|
738th Expeditionary Airlift Squadron
The 738th Expeditionary Airlift Squadron is a provisional United States Air Force unit. It is assigned to Air Combat Command (ACC) to activate or inactivate as needed. It operates Lockheed C-130 Hercules aircraft in theater airlift missions as part of the Global War on Terrorism. Its current status and duty location is undetermined. The squadron was first activated as the 738th Bombardment Squadron in June 1943. After training in the United States with the Consolidated B-24 Liberator, the squadron deployed to the Mediterranean Theater of Operations, participating in the strategic bombing campaign against Germany. It earned two Distinguished Unit Citations for its combat operations. Following V-E Day, the squadron returned to the United States for conversion as a very heavy bomber unit, but was inactivated instead. The squadron was activated in the reserves in 1947, but does not appear to have been fully staffed or equipped before inactivating in 1949. It was redes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ACC Shield
ACC most often refers to: *Atlantic Coast Conference, an NCAA Division I collegiate athletic conference located in the US *American College of Cardiology, A US-based nonprofit medical association that bestows credentials upon cardiovascular specialists *Air Combat Command, a major command of the US Air Force headquartered at Langley Air Force Base *Association of Corporate Counsel, a global organization serving attorneys who practice in corporate law departments *American Chemistry Council, an industry trade association for American chemical companies ACC may also refer to: Business * ACC Limited, an Indian cement manufacturer * ACCBank, an Irish commercial bank * American Campus Communities, a private student housing provider * American Chemistry Council, an industry trade association for American chemical companies * American Credit Corporation, renamed Barclays American * Asia Cement Corporation, a cement company in Taiwan * Associated Co-operative Creameries, or one of its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mediterranean Theater Of Operations
The Mediterranean Theater of Operations, United States Army (MTOUSA), originally called the North African Theater of Operations, United States Army (NATOUSA), was a military formation of the United States Army that supervised all U.S. Army forces which fought in North Africa and Italy during World War II. United States Army operations in the theater began with Operation Torch, when Allied forces landed on the beaches of northwest Africa on 8 November 1942, and concluded in the Italian Alps some 31 months later, with the German surrender in Italy on 2 May 1945. For administrative purposes, U.S. components were responsible to Headquarters North African Theater of Operations, United States Army (NATOUSA), which was created 14 February 1943. NATOUSA was redesignated Mediterranean Theater of Operations, United States Army (MTOUSA), on 26 October 1944. Origins Allied Force Headquarters (AFHQ) was created on 12 September 1942 to launch Operation Torch, the Allied invasion of Fre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Support
In military tactics, close air support (CAS) is defined as air action such as air strikes by fixed or rotary-winged aircraft against hostile targets near friendly forces and require detailed integration of each air mission with fire and movement of these forces and attacks with aerial bombs, glide bombs, missiles, rockets, autocannons, machine guns, and even directed-energy weapons such as lasers.''Close Air Support''. United States Department of Defense, 2014. The requirement for detailed integration because of proximity, fires or movement is the determining factor. CAS may need to be conducted during shaping operations with Special Operations Forces (SOF) if the mission requires detailed integration with the fire and movement of those forces. A closely related subset of air interdiction (AI), battlefield air interdiction, denotes interdiction against units with near-term effects on friendly units, but which does not require integration with friendly troop movements. The term "b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
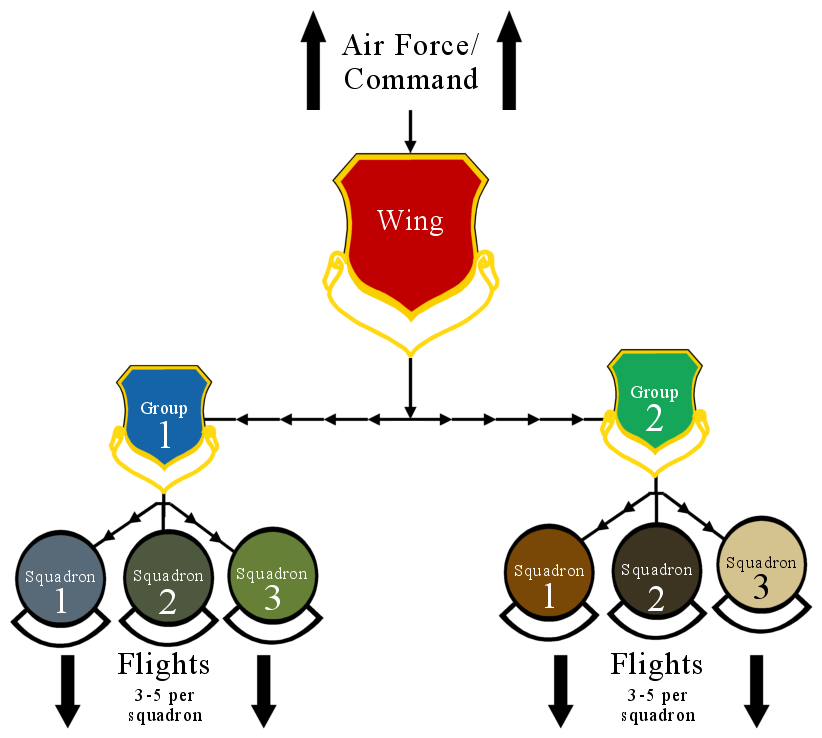
Wing (military Aviation Unit)
In military aviation, a wing is a unit of command. In most military aviation services, a wing is a relatively large formation of planes. In Commonwealth countries a wing usually comprises three squadrons, with several wings forming a group (around 10 squadrons). Each squadron will contain around 20 planes. Commonwealth usage Origins On its establishment in 1912, the British Royal Flying Corps (RFC) was intended to be an inter-service, combined force of the British Army and Royal Navy. Given the rivalry that existed between the army and navy, new terminology was used, in order to avoid marking the corps out as having an army or navy ethos. While the term "wing" had been used in the cavalry, its more general use predominated. Accordingly, the word "wing", with its allusion of flight, was chosen as the term of subdivision and the corps was split into a "Military Wing" (i.e. an army wing) and a "Naval Wing". Each wing consisted of a number of squadrons (the term "squadro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linz
Linz ( , ; cs, Linec) is the capital of Upper Austria and third-largest city in Austria. In the north of the country, it is on the Danube south of the Czech border. In 2018, the population was 204,846. In 2009, it was a European Capital of Culture. Geography Linz is in the centre of Europe, lying on the Paris–Budapest west–east axis and the Malmö–Trieste north–south axis. The Danube is the main tourism and transport connection that runs through the city. Approximately 29.27% of the city's wide area is grassland. A further 17.95% are covered with forest. All the rest areas fall on water (6.39%), traffic areas and land. Districts Since January 2014 the city has been divided into 16 statistical districts: Before 2014 Linz was divided into nine districts and 36 statistical quarters. They were: #Ebelsberg #Innenstadt: Altstadtviertel, Rathausviertel, Kaplanhofviertel, Neustadtviertel, Volksgartenviertel, Römerberg-Margarethen #Kleinmünchen: Kleinmünchen, Neue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bad Vöslau
Bad Vöslau (; Central Bavarian: ''Bod Vöslau'') is a spa town in the Lower Austria federal state of Austria. It is also known as the cradle of the Austrian red wine cultivation. Population (2008): 11,190. Geography Bad Vöslau is located 35 km south of Vienna. History In 1770s, Count Johann von Fries, whose vineyards were situated around Bad Vöslau, was the first from this region to grow red wine on a large scale. The red wine and the sparkling wine from Bad Vöslau were made famous worldwide by Robert Schlumberger. In 1954, Bad Vöslau became a city and the brand "Vöslauer Stadtsiegel" was born. On August 26, 1867, the Treaty of Vöslau was signed between the Kingdom of Greece and the Principality of Serbia. Populations Personalities * Ferdinand Piatnik (1819-1885), Austrian- Hungarian carpainter, manufacturer, philanthropist, founder of Piatnik & Söhne * Johann von Fries (1719-1785), the counts of Fries - with an interruption, from 1773 to 1902 owner o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Air Base
An air base (sometimes referred to as a military air base, military airfield, military airport, air station, naval air station, air force station, or air force base) is an aerodrome used as a military base by a military force for the operation of military aircraft. Air base facilities An air base typically has some facilities similar to a civilian airport—for example, air traffic control and firefighting. Some military aerodromes have passenger facilities; for example RAF Brize Norton in England has a terminal used by passengers for the Royal Air Force's flights. A number of military air bases also have a civil enclave for commercial passenger flights, e.g. Beijing Nanyuan Airport (China), Chandigarh Airport (India), Ibaraki Airport (Japan), Burlington International Airport (USA), Sheikh Ul-Alam International Airport Srinagar (India), Taipei Songshan Airport (Taiwan). Some air bases have revetments, hardened aircraft shelters, or even underground hangars, to protect aircraf ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San Giovanni Airfield
The Foggia Airfield Complex was a series of World War II military airfields located within a radius of Foggia, in the Province of Foggia, Italy. The airfields were used by the United States Army Air Force Fifteenth Air Force as part of the strategic bombardment campaign against Nazi Germany in 1944 and 1945, as well as the Twelfth Air Force, the Royal Air Force and the South African Air Force during the Italian Campaign (1943–1945). History Before World War II, the Italian Royal Air Force Regia Aeronautica constructed a series of airfields in the Foggia area. They consisted of hard-surfaced runways and taxiways, concrete parking areas and permanent buildings for the support units and barracks. After the Armistice between Italy and Allied armed forces in September, 1943 these airfields were seized by the German Luftwaffe. While under Axis control, the airfields were heavily bombed by the United States Army Air Force and Royal Air Force in 1943 before being seized by the Britis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
454th Bombardment Group
The 454th Bombardment Group is an inactive United States Air Force unit. It was last assigned to the 454th Troop Carrier Wing of Continental Air Command at Portland International Airport, Oregon. It was inactivated on 1 January 1953. The 454th Bombardment Group was activated in 1943 as a United States Army Air Forces combat military organization, unit. It served primarily in the Mediterranean Theater of Operations, Mediterranean Theater during World War II. While in combat the group earned two Distinguished Unit Citations. The group served as a bomber, bombardment and as a troop carrier unit in the reserves after World War II. In 1947 the group was activated as a reserve unit. It continued in this role until 1951 when it was called to active duty and its personnel used to fill out active duty organizations deploying to the Pacific. The group was reestablished later during the Korean War as the 454th Troop Carrier Group, a reserve organization at Portland International Airpor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alamogordo Army Air Field
Alamogordo () is the seat of Otero County, New Mexico, United States. A city in the Tularosa Basin of the Chihuahuan Desert, it is bordered on the east by the Sacramento Mountains and to the west by Holloman Air Force Base. The population was 31,358 as of the 2020 census. Alamogordo is known for its connection with the 1945 Trinity test, which was the first ever explosion of an atomic bomb. Humans have lived in the Alamogordo area for at least 11,000 years. The present settlement, established in 1898 to support the construction of the El Paso and Northeastern Railroad, is an early example of a planned community. The city was incorporated in 1912. Tourism became an important economic factor with the creation of White Sands National Monument in 1933, which is still one of the biggest attractions of the city today. During the 1950s–60s, Alamogordo was an unofficial center for research on pilot safety and the developing United States' space program. Alamogordo is a ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Air Mobility Command
Air Mobility Command (AMC) is a major command (MAJCOM) of the U.S. Air Force. It is headquartered at Scott Air Force Base, Illinois, east of St. Louis, Missouri. Air Mobility Command was established on 1 June 1992, and was formed from elements of the inactivated Military Airlift Command (MAC) and Strategic Air Command (SAC). AMC melded MAC's worldwide airlift system of primarily C-5 Galaxy, C-141 Starlifter (later replaced by C-17 Globemaster III beginning in 1995), and C-130 Hercules airlift aircraft with SAC's tanker force of KC-135 Stratotanker and KC-10 Extender aerial refueling aircraft, the latter air refueling aircraft having been freed from their strategic nuclear strike commitment to SAC's B-52 Stratofortress and B-1 Lancer bomber fleet by the end of the Cold War and the dissolution of the Soviet Union. Overview Air Mobility Command's mission is to provide global air mobility. The command also plays a crucial role in providing humanitarian support at home and arou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)

.jpg)
