. An order for three prototypes was placed on 18 May 1918.Bruce 1965, pp29-30. The Greyhound was a two-bay biplane of all-wooden construction.Mason 1992, p.133. The Greyhound's engine was covered by a conical cowling, with the cylinder heads protruding. The circular shape of the cowling continued down the fuselage. The upper and lower wings were almost ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Armstrong Whitworth Ara
The Armstrong Whitworth Ara was an unsuccessful British single-seat biplane fighter aircraft of the First World War built by Armstrong Whitworth. Design and development In early 1918, the British Air Ministry wrote RAF Specification Type 1 for a single-seat fighter to replace the Sopwith Snipe. The specified engine was the ABC Dragonfly, a new radial engine which had been ordered into production based on promised performance before any testing had been carried out. To meet this specification, Armstrong Whitworth's chief designer, Fred Murphy, produced the Armstrong Whitworth Ara, three prototypes being ordered.Bruce 1965, p.20. The Ara was a two-bay biplane. It had a square fuselage, the engine was covered in a pointed cowling, but with the cylinder heads exposed. The upper wing was low to give the pilot a better upwards view.Taylor 1990, p.48. As with the other fighters built to meet the Type 1 specification, the Dragonfly engine proved to be the Ara's undoing, demonstrating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rolls-Royce Eagle
The Rolls-Royce Eagle was the first aircraft engine to be developed by Rolls-Royce Limited. Introduced in 1915 to meet British military requirements during World War I, it was used to power the Handley Page Type O bombers and a number of other military aircraft. The Eagle was the first engine to make a non-stop trans-Atlantic crossing by aeroplane when two Eagles powered the converted Vickers Vimy bomber on the transatlantic flight of Alcock and Brown in June 1919. Background At the outbreak of World War I in August 1914, the Royal Aircraft Factory asked Rolls-Royce to develop a new air-cooled engine. Despite initial reluctance they agreed on condition that it be cooled by water rather than air, as this was the company's area of expertise. Design and development Development of the new 20 litre engine was led by Henry Royce from his home in Kent. Based initially on the 7.4 litre 40/50 Rolls-Royce Silver Ghost engine, and drawing also on the design of a 7.2 litre Daimler ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |