|
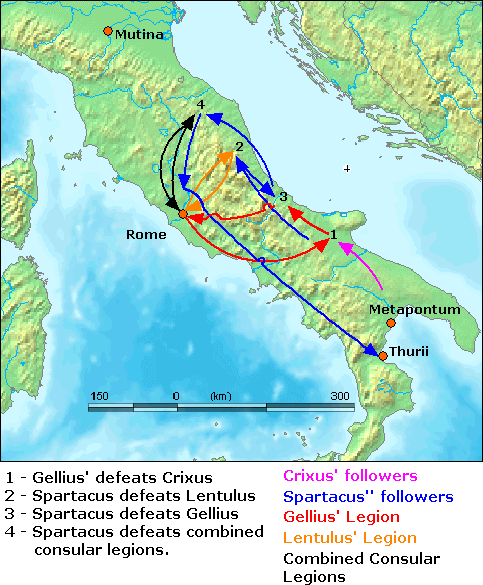
72 BC
__NOTOC__ Year 72 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Publicola and Lentulus (or, less frequently, year 682 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 72 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years Events By place Roman Republic * Third Servile War: Spartacus moves with his followers northward to the Po Valley. Roman forces under Lucius Gellius Publicola defeat a group of slaves (30,000 men) led by Crixus near Mount Gargano. He kills two-thirds of the rebels, including Crixus himself. * Summer – Spartacus and his followers defeat the Roman forces under Gnaeus Cornelius Lentulus Clodianus and Gellius, forcing the Roman legions to retreat in disarray. Both consuls are recalled to Rome in disgrace and relieved of their duties. * Spartacus moves north again, to cross the Alps into Gaul and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Po (river)
The Po ( , ; la, Padus or ; Ancient Ligurian: or ) is the longest river in Italy. It flows eastward across northern Italy starting from the Cottian Alps. The river's length is either or , if the Maira, a right bank tributary, is included. The headwaters of the Po are a spring seeping from a stony hillside at Pian del Re, a flat place at the head of the Val Po under the northwest face of Monviso. The Po then extends along the 45th parallel north before ending at a delta projecting into the Adriatic Sea near Venice. It is characterized by its large discharge (several rivers over 1,000 km have a discharge inferior or equal to the Po). It is, with the Rhône and Nile, one of the three Mediterranean rivers with the largest water discharge. As a result of its characteristics, the river is subject to heavy flooding. Consequently, over half its length is controlled with embankments. The river flows through many important Italian cities, including Turin, Piacenza, Cremona and Ferr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Pontus
Pontus ( grc-gre, Πόντος ) was a Hellenistic kingdom centered in the historical region of Pontus and ruled by the Mithridatic dynasty (of Persian origin), which possibly may have been directly related to Darius the Great of the Achaemenid dynasty. The kingdom was proclaimed by Mithridates I in 281BC and lasted until its conquest by the Roman Republic in 63BC. The Kingdom of Pontus reached its largest extent under Mithridates VI the Great, who conquered Colchis, Cappadocia, Bithynia, the Greek colonies of the Tauric Chersonesos, and for a brief time the Roman province of Asia. After a long struggle with Rome in the Mithridatic Wars, Pontus was defeated. The western part of it was incorporated into the Roman Republic as the province Bithynia et Pontus; the eastern half survived as a client kingdom until 62 AD. As the greater part of the kingdom lay within the region of Cappadocia, which in early ages extended from the borders of Cilicia to the Euxine (Black Sea), the king ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mithradates VI Eupator
Mithridates or Mithradates VI Eupator ( grc-gre, Μιθραδάτης; 135–63 BC) was ruler of the Kingdom of Pontus in northern Anatolia from 120 to 63 BC, and one of the Roman Republic's most formidable and determined opponents. He was an effective, ambitious and ruthless ruler who sought to dominate Asia Minor and the Black Sea region, waging several hard-fought but ultimately unsuccessful wars (the Mithridatic Wars) to break Roman dominion over Asia and the Hellenic world. He has been called the greatest ruler of the Kingdom of Pontus. He cultivated an immunity to poisons by regularly ingesting sub-lethal doses; this practice, now called mithridatism, is named after him. After his death he became known as Mithridates the Great. Etymology ''Mithridates'' is the Greek attestation of the Persian name ''Mihrdāt'', meaning "given by Mithra", the name of the ancient Iranian sun god. The name itself is derived from Old Iranian ''Miθra-dāta-''. Ancestry, family and early lif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucullus
Lucius Licinius Lucullus (; 118–57/56 BC) was a Roman general and statesman, closely connected with Lucius Cornelius Sulla. In culmination of over 20 years of almost continuous military and government service, he conquered the eastern kingdoms in the course of the Third Mithridatic War, exhibiting extraordinary generalship in diverse situations, most famously during the Siege of Cyzicus in 73–72 BC, and at the Battle of Tigranocerta in Armenian Arzanene in 69 BC. His command style received unusually favourable attention from ancient military experts, and his campaigns appear to have been studied as examples of skillful generalship. Lucullus returned to Rome from the east with so much captured booty that the vast sums of treasure, jewels, priceless works of art, and slaves could not be fully accounted for. On his return Lucullus poured enormous sums into private building projects, husbandry and even aquaculture projects, which shocked and amazed his contemporaries by their ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Cabira
The Battle of Cabira was fought in 72 or 71 BC between forces of the Roman Republic under proconsul Lucius Licinius Lucullus and those of the Kingdom of Pontus under Mithridates the Great. It was a decisive Roman victory. Background Rome had already fought two major conflicts with King Mithridates of Pontus; the so called First and Second Mithridatic Wars. During the first war, after taking the Roman province of Asia, Mithridates had slaughtered 80,000 Roman and other Italian civilians (the so called Asian Vespers). This was something Rome would never forgive him, therefore the stage was set for another conflict. When in 74 BC the Kingdom of Bithynia was bequeathed to the Roman Republic (on the death of King Nicomedes IV of Bithynia) things came ahead. Mithridates, who anticipated a war with Rome, invaded the country in 73 BC, he defeated the first Roman governor of Bithynia the proconsul Marcus Aurelius Cotta in battle and besieged him in the city of Chalcedon. Lucullus, Cotta ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palisade
A palisade, sometimes called a stakewall or a paling, is typically a fence or defensive wall made from iron or wooden stakes, or tree trunks, and used as a defensive structure or enclosure. Palisades can form a stockade. Etymology ''Palisade'' derives from ''pale'', from the Latin word ', meaning stake, specifically when used side by side to create a wood defensive wall. Typical construction Typical construction consisted of small or mid-sized tree trunks aligned vertically, with as little free space in between as possible. The trunks were sharpened or pointed at the top, and were driven into the ground and sometimes reinforced with additional construction. The height of a palisade ranged from around a metre to as high as 3–4 m. As a defensive structure, palisades were often used in conjunction with earthworks. Palisades were an excellent option for small forts or other hastily constructed fortifications. Since they were made of wood, they could often be quickly and easil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rampart (fortification)
In fortification architecture, a bank or rampart is a length of embankment or wall forming part of the defensive boundary of a castle, hillfort, settlement or other fortified site. It is usually broad-topped and made of excavated earth and/or masonry.Darvill, Timothy (2008). ''Oxford Concise Dictionary of Archaeology'', 2nd ed., Oxford University Press, Oxford and New York, p. 376. . Early fortifications Many types of early fortification, from prehistory through to the Early Middle Ages, employed earth ramparts usually in combination with external ditches to defend the outer perimeter of a fortified site or settlement. Hillforts, ringforts or "raths" and ringworks all made use of ditch and rampart defences, and they are the characteristic feature of circular ramparts. The ramparts could be reinforced and raised in height by the use of palisades. This type of arrangement was a feature of the motte and bailey castle of northern Europe in the early medieval period. Types of ram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical region. Italy is also considered part of Western Europe, and shares land borders with France, Switzerland, Austria, Slovenia and the enclaved microstates of Vatican City and San Marino. It has a territorial exclave in Switzerland, Campione. Italy covers an area of , with a population of over 60 million. It is the third-most populous member state of the European Union, the sixth-most populous country in Europe, and the tenth-largest country in the continent by land area. Italy's capital and largest city is Rome. Italy was the native place of many civilizations such as the Italic peoples and the Etruscans, while due to its central geographic location in Southern Europe and the Mediterranean, the country has also historically been home ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thurii
Thurii (; grc-gre, Θούριοι, Thoúrioi), called also by some Latin writers Thurium (compare grc-gre, Θούριον in Ptolemy), for a time also Copia and Copiae, was a city of Magna Graecia, situated on the Gulf of Taranto, Tarentine gulf, within a short distance of the site of Sybaris, whose place it may be considered as having taken. The ruins of the city can be found in the Sybaris archaeological park near Sibari in the Province of Cosenza, Calabria, Italy. History Foundation Thurii was an ancient Greek colony founded by people from Athens and Sybaris in 443 B.C. Justin (historian), Justin writes that people say that the city of Thurii was built by Philoctetes and his monument is seen there even to his days, as well as the arrows of Hercules which laid up in the temple of Apollo. The site of that city had remained desolate for a period of 58 years after its destruction by the Crotona, Crotoniats; when at length, in 452 BC, a number of the Sybarite exiles and their ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcus Licinius Crassus
Marcus Licinius Crassus (; 115 – 53 BC) was a Roman general and statesman who played a key role in the transformation of the Roman Republic into the Roman Empire. He is often called "the richest man in Rome." Wallechinsky, David & Wallace, Irving.Richest People in History Ancient Roman Crassus. Trivia-Library. ''The People's Almanac''. 1975–1981. Web. 23 December 2009."Often named as the richest man ever, a more accurate conversion of sesterce would put his modern figure between $200 million and $20 billion." Peter L. BernsteinThe 20 Richest People Of All Time/ref> Crassus began his public career as a military commander under Lucius Cornelius Sulla during his civil war. Following Sulla's assumption of the dictatorship, Crassus amassed an enormous fortune through real estate speculation. Crassus rose to political prominence following his victory over the slave revolt led by Spartacus, sharing the consulship with his rival Pompey the Great. A political and financi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Senate
A senate is a deliberative assembly, often the upper house or chamber of a bicameral legislature. The name comes from the ancient Roman Senate (Latin: ''Senatus''), so-called as an assembly of the senior (Latin: ''senex'' meaning "the elder" or "old man") and therefore considered wiser and more experienced members of the society or ruling class. However the Roman Senate was not the ancestor or predecessor of modern parliamentarism in any sense, because the Roman senate was not a legislative body. Many countries have an assembly named a ''senate'', composed of ''senators'' who may be elected, appointed, have inherited the title, or gained membership by other methods, depending on the country. Modern senates typically serve to provide a chamber of "sober second thought" to consider legislation passed by a lower house, whose members are usually elected. Most senates have asymmetrical duties and powers compared with their respective lower house meaning they have special dut ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |