|
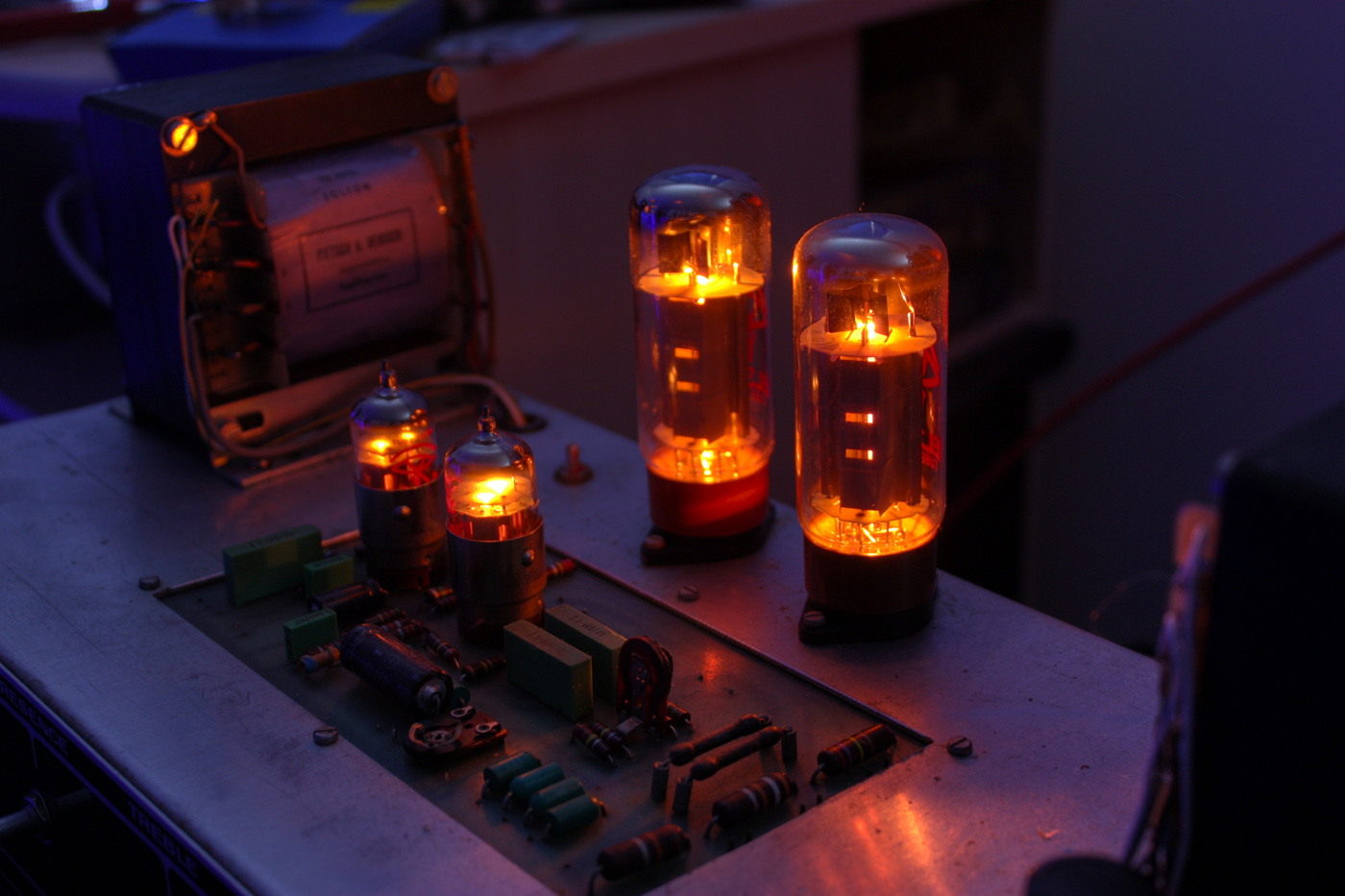
12AT7
12AT7 (also known in Europe by the Mullard–Philips tube designation of ECC81) is a miniature 9-pin medium-gain (60) dual-triode vacuum tube popular in guitar amplifiers. It belongs to a large family of dual triode vacuum tubes which share the same pinout (EIA 9A), including in particular the very commonly used low- mu 12AU7 and high-mu 12AX7. The 12AT7 has somewhat lower voltage gain than the 12AX7, but higher transconductance and plate current, which makes it suitable for high frequency applications. Originally the tube was intended for operation in VHF circuits, such as TV sets and FM tuners, as an oscillator/frequency converter, but it also found wide use in audio as a driver and phase-inverter in vacuum tube push–pull amplifier circuits. This tube is essentially two 6AB4/EC92s in a single envelope. Unlike the situation with the 6C4 and 12AU7, both the 6AB4 and the 12AT7 are described by manufacturer's data sheets as R.F. devices operating up to VHF frequencies.Tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
12AT7
12AT7 (also known in Europe by the Mullard–Philips tube designation of ECC81) is a miniature 9-pin medium-gain (60) dual-triode vacuum tube popular in guitar amplifiers. It belongs to a large family of dual triode vacuum tubes which share the same pinout (EIA 9A), including in particular the very commonly used low- mu 12AU7 and high-mu 12AX7. The 12AT7 has somewhat lower voltage gain than the 12AX7, but higher transconductance and plate current, which makes it suitable for high frequency applications. Originally the tube was intended for operation in VHF circuits, such as TV sets and FM tuners, as an oscillator/frequency converter, but it also found wide use in audio as a driver and phase-inverter in vacuum tube push–pull amplifier circuits. This tube is essentially two 6AB4/EC92s in a single envelope. Unlike the situation with the 6C4 and 12AU7, both the 6AB4 and the 12AT7 are described by manufacturer's data sheets as R.F. devices operating up to VHF frequencies.Tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Vacuum Tubes
This is a list of vacuum tubes or ''thermionic valves'', and low-pressure gas-filled tubes, or ''discharge tubes''. Before the advent of semiconductor devices, thousands of tube types were used in consumer electronics. Many industrial, military or otherwise professional tubes were also produced. Only a few types are still used today, mainly in high-power, high-frequency applications. Heater or filament ratings Receiving tubes have heaters or filaments intended for direct battery operation, parallel operation off a dedicated winding on a supply transformer, or series string operation on transformer-less sets. High-power RF power tubes are directly heated; the heater voltage must be much smaller than the signal voltage on the grid and is therefore in the 5...25 V range, drawing up to hundreds of amperes from a suitable heater transformer. In some valve part number series, the voltage class of the heater is given in the part number, and a similar valve might be available with s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
12AX7
12AX7 (also known as ECC83) is a miniature dual-triode 6AV6 vacuum tube with high voltage gain. Developed around 1946 by RCA engineers in Camden, New Jersey, under developmental number A-4522, it was released for public sale under the 12AX7 identifier on September 15, 1947. The 12AX7 was originally intended as replacement for the 6SL7 family of dual-triode amplifier tubes for audio applications. As a popular choice for guitar tube amplifiers, its ongoing use in such equipment makes it one of the few small-signal vacuum tubes in continuous production since it was introduced. History The 12AX7 is a twin triode basically composed of two of the triodes from a 6AV6, a double diode triode. The 6AV6 is a miniature repackaging (with just a single cathode) of the triode and twin diodes from the octal 6SQ7 (a double-diode triode used in AM radios), which itself is very similar to the older type 75 triode-diode dating from 1930. Application The 12AX7 is a high-gain (typical amplifica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
12AU7
The 12AU7 and its variants are miniature nine-pin (B9A base) medium-gain dual triode vacuum tubes. It belongs to a large family of dual triode vacuum tubes which share the same pinout (RETMA tube designation, RETMA 9A). 12AU7 is also known in Europe under its Mullard–Philips tube designation ECC82. There are many equivalent tubes with different names, some identical, some designed for ruggedness, long life, or other characteristics; examples are the US military 5814A and the European special-quality ECC82 and E182CC. The tube is popular in hi-fi vacuum tube audio as a low-noise line amplifier, driver (especially for tone stacks), and phase-inverter in vacuum tube push–pull amplifier circuits. It was widely used, in special-quality versions such as ECC82 and 5814A, in pre-semiconductor digital computer circuitry. Use of special-quality versions outside of the purpose they were designed for may not be optimal; for example, a version for digital computers may be designed for lo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
JJ Electronic
JJ Electronic, s.r.o is a Slovak electronic component manufacturer, and one of the world's remaining producers of vacuum tubes. It is based in Čadca, in the Kysuce region of Slovakia. Most of its products are audio receiving tubes, mainly used for guitar and hi-fi amplifiers. In technical terms, JJ produces triodes, beam tetrodes and power pentodes. Double diode vacuum tubes for full wave AC-to-DC rectifiers are also produced. JJ also produces electrolytic capacitors for higher-voltage purposes, generally for use in audio amplifiers. JJ also manufactures its own line of high-end audio amplifiers and guitar amplifiers. In 2015, the company sales amounted to EUR 8.5 million and net income came to EUR 3.8 million. Most production is exported to the United States. History Before 1989, Tesla was the main Czechoslovak producer of electron tubes. While Tesla vacuum tubes were exported all over the world, and were known for their quality, the company did not survive the change of e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum Tubes
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric potential difference has been applied. The type known as a thermionic tube or thermionic valve utilizes thermionic emission of electrons from a hot cathode for fundamental electronic functions such as signal amplification and current rectification. Non-thermionic types such as a vacuum phototube, however, achieve electron emission through the photoelectric effect, and are used for such purposes as the detection of light intensities. In both types, the electrons are accelerated from the cathode to the anode by the electric field in the tube. The simplest vacuum tube, the diode (i.e. Fleming valve), invented in 1904 by John Ambrose Fleming, contains only a heated electron-emitting cathode and an anode. Electrons can only flow in one direction through the device—from the cathode to the anode. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum Tubes
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric potential difference has been applied. The type known as a thermionic tube or thermionic valve utilizes thermionic emission of electrons from a hot cathode for fundamental electronic functions such as signal amplification and current rectification. Non-thermionic types such as a vacuum phototube, however, achieve electron emission through the photoelectric effect, and are used for such purposes as the detection of light intensities. In both types, the electrons are accelerated from the cathode to the anode by the electric field in the tube. The simplest vacuum tube, the diode (i.e. Fleming valve), invented in 1904 by John Ambrose Fleming, contains only a heated electron-emitting cathode and an anode. Electrons can only flow in one direction through the device—from the cathode to the anode. A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vacuum Tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric voltage, potential difference has been applied. The type known as a thermionic tube or thermionic valve utilizes thermionic emission of electrons from a hot cathode for fundamental electronic functions such as signal amplifier, amplification and current rectifier, rectification. Non-thermionic types such as a vacuum phototube, however, achieve electron emission through the photoelectric effect, and are used for such purposes as the detection of light intensities. In both types, the electrons are accelerated from the cathode to the anode by the electric field in the tube. The simplest vacuum tube, the diode (i.e. Fleming valve), invented in 1904 by John Ambrose Fleming, contains only a heated electron-emitting cathode and an anode. Electrons can only flow in one direction through the device—fro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transconductance
Transconductance (for transfer conductance), also infrequently called mutual conductance, is the electrical characteristic relating the current through the output of a device to the voltage across the input of a device. Conductance is the reciprocal of resistance. Transadmittance (or transfer admittance) is the AC equivalent of transconductance. Definition Transconductance is very often denoted as a conductance, ''g''m, with a subscript, m, for ''mutual''. It is defined as follows: :g_m = \frac For small signal alternating current, the definition is simpler: :g_m = \frac The SI unit for transconductance is the siemens, with the symbol S, as in conductance. Transresistance Transresistance (for transfer resistance), also infrequently referred to as mutual resistance, is the dual of transconductance. It refers to the ratio between a change of the voltage at two output points and a related change of current through two input points, and is notated as ''r''m: :r_m = \frac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
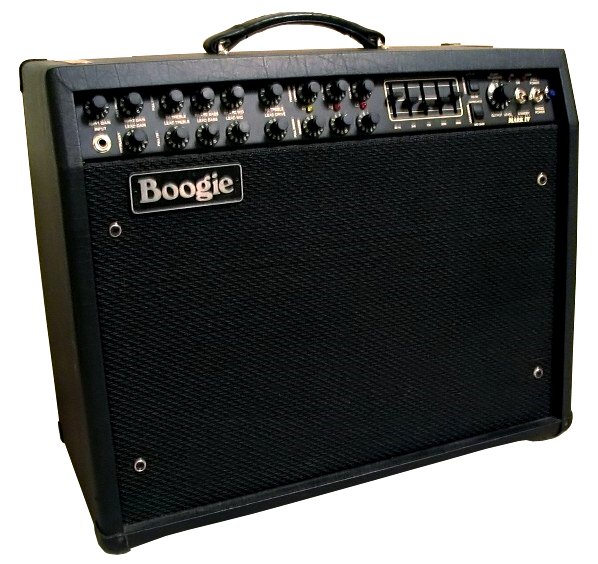
Guitar Amplifier
A guitar amplifier (or amp) is an electronic device or system that strengthens the electrical signal from a pickup on an electric guitar, bass guitar, or acoustic guitar so that it can produce sound through one or more loudspeakers, which are typically housed in a wooden cabinet. A guitar amplifier may be a standalone wood or metal cabinet that contains only the power amplifier (and preamplifier) circuits, requiring the use of a separate speaker cabinet–or it may be a "combo" amplifier, which contains both the amplifier and one or more speakers in a wooden cabinet. There is a wide range of sizes and power ratings for guitar amplifiers, from small, lightweight "practice amplifiers" with a single 6-inch speaker and a 10-watt amp to heavy combo amps with four 10-inch or four 12-inch speakers and a 100-watt amplifier, which are loud enough to use in a nightclub or bar performance. Guitar amplifiers can also modify an instrument's tone by emphasizing or de-emphasizing certain ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transconductance
Transconductance (for transfer conductance), also infrequently called mutual conductance, is the electrical characteristic relating the current through the output of a device to the voltage across the input of a device. Conductance is the reciprocal of resistance. Transadmittance (or transfer admittance) is the AC equivalent of transconductance. Definition Transconductance is very often denoted as a conductance, ''g''m, with a subscript, m, for ''mutual''. It is defined as follows: :g_m = \frac For small signal alternating current, the definition is simpler: :g_m = \frac The SI unit for transconductance is the siemens, with the symbol S, as in conductance. Transresistance Transresistance (for transfer resistance), also infrequently referred to as mutual resistance, is the dual of transconductance. It refers to the ratio between a change of the voltage at two output points and a related change of current through two input points, and is notated as ''r''m: :r_m = \frac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mullard–Philips Tube Designation
In Europe, the principal method of numbering vacuum tubes ("thermionic valves") was the nomenclature used by the Philips company and its subsidiaries Mullard in the UK, Valvo( de, it) in Germany, Radiotechnique (''Miniwatt-Dario'' brand) in France, and Amperex in the United States, from 1934 on. Adhering manufacturers include AEG (de), CdL (1921, ''French Mazda'' brand), CIFTE (fr, ''Mazda-Belvu'' brand), EdiSwan (''British Mazda'' brand), Lorenz (de), MBLE( fr, nl) (be, ''Adzam'' brand), RCA (us), RFT( de, sv) (de), Siemens (de), Telefunken (de), Tesla (cz), Toshiba (ja), Tungsram (hu), and Unitra (pl; ''Dolam'', ''Polam'', ''Telam'' brands). This system allocated meaningful codes to tubes based on their function and became the starting point for the Pro Electron naming scheme for active devices (including tubes and transistors). Nomenclature systems ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |