|
A-frame Complex
In organometallic chemistry, A-frame complexes are coordination compounds that contain two bridging bidentate ligands and a single atom bridge. They have the formula , where ''bd'' is a bidentate ligand like dppm, and X and L are a wide variety of ligands. The term was coined to describe products arising from the oxidative addition to Rh(I)Rh(I) complexes. Scope of compounds A-frame complexes typically consist of a pair of square-planar metal centres. Consequently, this family of complexes is found for those metals that tend to adopt that geometry, Rh, Ir, Ni, Pd, Pt, and Au. In addition to dppm, the analogous tetramethyldiphosphine (dmpm) also forms such complexes as do some related ligands, such as diphenyl-2-pyridylphosphine. The bridging site can be occupied by a variety of ligands, including CO, SO, NO, CH2, hydride, and chloride. Preparation A frame complexes are often produced by the addition of reagents of the type AX2 to low valent complexes of dppm: :2 M(0) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organometallic Chemistry
Organometallic chemistry is the study of organometallic compounds, chemical compounds containing at least one chemical bond between a carbon atom of an organic molecule and a metal, including alkali, alkaline earth, and transition metals, and sometimes broadened to include metalloids like boron, silicon, and selenium, as well. Aside from bonds to organyl fragments or molecules, bonds to 'inorganic' carbon, like carbon monoxide (metal carbonyls), cyanide, or carbide, are generally considered to be organometallic as well. Some related compounds such as transition metal hydrides and metal phosphine complexes are often included in discussions of organometallic compounds, though strictly speaking, they are not necessarily organometallic. The related but distinct term " metalorganic compound" refers to metal-containing compounds lacking direct metal-carbon bonds but which contain organic ligands. Metal β-diketonates, alkoxides, dialkylamides, and metal phosphine complexes are repres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coordination Compound
A coordination complex consists of a central atom or ion, which is usually metallic and is called the ''coordination centre'', and a surrounding array of bound molecules or ions, that are in turn known as ''ligands'' or complexing agents. Many metal-containing compounds, especially those that include transition metals (elements like titanium that belong to the Periodic Table's d-block), are coordination complexes. Nomenclature and terminology Coordination complexes are so pervasive that their structures and reactions are described in many ways, sometimes confusingly. The atom within a ligand that is bonded to the central metal atom or ion is called the donor atom. In a typical complex, a metal ion is bonded to several donor atoms, which can be the same or different. A polydentate (multiple bonded) ligand is a molecule or ion that bonds to the central atom through several of the ligand's atoms; ligands with 2, 3, 4 or even 6 bonds to the central atom are common. These compl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
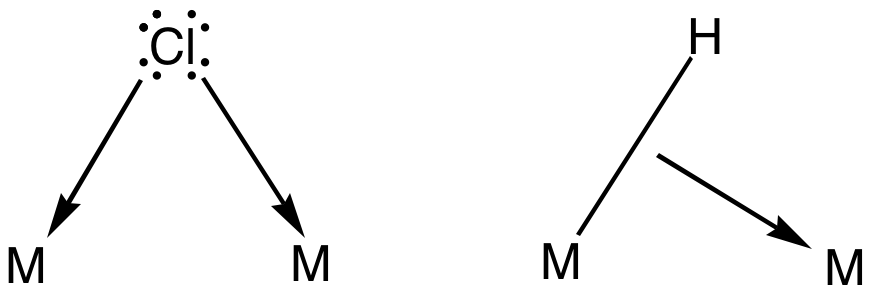
Bridging Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a bridging ligand is a ligand that connects two or more atoms, usually metal ions. The ligand may be atomic or polyatomic. Virtually all complex organic compounds can serve as bridging ligands, so the term is usually restricted to small ligands such as pseudohalides or to ligands that are specifically designed to link two metals. In naming a complex wherein a single atom bridges two metals, the bridging ligand is preceded by the Greek letter mu, μ, with a subscript number denoting the number of metals bound to the bridging ligand. μ2 is often denoted simply as μ. When describing coordination complexes care should be taken not to confuse μ with η ('eta'), which relates to hapticity. Ligands that are not bridging are called terminal ligands. List of bridging ligands Virtually all ligands are known to bridge, with the exception of amines and ammonia. Common bridging ligands include most of the common anions. Many simple organic ligands form str ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ligand
In coordination chemistry, a ligand is an ion or molecule (functional group) that binds to a central metal atom to form a coordination complex. The bonding with the metal generally involves formal donation of one or more of the ligand's electron pairs, often through Lewis bases. The nature of metal–ligand bonding can range from covalent to ionic. Furthermore, the metal–ligand bond order can range from one to three. Ligands are viewed as Lewis bases, although rare cases are known to involve Lewis acidic "ligands". Metals and metalloids are bound to ligands in almost all circumstances, although gaseous "naked" metal ions can be generated in a high vacuum. Ligands in a complex dictate the reactivity of the central atom, including ligand substitution rates, the reactivity of the ligands themselves, and redox. Ligand selection requires critical consideration in many practical areas, including bioinorganic and medicinal chemistry, homogeneous catalysis, and environmental chemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1,1-bis(diphenylphosphino)methane
1,1-Bis(diphenylphosphino)methane (dppm), is an organophosphorus compound with the formula CH2(PPh2)2. Dppm, a white, crystalline powder, is used in inorganic and organometallic chemistry as a ligand. It is more specifically a chelating ligand because it is a ligand that can bond to metals with two phosphorus donor atoms. The natural bite angle is 73°. Synthesis and reactivity 1,1-Bis(diphenylphosphino)methane was first prepared by the reaction of sodium diphenylphosphide (Ph2PNa) with dichloromethane: :Ph3P + 2 Na → Ph2PNa + NaPh :2NaPPh2 + CH2Cl2 → Ph2PCH2PPh2 + 2 NaCl The methylene group (CH2) in dppm (and especially its complexes) is mildly acidic. The ligand can be oxidized to give the corresponding oxides and sulfides CH2 (E)Ph2sub>2 (E = O, S). The methylene group is even more acidic in these derivatives. Coordination chemistry As a chelating ligand, 1,1-bis(diphenylphosphino)methane forms a four-membered ring with the constituents MP2C. The ligand promotes the format ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diphenyl-2-pyridylphosphine
Diphenyl-2-pyridylphosphine is an organophosphorus compound with the formula P(C6H5)2(2-C5H4N). It is the most widely used mono-pyridylphosphine ligand. Other mono-pyridylphosphines ligands (3-, 4-) are not common in chemical literature; however, tris-pyridylphosphines have been thoroughly investigated as ligands in transition metal complexes used for catalysis. Pyridylphosphines, including diphenyl-2-pyridylphosphine, may bind transition metals as monodentate or bidentate ligands4. Diphenyl-2-pyridylphosphine behaves as a P-bound monodentate ligand, or a P,N-bound bidentate ligand. Diphenyl-2-pyridylphosphine is a sought after ligand for its ability to relay protons to transition metals such as palladium(II) in homogeneous catalysis. Synthesis Diphenyl-2-pyridylphosphine is prepared from 2-lithiopyridine with chlorodiphenylphosphine Chlorodiphenylphosphine is an organophosphorus compound with the formula (C6H5)2PCl, abbreviated Ph2PCl. It is a colourless oily liquid with a pung ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sulfur Monoxide
Sulfur monoxide is an inorganic compound with formula . It is only found as a dilute gas phase. When concentrated or condensed, it converts to S2O2 (disulfur dioxide). It has been detected in space but is rarely encountered intact otherwise. Structure and bonding The SO molecule has a triplet ground state similar to O2 and S2, that is, each molecule has two unpaired electrons. The S−O bond length of 148.1 pm is similar to that found in lower sulfur oxides (e.g. S8O, S−O = 148 pm) but is longer than the S−O bond in gaseous S2O (146 pm), SO2 (143.1 pm) and SO3 (142 pm). The molecule is excited with near infrared radiation to the singlet state (with no unpaired electrons). The singlet state is believed to be more reactive than the ground triplet state, in the same way that singlet oxygen is more reactive than triplet oxygen. Production and reactions Production of SO as a reagent in organic syntheses has centred on using compounds that "extrude" S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metal Nitric Oxide Complex
Sodium nitroprusside, a medicinally significant metal nitrosyl-pentacyanoferrate (Fe-III) compound, used to treat hypertension. Metal nitrosyl complexes are complex (chemistry), complexes that contain nitric oxide, NO, bonded to a transition metal. Many kinds of nitrosyl complexes are known, which vary both in structure and coligand. Bonding and structure Most complexes containing the NO ligand can be viewed as derivatives of the nitrosyl cation, NO+. The nitrosyl cation is isoelectronic with carbon monoxide, thus the bonding between a nitrosyl ligand and a metal follows the same principles as the bonding in carbonyl complexes. The nitrosyl cation serves as a two-electron donor to the metal and accepts electrons from the metal via back-bonding. The compounds Co(NO)(CO)3 and Ni(CO)4 illustrate the analogy between NO+ and CO. In an electron-counting sense, two linear NO ligands are equivalent to three CO groups. This trend is illustrated by the isoelectronic pair Fe(CO)2(NO)2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydride
In chemistry, a hydride is formally the anion of hydrogen( H−). The term is applied loosely. At one extreme, all compounds containing covalently bound H atoms are called hydrides: water (H2O) is a hydride of oxygen, ammonia is a hydride of nitrogen, etc. For inorganic chemists, hydrides refer to compounds and ions in which hydrogen is covalently attached to a less electronegative element. In such cases, the H centre has nucleophilic character, which contrasts with the protic character of acids. The hydride anion is very rarely observed. Almost all of the elements form binary compounds with hydrogen, the exceptions being He, Ne, Ar, Kr, Pm, Os, Ir, Rn, Fr, and Ra. Exotic molecules such as positronium hydride have also been made. Bonds Bonds between hydrogen and the other elements range from highly to somewhat covalent. Some hydrides, e.g. boron hydrides, do not conform to classical electron-counting rules and the bonding is described in terms of multi-centered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pd2Cl2(CO)(dppm)2
PD, P.D., or Pd may refer to: Arts and media * ''People's Democracy'' (newspaper), weekly organ of the Communist Party of India (Marxist) * ''The Plain Dealer'', a Cleveland, Ohio, US newspaper * Post Diaspora, a time frame in the ''Honorverse'' series of science fiction novels * ''Principia Discordia'', a 1965 holy text in Discordianism * Production designer, a profession in film or television * Production diary, a promotional video podcast * Public domain, a copyright status Economics and business * Personnel department, of an organization * Price discrimination, a microeconomic pricing strategy * Probability of default, used in finance (Basel II) * Professional degree, or first professional degree * Professional development, learning to earn or maintain professional credentials * Program director, in service industries * Public Debt, of a government Organizations Companies * Phelps Dodge, a former American mining company, now part of Freeport-McMoRan * Polyphony Digital, d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sawhorse
In woodworking, a saw-horse or sawhorse (saw-buck, trestle, buck) is a trestle structure used to support a board or plank for sawing. A pair of sawhorses can support a plank, forming a scaffold. In certain circles, it is also known as a ''mule'' and a short sawhorse is known as a pony. The names come from the shape of the frame, which resembles a horse. A sawhorse may also be a rack for supporting logs for sawing, known in the US as a sawbuck. The sawhorse may be designed to fold for storage. A sawhorse with a wide top is particularly useful to support a board for sawing or as a field workbench, and is more useful as a single, but also more difficult to store. A sawhorse can also be used as the base for a portable work table by placing a sheet of plywood or even a door across two sawhorses. If the sawhorses are strong enough, the portable table can be used as a platform for tools like a table saw, although with caution if the top is not secured to the sawhorses. In boatma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxidative Addition
Oxidative addition and reductive elimination are two important and related classes of reactions in organometallic chemistry. Oxidative addition is a process that increases both the oxidation state and coordination number of a metal centre. Oxidative addition is often a step in catalytic cycles, in conjunction with its reverse reaction, reductive elimination. Role in transition metal chemistry For transition metals, oxidative reaction results in the decrease in the d''n'' to a configuration with fewer electrons, often 2e fewer. Oxidative addition is favored for metals that are (i) basic and/or (ii) easily oxidized. Metals with a relatively low oxidation state often satisfy one of these requirements, but even high oxidation state metals undergo oxidative addition, as illustrated by the oxidation of Pt(II) with chlorine: : tCl4sup>2− + Cl2 → tCl6sup>2− In classical organometallic chemistry, the formal oxidation state of the metal and the electron count of the complex both in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
(dppm)2.png)


4-3D-balls.png)
2-from-xtal-3D-ball-stick-hybrid.png)




