|
5814A
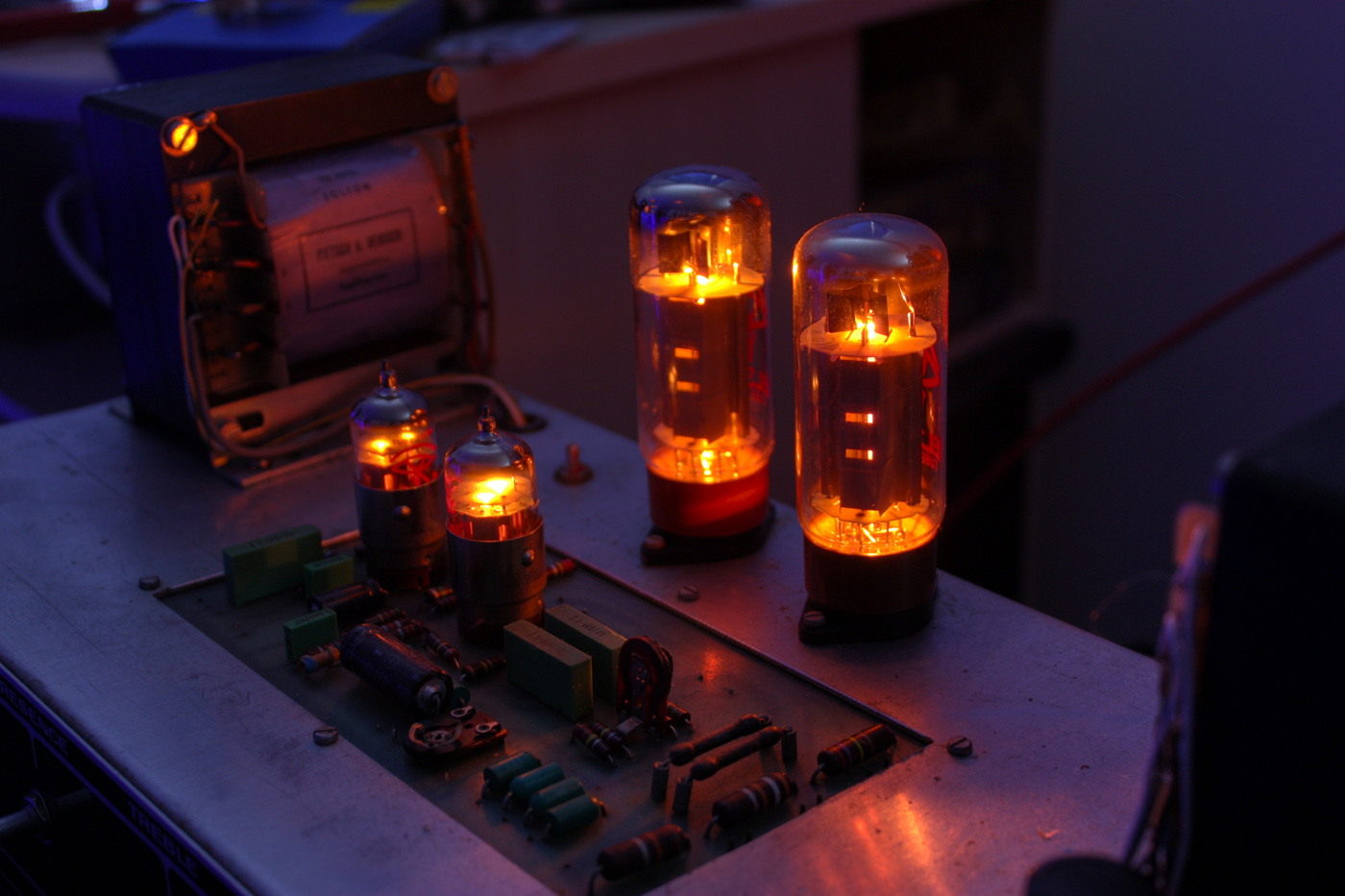
The 12AU7 and its variants are miniature nine-pin (B9A base) medium-gain dual triode vacuum tubes. It belongs to a large family of dual triode vacuum tubes which share the same pinout ( RETMA 9A). 12AU7 is also known in Europe under its Mullard–Philips tube designation ECC82. There are many equivalent tubes with different names, some identical, some designed for ruggedness, long life, or other characteristics; examples are the US military 5814A and the European special-quality ECC82 and E182CC. The tube is popular in hi-fi vacuum tube audio as a low-noise line amplifier, driver (especially for tone stacks), and phase-inverter in vacuum tube push–pull amplifier circuits. It was widely used, in special-quality versions such as ECC82 and 5814A, in pre-semiconductor digital computer circuitry. Use of special-quality versions outside of the purpose they were designed for may not be optimal; for example, a version for digital computers may be designed for long life without ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum Tubes
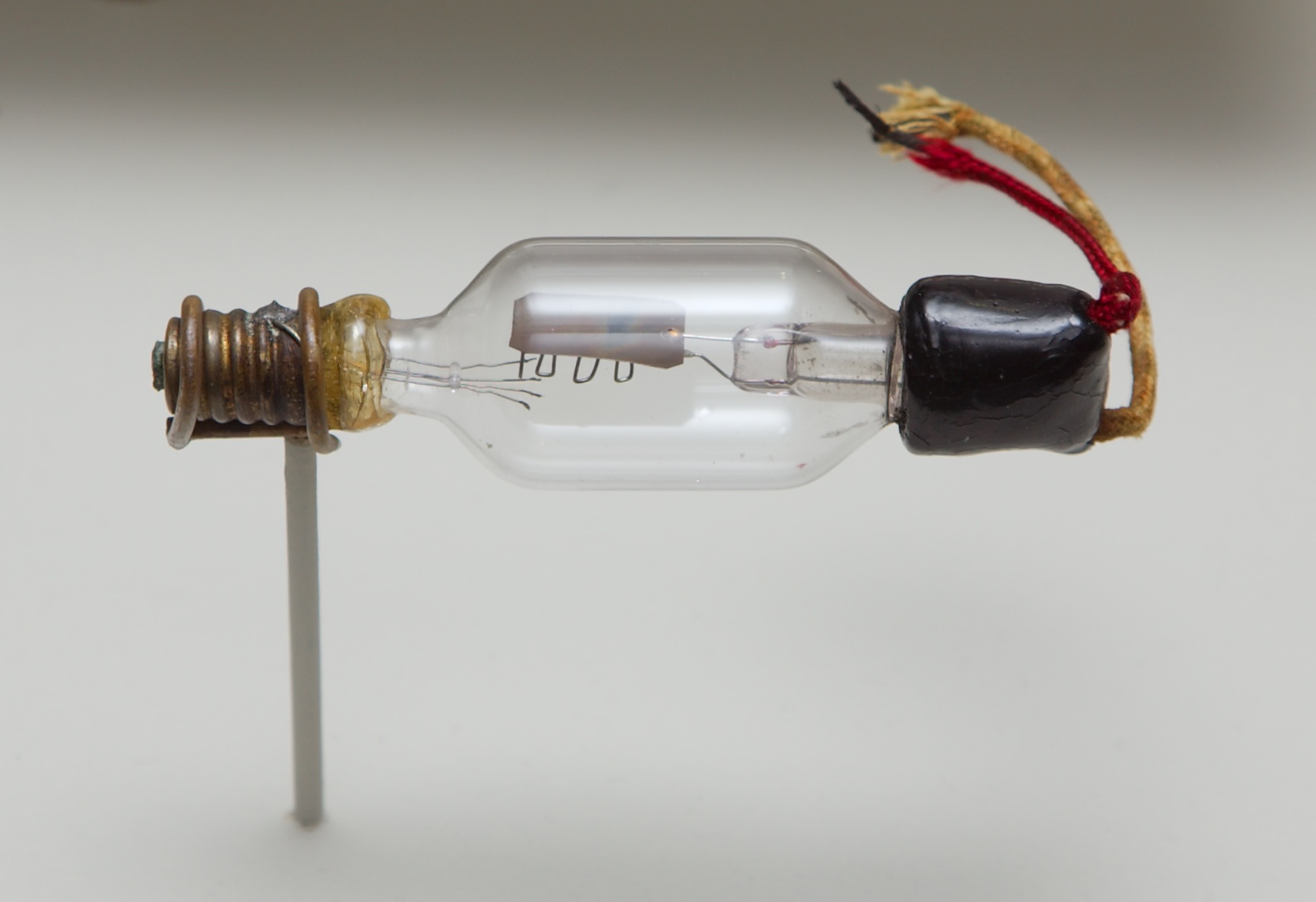
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric potential difference has been applied. The type known as a thermionic tube or thermionic valve utilizes thermionic emission of electrons from a hot cathode for fundamental electronic functions such as signal amplification and current rectification. Non-thermionic types such as a vacuum phototube, however, achieve electron emission through the photoelectric effect, and are used for such purposes as the detection of light intensities. In both types, the electrons are accelerated from the cathode to the anode by the electric field in the tube. The simplest vacuum tube, the diode (i.e. Fleming valve), invented in 1904 by John Ambrose Fleming, contains only a heated electron-emitting cathode and an anode. Electrons can only flow in one direction through the device—from the cathode to the anode. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum Tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric voltage, potential difference has been applied. The type known as a thermionic tube or thermionic valve utilizes thermionic emission of electrons from a hot cathode for fundamental electronic functions such as signal amplifier, amplification and current rectifier, rectification. Non-thermionic types such as a vacuum phototube, however, achieve electron emission through the photoelectric effect, and are used for such purposes as the detection of light intensities. In both types, the electrons are accelerated from the cathode to the anode by the electric field in the tube. The simplest vacuum tube, the diode (i.e. Fleming valve), invented in 1904 by John Ambrose Fleming, contains only a heated electron-emitting cathode and an anode. Electrons can only flow in one direction through the device—fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Triode
A triode is an electronic amplifying vacuum tube (or ''valve'' in British English) consisting of three electrodes inside an evacuated glass envelope: a heated filament or cathode, a grid, and a plate (anode). Developed from Lee De Forest's 1906 Audion, a partial vacuum tube that added a grid electrode to the thermionic diode (Fleming valve), the triode was the first practical electronic amplifier and the ancestor of other types of vacuum tubes such as the tetrode and pentode. Its invention founded the electronics age, making possible amplified radio technology and long-distance telephony. Triodes were widely used in consumer electronics devices such as radios and televisions until the 1970s, when transistors replaced them. Today, their main remaining use is in high-power RF amplifiers in radio transmitters and industrial RF heating devices. In recent years there has been a resurgence in demand for low power triodes due to renewed interest in tube-type audio systems by audiophi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
RETMA Tube Designation
The Radio Electronics Television Manufacturers' Association was formed in 1953, as a result of mergers with other trade standards organisations, such as the RMA. It was principally responsible for the standardised nomenclature for American vacuum tubes - however the standard itself had already been in use for a long time before 1953; for example, the 6L6 was introduced in July 1936. American-made tubes bear a RETMA designation to allow for easy cross-referencing. The RETMA tube designation does not incorporate the purpose of each tube in the designation. The Anglo-European Mullard–Philips tube designation does include tube use information in the designation. *First figure group: indicates heater/filament voltage; 0 means a cold-cathode tube. * Letter group: letter(s) indicate the serial order of assignment of the designation; combinations like AB, AC, AD, AE... were used, avoiding same-letter repetitions, after the single letters were exhausted. Wherever possible, the 12V equiva ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mullard–Philips Tube Designation
In Europe, the principal method of numbering vacuum tubes ("thermionic valves") was the nomenclature used by the Philips company and its subsidiaries Mullard in the UK, Valvo( de, it) in Germany, Radiotechnique (''Miniwatt-Dario'' brand) in France, and Amperex in the United States, from 1934 on. Adhering manufacturers include AEG (de), CdL (1921, ''French Mazda'' brand), CIFTE (fr, ''Mazda-Belvu'' brand), EdiSwan (''British Mazda'' brand), Lorenz (de), MBLE( fr, nl) (be, ''Adzam'' brand), RCA (us), RFT( de, sv) (de), Siemens (de), Telefunken (de), Tesla (cz), Toshiba (ja), Tungsram (hu), and Unitra (pl; ''Dolam'', ''Polam'', ''Telam'' brands). This system allocated meaningful codes to tubes based on their function and became the starting point for the Pro Electron naming scheme for active devices (including tubes and transistors). Nomenclature systems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Push–pull Amplifier
Push–pull may refer to: In electronic technology * Push–pull output, type of electronic circuit * Push–pull converter, in electronics, is a type of DC to DC converter that uses a transformer *Push–pull connector, an electronic cable connector * Push technology / Pull technology, in network communications In transport technology *Push–pull configuration, on aircraft * Push–pull train, a train able to be operated by a driver at either end *Push-to-pull compression fittings, a type of compression fitting that allows air line to be attached without the use of tools In other technology * Push processing, and its counterpart "pull processing" in photography *Push-and-pull enteroscopy, an endoscopic technique for visualization of the small bowel *Push–pull olefin, in organic chemistry * Push–pull perfusion, an ''in vivo'' sampling method * Push–pull technology, in agricultural pest management In the arts * ''Push Pull'' (Hoobastank album), 2018 *"(Do The) Push and Pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Computer
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations ( computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as programs. These programs enable computers to perform a wide range of tasks. A computer system is a nominally complete computer that includes the hardware, operating system (main software), and peripheral equipment needed and used for full operation. This term may also refer to a group of computers that are linked and function together, such as a computer network or computer cluster. A broad range of industrial and consumer products use computers as control systems. Simple special-purpose devices like microwave ovens and remote controls are included, as are factory devices like industrial robots and computer-aided design, as well as general-purpose devices like personal computers and mobile devices like smartphones. Computers power the Internet, which li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
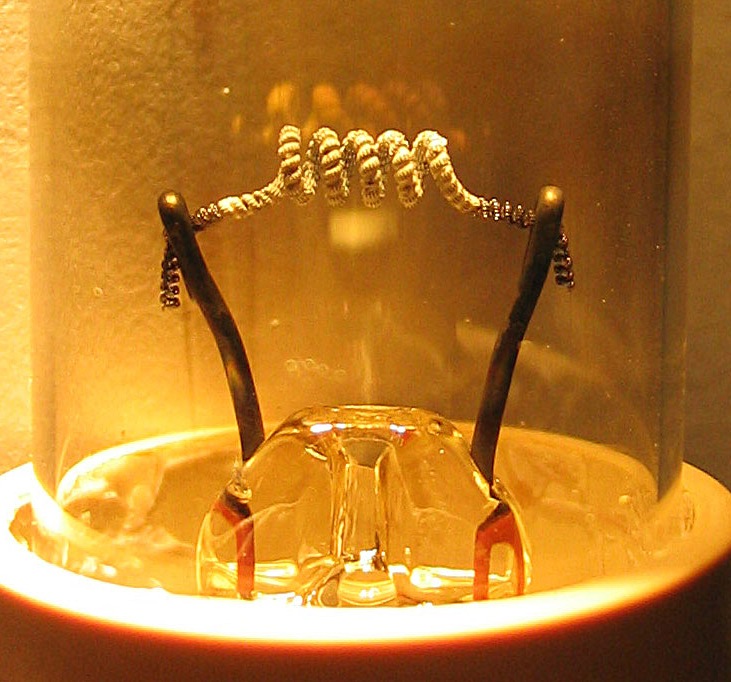
Cathode Poisoning
In vacuum tubes and gas-filled tubes, a hot cathode or thermionic cathode is a cathode electrode which is heated to make it emit electrons due to thermionic emission. This is in contrast to a cold cathode, which does not have a heating element. The heating element is usually an electrical filament heated by a separate electric current passing through it. Hot cathodes typically achieve much higher power density than cold cathodes, emitting significantly more electrons from the same surface area. Cold cathodes rely on field electron emission or secondary electron emission from positive ion bombardment, and do not require heating. There are two types of hot cathode. In a ''directly heated cathode'', the filament is the cathode and emits the electrons. In an ''indirectly heated cathode'', the filament or ''heater'' heats a separate metal cathode electrode which emits the electrons. From the 1920s to the 1960s, a wide variety of electronic devices used hot-cathode vacuum tubes. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microphony
Microphonics, microphony, or microphonism describes the phenomenon wherein certain components in electronic devices transform mechanical vibrations into an undesired electrical signal (noise). The term comes from analogy with a microphone, which is intentionally designed to convert vibrations to electrical signals. Description When electronic equipment was built using vacuum tubes, microphonics were often a serious design problem. The charged elements in the vacuum tubes can mechanically vibrate, changing the distance between the elements, producing charge flows in and out of the tube in a manner identical to a capacitor microphone. A system sufficiently susceptible to microphonics could experience audio feedback, and make noises if jarred or bumped. To minimize these effects, some vacuum tubes were made with thicker internal insulating plates and more supports, and tube-socket assemblies were sometimes shock-mounted by means of small rubber grommets placed in the screw holes to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
12AT7
12AT7 (also known in Europe by the Mullard–Philips tube designation of ECC81) is a miniature 9-pin medium-gain (60) dual-triode vacuum tube popular in guitar amplifiers. It belongs to a large family of dual triode vacuum tubes which share the same pinout (EIA 9A), including in particular the very commonly used low- mu 12AU7 and high-mu 12AX7. The 12AT7 has somewhat lower voltage gain than the 12AX7, but higher transconductance and plate current, which makes it suitable for high frequency applications. Originally the tube was intended for operation in VHF circuits, such as TV sets and FM tuners, as an oscillator/frequency converter, but it also found wide use in audio as a driver and phase-inverter in vacuum tube push–pull amplifier circuits. This tube is essentially two 6AB4/EC92s in a single envelope. Unlike the situation with the 6C4 and 12AU7, both the 6AB4 and the 12AT7 are described by manufacturer's data sheets as R.F. devices operating up to VHF frequencies.Tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |