|
A400 Road
A4 most often refers to: *A4 paper, a paper size defined by the ISO 216 standard, measuring 210 × 297 mm A4 and variants may also refer to: Science and mathematics * British NVC community A4 (''Hydrocharis morsus-ranae - Stratiotes aloides'' community), one type of Aquatic communities in the British National Vegetation Classification system * Combretastatin A-4, a stilbenoid chemical compound * ''A''4, the alternating group on four elements * A4, a type of stainless steel, as defined by ISO 3506, equivalent to SAE steel grade 316L * Subfamily A4, a rhodopsin-like receptors subfamily Medicine * ATC code A04 ''Antiemetics and antinauseants'', a subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System * Lipoxin A4, a lipoxin * Androstenedione, an androgen steroid hormone Transportation Aeronautics and astronautics * "A-4 Helldiver", the civil version of the Curtiss Falcon an attack aircraft manufactured by Curtiss Aircraft Company * Douglas A-4 Skyhaw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
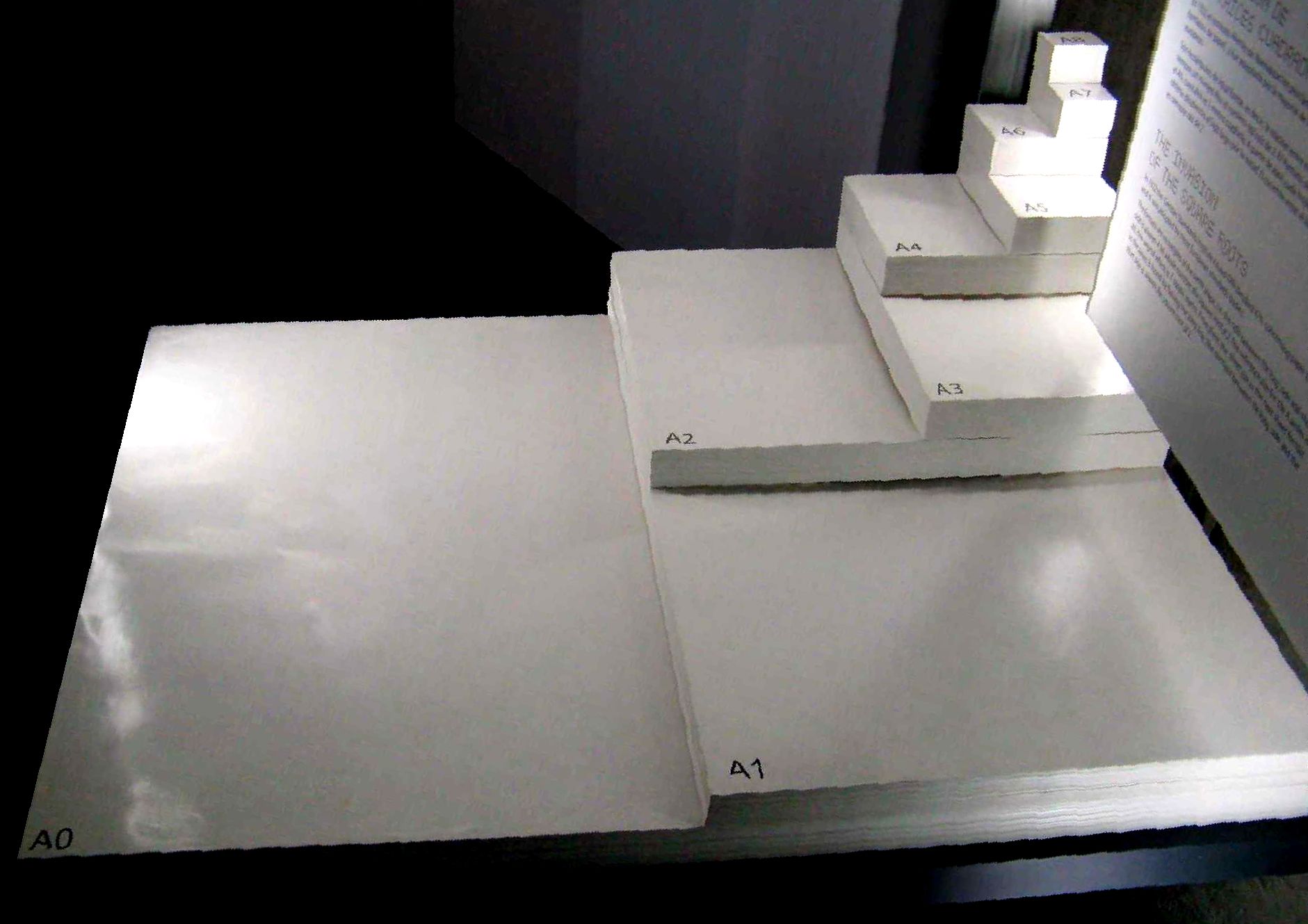
A4 Paper
ISO 216 is an international standard for paper sizes, used around the world except in North America and parts of Latin America. The standard defines the "A", "B" and "C" series of paper sizes, including A4, the most commonly available paper size worldwide. Two supplementary standards, ISO 217 and ISO 269, define related paper sizes; the ISO 269 "C" series is commonly listed alongside the A and B sizes. All ISO 216, ISO 217 and ISO 269 paper sizes (except some envelopes) have the same aspect ratio, , within rounding to millimetres. This ratio has the unique property that when cut or folded in half widthways, the halves also have the same aspect ratio. Each ISO paper size is one half of the area of the next larger size in the same series. Dimensions of A, B and C series History The oldest known mention of the advantages of basing a paper size on an aspect ratio of is found in a letter written on 25 October 1786 by the German scientist Georg Christoph Lichtenberg to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bavarian A IV
Bavarian A IV engines were German 2-2-2 steam locomotives with the Royal Bavarian State Railways (''Königlich Bayerische Staatsbahn''). The vehicles were developed for night journeys and operations on the North-South Railway. In order to increase the area of the evaporator, the boiler was increased in length to 3,080 mm and in diameter to 1,219 mm. In addition, the weight and the boiler overpressure were raised. These were the first engines to have an outside frame with outside cylinders. This class was used widely, especially in south Germany and in Austria. All the engines bar one were retired by 1883. The survivor was initially converted to a 0-6-0, and later a 0-4-2 wheel arrangement. They were coupled to 3 T 5 tenders. See also * List of Bavarian locomotives and railbuses A ''list'' is any set of items in a row. List or lists may also refer to: People * List (surname) Organizations * List College, an undergraduate division of the Jewish Theological Seminary of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Norrlands Artilleriregemente
The Norrland Artillery Regiment ( sv, Norrlands artilleriregemente), designation A 4, was a Swedish Army artillery regiment that traced its origins back to the 19th century. The regiment's soldiers were originally recruited from the provinces of Norrland. The regiment was disbanded in 1997. From 1998 to 2000, the Boden Artillery Regiment was known by this name. History The regiment was created in 1893 by splitting off two batteries from 1st Svea Artillery Regiment and two batteries from 1st Göta Artillery Regiment which formed six batteries of Norrland Artillery Regiment. The regiment was garrisoned in Östersund but a detachment in Boden was created in 1910, this detachment was split off in 1928 and created Norrbotten Artillery Corps. The regiment's designation was A 4 (4th Artillery Regiment). Norrland Artillery Regiment was disbanded in 1997. Campaigns *None Organisation *Unknown Heraldry and traditions Colours, standards and guidons The regimental standard was p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gotlands Artilleriregemente
The Gotland Artillery Regiment ( sv, Gotlands artilleriregemente, designation A 7) was a Swedish Army artillery regiment that was in active service between 1811 and 2000. The regiment was based in Visby as part of the Gotland Garrison. History The regiment origins from the Artillery Conscripts of the Gotland National Conscription (''Gotlands nationalbevärings artilleribeväring''), which were organized in 1811 as a result of the Russian occupation of Gotland in 1808 and by a convention adopted by the islanders in December 1810, which was ratified by King Charles XIII on 5 February 1811. It consisted then of two artillery batteries and a fortification company with a squad of 100 men, located in Visby. The unit was reorganized in 1861 into Gotland National Conscription Artillery Corps (''Gotlands nationalbevärings artillerikår'') and was given the designation No 4. In 1887 the corps changed its name to Gotland Artillery Corps (No 4). The Gotland Artillery Corps was rede ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Swedish Regiments
This is a list of Swedish regiments and other military units ( divisions, brigades, battalions, companies) that have existed since the 16th century. Most formations have changed names several times during their existence. Listed here are commonly used names. Regiments were the highest organized organic units in the Swedish Army from the time of Gustavus Adolphus on to the Second World War. In 1949, the Swedish Army was reorganised, with the regiments being used as training units for conscripts during peacetime. The new main fighting unit was the brigade, only organised in wartime (with a few exceptions). The division (''fördelning'') is not a static organization, but can have brigades assigned and removed when needed, similar to other countries' corps formations. For a short background of the Swedish conscription system historically used, see the article on the Swedish allotment system. Grand regiments ''Storregementen'' or ''landsregementen'' (regiments of the land), these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joint Force Air Component Headquarters
The Joint Force Air Component Headquarters (JFACHQ) is the United Kingdom's deployable air command and control unit. The JFACHQ is run by the Royal Air Force with representation from the other services. The JFACHQ has members from the operations and operations support branches of the RAF to both plan and execute the air war as well as support the deployed air components from A1 to A9. The unit is based at RAF High Wycombe. It can deploy worldwide at short notice to run an air campaign. The constituent parts of the JFAC are broken down according to the Continental staff system: *A1 – PANDA (Personnel and administration) *A2 – RAF Intelligence Intelligence services in the Royal Air Force are delivered by Officers of the Royal Air Force Intelligence Branch and Airmen from the Intelligence Analyst Trade and Intelligence Analyst (Voice) Trade. The specialisation has around 1,200 person ... *A3 – Air operations (both plans and current operations) *A4 – Air logistics ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Staff (military)
A military staff or general staff (also referred to as army staff, navy staff, or air staff within the individual services) is a group of officers, enlisted and civilian staff who serve the commander of a division or other large military unit in their command and control role through planning, analysis, and information gathering, as well as by relaying, coordinating, and supervising the execution of their plans and orders, especially in case of multiple simultaneous and rapidly changing complex operations. They are organised into functional groups such as administration, logistics, operations, intelligence, training, etc. They provide multi-directional flow of information between a commanding officer, subordinate military units and other stakeholders.PK Mallick, 2011Staff System in the Indian Army: Time for Change Centre for Land Warfare Studies, New Delhi, vol 31. A centralised general staff results in tighter top-down control but requires larger staff at headquarters (H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Metrobus Routes (Washington, D
List of Metrobus routes may refer to: * List of Metrobus routes (Miami-Dade County) Over 100 Metrobus routes are operated by Miami-Dade Transit with some routes contracted by LSF, serving Miami-Dade County, Florida and connecting with several routes in adjacent counties. Most routes are identified by number or letter, however s ... * List of Metrobus routes (Washington, D.C.) {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of A4 Roads
This is a list of roads designated A4. A4 is the name of several roads: * A004 road (Argentina), a road connecting Buenos Aires-La Plata highway with the Juan María Gutiérrez circle * A4 motorway (Austria), a road connecting Vienna and Nickelsdorf on the Hungarian border * ''A4 highway (Australia)'' may refer to : ** A4/M4 (Sydney), a road linking the Blue Mountains and Sydney ** A4 highway (Queensland), a road connecting Rockhampton with the Landsborough Highway at Barcaldine ** A4 highway (Tasmania), a road connecting the Midland Highway with the Tasman Highway * A4 motorway (Belgium), a road connecting Brussel and the A6 in Luxembourg * A4 motorway (Bulgaria), a road connecting A1 at Chirpan and the border crossing to Turkey, at the village of Kapitan Andreevo * ''A4 road (China)'' may refer to : ** A4 road (Shanghai), a road in Shanghai connecting Xinzhuang Interchange and Fengjing Interchange * A4 motorway (Croatia), a road connecting Zagreb to Hungary * A4 motorway (Cu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Prussian Locomotives And Railbuses
This list gives an overview of the locomotives and railcars that were in the Prussian state railways. Also included are the locomotives of the Grand Duchy of Hesse State Railways (''Grossherzoglich Hessischen Staatseisenbahnen'') and the Prussian-Hessian Railway Company (''Preussisch-Hessischen Eisenbahngemeinschaft''). Locomotive classification 1883 classification system Up to 1 April 1883 the Prussian state railways or acquired private railways designated their locomotives with names and/or numbers. From that date the following numbering scheme was introduced into all the railway divisions. This scheme applied to all state railway divisions and state-managed private railways. Locomotive numbering was organised according to the above system. However a locomotive could only be identified exactly by using the divisional name and running number in combination. Because of the increasing numbers of locomotives being procured, the classification scheme and its range of number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arrows A4
The Arrows A4 was the car which the Arrows Formula One team used to compete in the 1982 Formula One season. Complete Formula One results (key Key or The Key may refer to: Common meanings * Key (cryptography), a piece of information that controls the operation of a cryptography algorithm * Key (lock), device used to control access to places or facilities restricted by a lock * Key (map ...) References A04 {{F1-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Audi A4
The Audi A4 is a line of compact executive cars produced since 1994 by the German car manufacturer Audi, a subsidiary of the Volkswagen Group. The A4 has been built in five generations and is based on the Volkswagen Group B platform. The first generation A4 succeeded the Audi 80. The automaker's internal numbering treats the A4 as a continuation of the Audi 80 lineage, with the initial A4 designated as the B5-series, followed by the B6, B7, B8, and the B9. The B8 and B9 versions of the A4 are built on the Volkswagen Group MLB platform shared with several models and brands across the Volkswagen Group. The Audi A4 automobile layout consists of a front-engine design, with transaxle-type transmissions mounted at the rear of the engine. The cars are front-wheel drive, or on some models, " quattro" all-wheel drive. The A4 is available as a sedan and station wagon. Historically, the second (B6) and third generations (B7) of the A4 also included a convertible version. For the fourth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |