|
72 Names Of God
''Shem HaMephorash'' ( he, שֵׁם הַמְּפֹרָשׁ ''Šēm hamMəfōrāš'', also ''Shem ha-Mephorash''), meaning "the explicit name," is originally a Tannaitic term describing the Tetragrammaton. In Kabbalah, it may refer to a name of God composed of either 4, 12, 22, 42, or 72 letters (or triads of letters), the latter version being the most common. 12-, 22-, and 42-letter names Early sources, from the Mishnah to Maimonides, only use "Shem ha-Mephorash" to refer to the four letter Tetragrammaton. b. Qiddushin 72a describes a 12-letter name (apparently a mundane euphemism, YHWH-EHYH-ADNY or YHWH-YHWH-YHWH) and a 42-letter name (holy but unknown; Hayy Gaon says it is the acronym of the medieval piyyut Ana b'Koachתשובה אל יוסף בן ברכיה ותלמידי יעקב בן נסים בעניין שמות והשבעות, קונטרס "הדר עם הנכרי בחצר"). A 22-letter name appears in ''Sefer Raziel HaMalakh'', without interpretation, as ('). Its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tannaim
''Tannaim'' ( Amoraic Hebrew: תנאים , singular , ''Tanna'' "repeaters", "teachers") were the rabbinic sages whose views are recorded in the Mishnah, from approximately 10–220 CE. The period of the ''Tannaim'', also referred to as the Mishnaic period, lasted about 210 years. It came after the period of the ''Zugot'' ("pairs"), and was immediately followed by the period of the '' Amoraim'' ("interpreters"). The root ''tanna'' () is the Talmudic Aramaic equivalent for the Hebrew root ''shanah'' (), which also is the root-word of ''Mishnah''. The verb ''shanah'' () literally means "to repeat hat one was taught and is used to mean "to learn". The Mishnaic period is commonly divided up into five periods according to generations. There are approximately 120 known ''Tannaim''. The ''Tannaim'' lived in several areas of the Land of Israel. The spiritual center of Judaism at that time was Jerusalem, but after the destruction of the city and the Second Temple, Yohanan ben Zakkai an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solomon
Solomon (; , ),, ; ar, سُلَيْمَان, ', , ; el, Σολομών, ; la, Salomon also called Jedidiah (Hebrew language, Hebrew: , Modern Hebrew, Modern: , Tiberian Hebrew, Tiberian: ''Yăḏīḏăyāh'', "beloved of Yahweh, Yah"), was a monarch of ancient Israel and the son and successor of David, according to the Hebrew Bible and the Old Testament. He is described as having been the penultimate ruler of an amalgamated Kingdom of Israel (united monarchy), Israel and Judah. The hypothesized dates of Solomon's reign are 970–931 BCE. After his death, his son and successor Rehoboam would adopt harsh policy towards the northern tribes, eventually leading to the splitting of the Israelites between the Kingdom of Israel (Samaria), Kingdom of Israel in the north and the Kingdom of Judah in the south. Following the split, his Patrilineality#In the Bible, patrilineal descendants ruled over Judah alone. The Bible says Solomon built the Solomon's Temple, First Temple in Jerus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
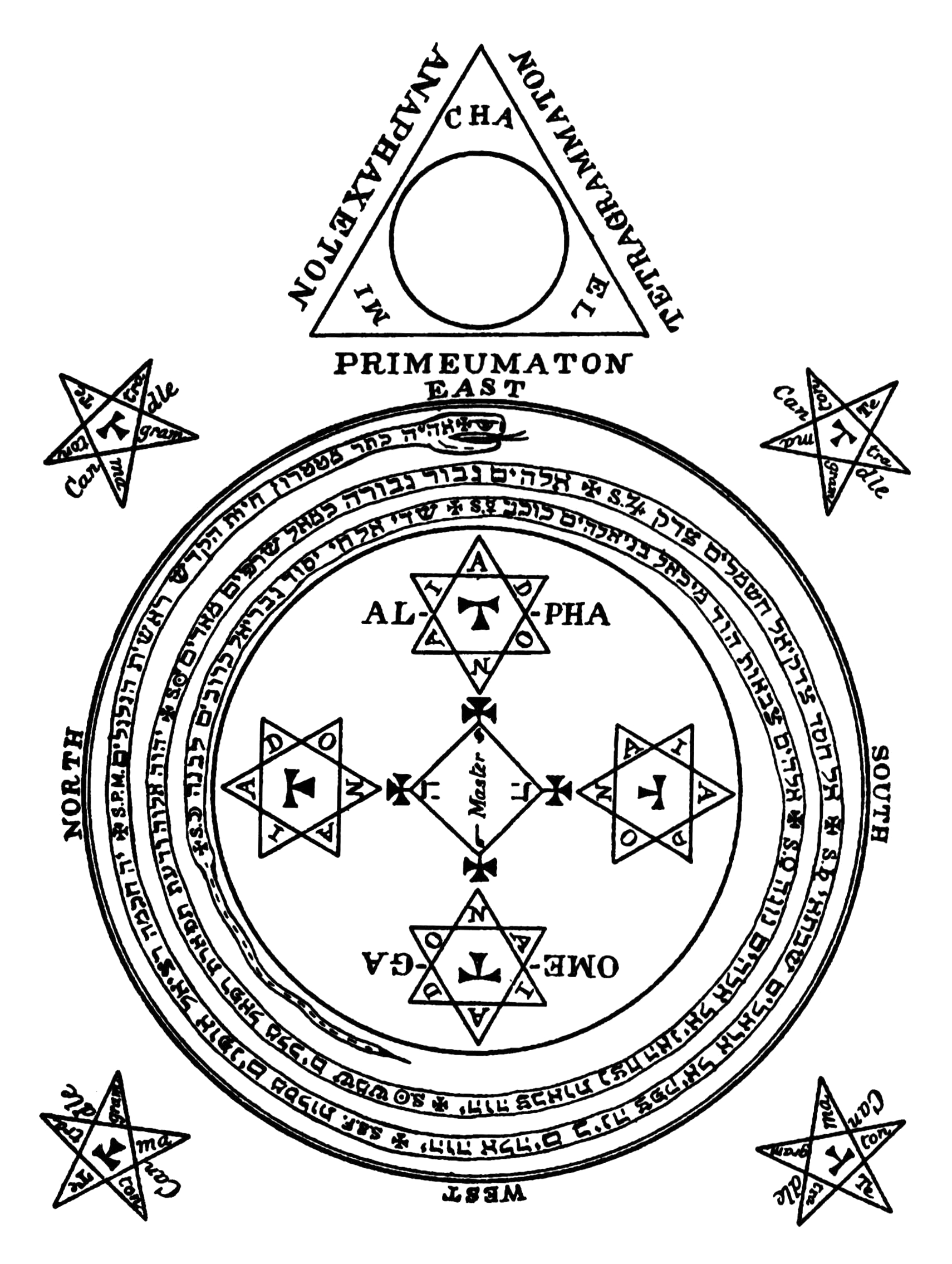
Lesser Key Of Solomon
''The Lesser Key of Solomon'', also known as ''Lemegeton Clavicula Salomonis'' or simply ''Lemegeton'', is an anonymous grimoire on demonology. It was compiled in the mid-17th century, mostly from materials a couple of centuries older.''Lemegeton Clavicula Salomonis: The Lesser Key of Solomon, Detailing the Ceremonial Art of Commanding Spirits Both Good and Evil''; ed. Joseph H. Peterson; Weiser Books Maine; 2001. pp. xi–xvii.''The Goetia of Dr Rudd''; Thomas Rudd, Eds. Stephen Skinner & David Rankine; 2007, Golden Hoard Press. p. 399. It is divided into five books—the ''Ars Goetia'', ''Ars Theurgia-Goetia'', ''Ars Paulina'', ''Ars Almadel'', and ''Ars Notoria''. ''Ars Goetia'' Etymology The text is more properly called "Lemegeton Clavicula Salomonis, or, The little Key of Solomon". The title most commonly used, "The Lesser Key of Solomon," does not in fact occur in the manuscripts. A.E. Waite, in his 1898 ''Book of Black Magic and of Pacts'' does use the ter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Rudd
Thomas Rudd (1583?–1656) was an English military engineer and mathematician. Life The eldest son of Thomas Rudd of Higham Ferrers, Northamptonshire, he was born in 1583 or 1584. He served during his earlier years as a military engineer in the Low Countries. On 10 July 1627, King Charles I appointed him ‘chief engineer of all castles, forts, and fortifications within Wales,’ at a salary of £240 per annum. Subsequently, he was appointed the King's principal engineer for fortifications, and in 1635 he visited Portsmouth in this capacity to settle a question between the governor and the admiralty as to the removal of some naval buildings which interfered with proposed fortifications. In 1638, he visited Guernsey and Jersey at the request of the governors, Charles Danvers, Earl of Danby and Sir Thomas Jermyn, to survey the castles on those islands and report upon them to the board of ordnance. In February of the following year, Rudd petitioned the board of ordnance for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blaise De Vigenère
Blaise de Vigenère (5 April 1523 – 19 February 1596) () was a French diplomat, cryptographer, translator and alchemist. Biography Vigenère was born into a respectable family in the village of Saint-Pourçain. His mother, Jean, arranged for him to have a classical education in France. He studied Greek, Hebrew and Italian under Adrianus Turnebus and Jean Dorat. At age 26 he entered the diplomatic service and remained there for 30 years, retiring in 1570. Five years into his career he accompanied the French envoy Louis Adhémar de Grignan to the Diet of Worms as a junior secretary. At age 24, he entered the service of the Duke of Nevers as his secretary, a position he held until the deaths of the Duke and his son in 1562. He also served as a secretary to Henry III. In 1549 he visited Rome on a two-year diplomatic mission, and again in 1566. On both trips, he read books about cryptography and came in contact with cryptologists. When Vigenère retired aged 47, he donat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Three Books Of Occult Philosophy
''Three Books of Occult Philosophy'' (''De Occulta Philosophia libri III'') is Heinrich Cornelius Agrippa's study of occult philosophy, acknowledged as a significant contribution to the Renaissance philosophical discussion concerning the powers of magic, and its relationship with religion. The first book was printed in 1531 in Paris, Cologne, and Antwerp, while the full three volumes first appeared in Cologne in 1533. The three books deal with elemental, celestial and intellectual magic. The books outline the four elements, astrology, Kabbalah, numerology, angels, names of God, the virtues and relationships with each other as well as methods of utilizing these relationships and laws in medicine, scrying, alchemy, ceremonial magic, origins of what are from the Hebrew, Greek and Chaldean context. These arguments were common amongst other hermetic philosophers at the time and before. In fact, Agrippa's interpretation of magic is similar to the authors Marsilio Ficino, Pico della ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
In Judaic Kabbalah
IN, In or in may refer to: Places * India (country code IN) * Indiana, United States (postal code IN) * Ingolstadt, Germany (license plate code IN) * In, Russia, a town in the Jewish Autonomous Oblast Businesses and organizations * Independent Network, a UK-based political association * Indiana Northeastern Railroad (Association of American Railroads reporting mark) * Indian Navy, a part of the India military * Infantry, the branch of a military force that fights on foot * IN Groupe , the producer of French official documents * MAT Macedonian Airlines (IATA designator IN) * Nam Air (IATA designator IN) Science and technology * .in, the internet top-level domain of India * Inch (in), a unit of length * Indium, symbol In, a chemical element * Intelligent Network, a telecommunication network standard * Intra-nasal (insufflation), a method of administrating some medications and vaccines * Integrase, a retroviral enzyme Other uses * ''In'' (album), by the Outsiders, 1967 * In ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athanasius Kircher
Athanasius Kircher (2 May 1602 – 27 November 1680) was a German Jesuit scholar and polymath A polymath ( el, πολυμαθής, , "having learned much"; la, homo universalis, "universal human") is an individual whose knowledge spans a substantial number of subjects, known to draw on complex bodies of knowledge to solve specific pro ... who published around 40 major works, most notably in the fields of comparative religion, geology, and medicine. Kircher has been compared to fellow Jesuit Roger Joseph Boscovich and to Leonardo da Vinci for his enormous range of interests, and has been honoured with the title "Master of a Hundred Arts".Woods, p. 108. He taught for more than 40 years at the Roman College, where he set up a wunderkammer. A resurgence of interest in Kircher has occurred within the scholarly community in recent decades. Kircher claimed to have deciphered the Egyptian hieroglyphs, hieroglyphic writing of the ancient Egyptian language, but most of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heinrich Cornelius Agrippa
Heinrich Cornelius Agrippa von Nettesheim (; ; 14 September 1486 – 18 February 1535) was a German polymath, physician, legal scholar, soldier, theologian, and occult writer. Agrippa's ''Three Books of Occult Philosophy'' published in 1533 drew heavily upon Kabbalah, Hermeticism, and neo-Platonism. His book was widely influential among occultists of the early modern period, and was condemned as heretical by the inquisitor of Cologne. Life Agrippa was born in Nettersheim, near Cologne on 14 September 1486 to a family of middle nobility.Valente, Michaela "Agrippa, Heinrich Cornelius". In: ''Dictionary of Gnosis and Western Esotericism'' (Wouter J. Hanegraaff, ed.), pp. 4–8. Brill, 2006. . Many members of his family had been in the service of the House of Habsburg. Agrippa studied at the University of Cologne from 1499 to 1502, (age 13–16) when he received the degree of ''magister artium''. The University of Cologne was one of the centers of Thomism, and the faculty of art ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Arte Cabbalistica
''De Arte Cabbalistica'' (Latin for ''On the Art of Kabbalah'') is a 1517 text by the German Renaissance humanist scholar Johann Reuchlin, which deals with his thoughts on Kabbalah. In it, he puts forward the view that the theosophic philosophy of Kabbalah could be of great use in the defence of Christianity and the reconciliation of science with the mysteries of faith. It builds on his earlier work ''De Verbo Mirifico''. See also * Humanist Latin * Scholasticism Scholasticism was a medieval school of philosophy that employed a critical organic method of philosophical analysis predicated upon the Aristotelian 10 Categories. Christian scholasticism emerged within the monastic schools that translate ... References Christian Kabbalah Christian apologetic works Kabbalah texts Renaissance literature Renaissance humanism 1517 books 16th-century Latin books {{Kabbalah-book-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Angels Of The Shem Hamephorash
In various theistic religious traditions an angel is a supernatural spiritual being who serves God. Abrahamic religions often depict angels as benevolent celestial intermediaries between God (or Heaven) and humanity. Other roles include protectors and guides for humans, and servants of God. Abrahamic religions describe angelic hierarchies, which vary by religion and sect. Some angels have specific names (such as Gabriel or Michael) or titles (such as seraph or archangel). Those expelled from Heaven are called fallen angels, distinct from the heavenly host. Angels in art are usually shaped like humans of extraordinary beauty. They are often identified in Christian artwork with bird wings, halos, and divine light. Etymology The word ''angel'' arrives in modern English from Old English ''engel'' (with a hard ''g'') and the Old French ''angele''. Both of these derive from Late Latin ''angelus'', which in turn was borrowed from Late Greek ''angelos'' (literally "messenge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |