|
883 Deaths
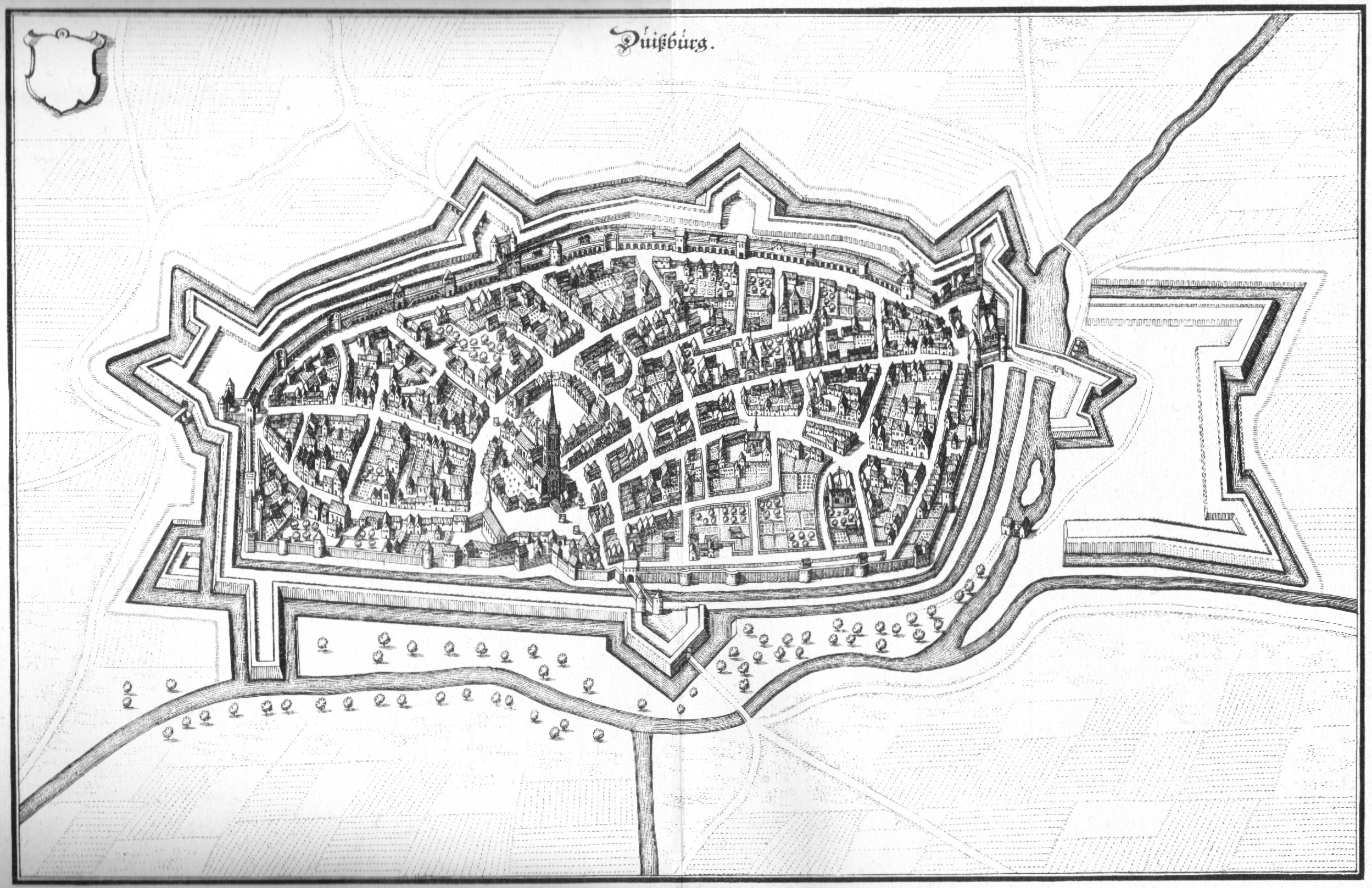
__NOTOC__ Year 883 ( DCCCLXXXIII) was a common year starting on Tuesday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. Events By place Europe * Spring – Viking raiders ravage Flanders, and sack the abbey at Saint-Quentin. King Carloman II blocks their passage at Laviers, which had been on the banks of the Somme. Meanwhile, Vikings enter the Rhine, but are turned back by Henry of Franconia (possibly a margrave of Saxony). They over-winter at Duisburg. * King Charles the Fat travels to Nonantola (Northern Italy), where he meets Pope Marinus I. He receives complaints of Guy II of Spoleto, who is the official "protector" of Rome, and invades the Papal States. King Charles orders Guy to appear before a tribunal. * Guy II of Spoleto begins a revolt, and assembles an army supported with Arab auxiliaries. King Charles the Fat sends Berengar of Friuli with an expeditionary force to deprive him of Spoleto. An epidemic ravages Berengar's army, and forc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marinus I
Pope Marinus I (; died 15 May 884) was the bishop of Rome and ruler of the Papal States from 882 until his death. Controversially at the time, he was already a bishop when he became pope, and had served as papal legate to Constantinople. He was also erroneously called Martin II (Martinus II) leading to the second pope named Martin to take the name Martin IV. Ecclesiastical career Born at Gallese, Marinus was the son of a priest. He was ordained as a deacon by Pope Nicholas I. He first served as bishop of Caere. On three separate occasions, he had been employed by the three popes who preceded him as legate to Constantinople, his mission in each case having reference to the controversy started by Patriarch Photios I of Constantinople. In 882, he was sent on behalf of Pope John VIII to Duke Athanasius of Naples to warn him not to trade with the Muslims of southern Italy. Marinus I was elected to succeed John VIII as bishop of Rome from around the end of December 882. This pap ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and Slovenia to the southwest, and Austria to the west. Hungary has a population of nearly 9 million, mostly ethnic Hungarians and a significant Romani minority. Hungarian, the official language, is the world's most widely spoken Uralic language and among the few non- Indo-European languages widely spoken in Europe. Budapest is the country's capital and largest city; other major urban areas include Debrecen, Szeged, Miskolc, Pécs, and Győr. The territory of present-day Hungary has for centuries been a crossroads for various peoples, including Celts, Romans, Germanic tribes, Huns, West Slavs and the Avars. The foundation of the Hungarian state was established in the late 9th century AD with the conquest of the Carpat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pannonian Slavs
Early Slavs settled in the eastern and southern parts of the former Roman province of Pannonia. The term ''Lower Pannonia'' ( la, Pannonia inferior, hu, Alsó-pannoniai grófság, sh-Latn-Cyrl, Donja Panonija, Доња Панонија, sl, Spodnja Panonija) was used to designate those areas of the Pannonian plain that lie to the east and south of the river Rába, with the division into ''Upper'' and ''Lower'' inherited from the Roman terminology. From the middle of the 6th to the end of the 8th century, the region was under the domination of the Avars, while the Slavic inhabitants lived under Avar rule. By the beginning of the 9th century, that state was destroyed and replaced by the supreme rule of the Frankish Empire, which lasted until the Magyar conquest (c. 900). During the Frankish period, the region of Lower Pannonia was governed by local Slavic rulers, who were under the suzerainty of Frankish kings. Within the Frankish administrative system, the March of Pannoni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Moravia
Great Moravia ( la, Regnum Marahensium; el, Μεγάλη Μοραβία, ''Meghálī Moravía''; cz, Velká Morava ; sk, Veľká Morava ; pl, Wielkie Morawy), or simply Moravia, was the first major state that was predominantly West Slavs, West Slavic to emerge in the area of Central Europe, possibly including territories which are today part of the Czech Republic, Slovakia, Hungary, Austria, Germany, Poland, Romania, Croatia, Serbia and Ukraine. The only formation preceding it in these territories was Samo's Empire, Samo's tribal union known from between 631 and 658 AD. Its core territory is the region now called Moravia in the eastern part of the Czech Republic alongside the Morava (river), Morava River, which gave its name to the kingdom. The kingdom saw the rise of the first ever Slavic literary culture in the Old Church Slavonic language as well as the expansion of Christianity, first via missionaries from East Francia, and later after the arrival of Saints Cyril and Metho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knyaz
, or (Old Church Slavonic: Кнѧзь) is a historical Slavic title, used both as a royal and noble title in different times of history and different ancient Slavic lands. It is usually translated into English as prince or duke, depending on specific historical context and the potentially known Latin equivalents of the title for each bearer of the name. In Latin sources the title is usually translated as , but the word was originally derived from the common Germanic (king). The female form transliterated from Bulgarian and Russian is (), in Slovene and Serbo-Croatian (Serbian Cyrillic: ), ''kniahinia'' (княгіня) in Belarusian and ''kniazioŭna'' (князёўна) is the daughter of the prince, (княгиня) in Ukrainian. In Russian, the daughter of a knyaz is (). In Russian, the son of a knyaz is ( in its old form). The title is pronounced and written similarly in different European languages. In Serbo-Croatian and some West Slavic languages, the w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Svatopluk I Of Moravia
Svatopluk I or Svätopluk I, also known as Svatopluk the Great ( Latin: ''Zuentepulc'', ''Zuentibald'', ''Sventopulch'', ''Zvataplug''; Old Church Slavic: Свѧтопълкъ and transliterated ''Svętopъłkъ''; Polish: ''Świętopełk''; Greek: Σφενδοπλόκος, ''Sphendoplókos''), was a ruler of Great Moravia, which attained its maximum territorial expansion during his reign (870–871, 871–894). Svatopluk's career started in the 860s, when he governed a principality within Moravia, the location of which is still a matter of debate among historians, under the suzerainty of his uncle, Rastislav. In 870 Svatopluk dethroned Rastislav, who was a vassal of Louis the German, and betrayed him to the Franks. Within a year, however, the Franks also imprisoned Svatopluk. After the Moravians rebelled against the Franks, Svatopluk was released and led the rebels to victory over the invaders. Although he was obliged to pay tribute to East Francia under the peace ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epidemic
An epidemic (from Greek ἐπί ''epi'' "upon or above" and δῆμος ''demos'' "people") is the rapid spread of disease to a large number of patients among a given population within an area in a short period of time. Epidemics of infectious diseases are generally caused by several factors including a significant change in the ecology of the areal population (e.g., increased stress maybe additional reason or increase in the density of a vector species), the introduction of an emerging pathogen to an areal population (by movement of pathogen or host) or an unexpected genetic change that is in the pathogen reservoir. Generally, epidemics concerns with the patterns of infectious disease spread. An epidemic may occur when host immunity to either an established pathogen or newly emerging novel pathogen is suddenly reduced below that found in the endemic equilibrium and the transmission threshold is exceeded. For example, in meningococcal infections, an attack rate in excess of 15 c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Spoleto
The Duchy of Spoleto (, ) was a Lombard territory founded about 570 in central Italy by the Lombard '' dux'' Faroald. Its capital was the city of Spoleto. Lombards The Lombards had invaded Italy in 568 AD and conquered much of it, establishing the Kingdom of the Lombards, which was divided among several dukes dependent on the King. The King himself had established his seat in Pavia in 572. In the following years they also conquered much of southern and central Italy, conquering the important hub of Spoleto, in what is now Umbria, in 570. A decade of interregnum after the death of Alboin's successor (574), however, left the Lombard dukes (especially the southern ones) well settled in their new territories and quite independent of the Lombard kings at Pavia. By 575 or 576 Faroald had seized Nursia and Spoleto, establishing his duchy and sponsoring an Arian bishop. Within Spoleto, the Roman '' capitolium'' dedicated to Jupiter, Juno and Minerva had already been occup ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berengar I Of Italy
Berengar I ( la, Berengarius, Perngarius; it, Berengario; – 7 April 924) was the king of Italy from 887. He was Holy Roman Emperor between 915 and his death in 924. He is usually known as Berengar of Friuli, since he ruled the March of Friuli from 874 until at least 890, but he had lost control of the region by 896. Berengar rose to become one of the most influential laymen in the empire of Charles the Fat, and he was elected to replace Charles in Italy after the latter's deposition in November 887. His long reign of 36 years saw him opposed by no less than seven other claimants to the Italian throne. His reign is usually characterised as ''troubled'' because of the many competitors for the crown and because of the arrival of Magyar raiders in Western Europe. His death was followed by an imperial interregnum that lasted 38 years until Otto I was crowned emperor in 962. Margrave of Friuli, 874–887 His family was called the Unruochings after his grandfather, Unruoch II. B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Auxiliaries
Auxiliaries are support personnel that assist the military or police but are organised differently from regular forces. Auxiliary may be military volunteers undertaking support functions or performing certain duties such as garrison troops, usually on a part-time basis. Unlike a military reserve force, an auxiliary force does not necessarily have the same degree of training or ranking structure as regular soldiers, and it may or may not be integrated into a fighting force. Some auxiliaries, however, are militias composed of former active duty military personnel and actually have better training and combat experience than their regular counterparts. Historically, the designation ''auxiliary'' has also been given to foreign or allied troops in the service of a nation at war, most famously the eponymous '' Auxilia'' serving the Roman Empire. In the context of colonial troops, locally-recruited irregulars were often described as auxiliaries. Historical usage Roman auxilia ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribunal
A tribunal, generally, is any person or institution with authority to judge, adjudicate on, or determine claims or disputes—whether or not it is called a tribunal in its title. For example, an advocate who appears before a court with a single judge could describe that judge as "their tribunal." Many governmental bodies that are titled as "tribunals" are described so in order to emphasize that they are not courts of normal jurisdiction. For example, the International Criminal Tribunal for Rwanda was a body specially constituted under international law; in Great Britain, employment tribunals are bodies set up to hear specific employment disputes. In many (but not all) cases, the word ''tribunal'' implies a judicial (or quasi-judicial) body with a lesser degree of formality than a court, in which the normal rules of evidence and procedure may not apply, and whose presiding officers are frequently neither judges, nor magistrates. Private judicial bodies are also often style ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |