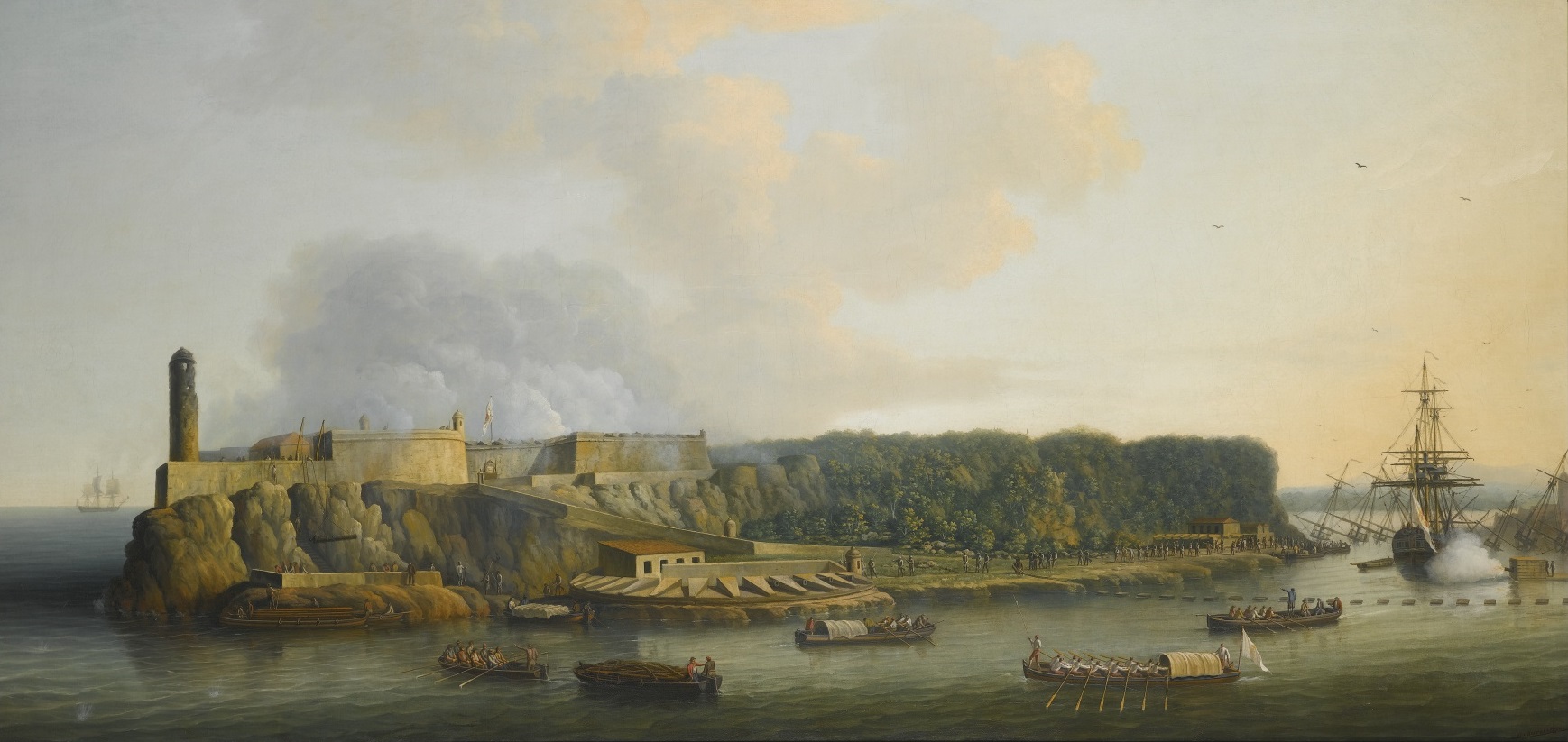|
56th Regiment Of Foot
The 56th (West Essex) Regiment of Foot was an infantry regiment in the British Army, active from 1755 to 1881. It was originally raised in Northumbria as the 58th Regiment, and renumbered the 56th the following year when two senior regiments were disbanded. It saw service in Cuba at the capture of Havana in the Seven Years' War, and was later part of the garrison during the Great Siege of Gibraltar in the American Revolutionary War. During the French Revolutionary Wars it fought in the Caribbean and then in Holland. On the outbreak of the Napoleonic Wars the 56th raised a second battalion in 1804 as part of the anti-invasion preparations; both saw service in India and in the Indian Ocean, with the first capturing Réunion and Mauritius. A third battalion was formed in the later years of the war, but was disbanded after a brief period of service in the Netherlands. The regiment spent much of the following period on foreign garrison duties, and saw service in the later stages of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battalion
A battalion is a military unit, typically consisting of 300 to 1,200 soldiers commanded by a lieutenant colonel, and subdivided into a number of companies (usually each commanded by a major or a captain). In some countries, battalions are exclusively infantry, while in others battalions are unit-level organizations. The word battalion came into the English language in the 16th century from the French language ( French: ''bataillon'' meaning "battle squadron"; Italian: ''battaglione'' meaning the same thing; derived from the Vulgar Latin word ''battalia'' meaning "battle" and from the Latin word ''bauttere'' meaning "to beat" or "to strike"). The first use of the word in English was in the 1580s. Description A battalion comprises two or more primary mission companies which are often of a common type (e.g., infantry, tank, or maintenance), although there are exceptions such as combined arms battalions in the U.S. Army. In addition to the primary mission companies, a battal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Réunion
Réunion (; french: La Réunion, ; previously ''Île Bourbon''; rcf, label= Reunionese Creole, La Rényon) is an island in the Indian Ocean that is an overseas department and region of France. It is located approximately east of the island of Madagascar and southwest of the island of Mauritius. , it had a population of 868,846. Like the other four overseas departments, Réunion also holds the status of a region of France, and is an integral part of the French Republic. Réunion is an outermost region of the European Union and is part of the eurozone. Réunion and the fellow French overseas department of Mayotte are the only eurozone regions located in the Southern Hemisphere. As in the rest of France, the official language of Réunion is French. In addition, a majority of the region's population speaks Réunion Creole. Toponymy When France took possession of the island in the seventeenth century, it was named Bourbon, after the dynasty that then ruled France. To break ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berwick-upon-Tweed
Berwick-upon-Tweed (), sometimes known as Berwick-on-Tweed or simply Berwick, is a town and civil parish in Northumberland, England, south of the Anglo-Scottish border, and the northernmost town in England. The 2011 United Kingdom census recorded Berwick's population as 12,043. The town is at the mouth of the River Tweed on the east coast, south east of Edinburgh, north of Newcastle upon Tyne, and north of London. Uniquely for England, the town is slightly further north than Denmark's capital Copenhagen and the southern tip of Sweden further east of the North Sea, which Berwick borders. Berwick was founded as an Anglo-Saxon settlement in the Kingdom of Northumbria, which was annexed by England in the 10th century. A civil parish and town council were formed in 2008 comprising the communities of Berwick, Spittal and Tweedmouth. It is the northernmost civil parish in England. The area was for more than 400 years central to historic border wars between the Kingdoms of Engla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pepperrell's Regiment
The 51st, or Pepperrell's Regiment of Foot was a British Army regiment first raised in 1745. History The regiment was first raised by Sir William Pepperrell in Massachusetts as Sir William Pepperell's Regiment of Foot and ranked as the 66th Regiment of Foot in September 1745. It was disbanded in May 1749. The regiment was re-raised in New England as the 51st Regiment of Foot (Cape Breton Regiment) in December 1754 for service in the French and Indian War The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the ... but, following the disastrous loss of Oswego, it was disbanded in December 1756. References {{Regiments of Foot Infantry regiments of the British Army Military units and formations of the French and Indian War Military units and formations established in 1754 1754 establi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shirley's Regiment
The 50th, or Shirley's Regiment of Foot was a British Army regiment first raised in 1745. History The regiment was first raised by William Shirley in New England as William Shirley's Regiment of Foot and ranked as the 65th Regiment of Foot in September 1745. It was disbanded in May 1749. The regiment was re-raised in New England as the 50th Regiment of Foot (American Provincials) in December 1754 for service in the French and Indian War The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the ... but, following the disastrous loss of Oswego, it was disbanded in December 1756. References Infantry regiments of the British Army Military units and formations of the French and Indian War Military units and formations established in 1754 1754 establishments in the British Empire { ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lord Charles Manners (British Army Officer, Died 1761)
Major-General Lord Charles Manners (died 5 December 1761) was a British soldier, the ninth and youngest son of John Manners, 2nd Duke of Rutland. Military career He served as an officer in the 3rd Foot Guards. He was appointed a captain in the regiment on 4 June 1745. He was issued a warrant to raise and organise a regiment of infantry in December 1755, and appointed to its colonelcy shortly before the end of the year. This was the 58th Regiment of Foot, shortly thereafter renumbered the 56th Regiment of Foot. He was appointed major-general on 15 September 1759, and died in 1761. References ;Notes ;Sources Digitised copy British Army generals Scots Guards officers Younger sons of dukes 1761 deaths Charles Charles is a masculine given name predominantly found in English language, English and French language, French speaking countries. It is from the French form ''Charles'' of the Proto-Germanic, Proto-Germanic name (in runic alphabet) or ''*k ... Sherard famil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gateshead
Gateshead () is a large town in northern England. It is on the River Tyne's southern bank, opposite Newcastle upon Tyne, Newcastle to which it is joined by seven bridges. The town contains the Gateshead Millennium Bridge, Millennium Bridge, Sage Gateshead, The Sage, and the Baltic Centre for Contemporary Art, and has on its outskirts the twenty metre tall Angel of the North sculpture. Historic counties of England, Historically part of County Durham, under the Local Government Act 1888 the town was made a county borough, meaning it was administered independently of the county council. Since 1974, the town has been administered as part of the Metropolitan Borough of Gateshead within Tyne and Wear. In the 2011 Census, town had a population 120,046 while the wider borough had 200,214. Toponymy Gateshead is first mentioned in Latin translation in Bede, Bede's ''Ecclesiastical History of the English People'' as ''ad caput caprae'' ("at the goat's head"). This interpretation is consis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Newcastle Upon Tyne
Newcastle upon Tyne ( RP: , ), or simply Newcastle, is a city and metropolitan borough in Tyne and Wear, England. The city is located on the River Tyne's northern bank and forms the largest part of the Tyneside built-up area. Newcastle is also the most populous city of North East England. Newcastle developed around a Roman settlement called Pons Aelius and the settlement later took the name of a castle built in 1080 by William the Conqueror's eldest son, Robert Curthose. Historically, the city’s economy was dependent on its port and in particular, its status as one of the world's largest ship building and repair centres. Today, the city's economy is diverse with major economic output in science, finance, retail, education, tourism, and nightlife. Newcastle is one of the UK Core Cities, as well as part of the Eurocities network. Famous landmarks in Newcastle include the Tyne Bridge; the Swing Bridge; Newcastle Castle; St Thomas’ Church; Grainger Town including G ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mechanized Infantry
Mechanized infantry are infantry units equipped with armored personnel carriers (APCs) or infantry fighting vehicles (IFVs) for transport and combat (see also mechanized force). As defined by the United States Army, mechanized infantry is distinguished from motorized infantry in that its vehicles provide a degree of armor protection and armament for use in combat, whereas motorized infantry are provided with "soft-skinned" wheeled vehicles for transportation only.Infantry Division Transportation Battalion and Transportation, Tactical Carrier Units. (1962). United States: Headquarters, Department of the Army. p. 15 Most APCs and IFVs are fully tracked or are all-wheel drive vehicles (6×6 or 8×8), for mobility across rough ground. Some nations distinguish between mechanized and armored (or armoured) infantry, designating troops carried by APCs as mechanized and those in IFVs as armored. The support weapons for mechanized infantry are also provided with motorized transport ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Anglian Regiment
The Royal Anglian Regiment (R ANGLIAN) is an infantry regiment of the British Army. It consists of two Regular battalions and one Reserve battalion. The modern regiment was formed in 1964, making it the oldest of the Line Regiments now operating in the British Army, and can trace its history back to 1685. The regiment was the first of the large infantry regiments and is one of the three regiments of the Queen's Division. History Formation The regiment was formed on 1 September 1964 as the first of the new large infantry regiments, through the amalgamation of the four regiments of the East Anglian Brigade: * 1st (Norfolk and Suffolk) Battalion from the 1st Battalion of the 1st East Anglian Regiment (Royal Norfolk and Suffolk) * 2nd (Duchess of Gloucester's Own Lincolnshire and Northamptonshire) Battalion – 1st Battalion, 2nd East Anglian Regiment (Duchess of Gloucester's Own Royal Lincolnshire and Northamptonshire) * 3rd (16th/44th Foot) Battalion – 1st Battalion, 3rd East ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Childers Reforms
The Childers Reforms of 1881 reorganised the infantry regiments of the British Army. The reforms were done by Secretary of State for War Hugh Childers during 1881, and were a continuation of the earlier Cardwell Reforms. The reorganisation was effected by General Order 41/1881, issued on 1 May 1881, amended by G.O. 70/1881 dated 1 July, which created a network of multi-battalion regiments. In England, Wales and Scotland, each regiment was to have two regular or "line" battalions and two Militia (United Kingdom), militia battalions. In Ireland, there were to be two line and three militia battalions. This was done by renaming the numbered regiments of foot and county militia regiments. In addition, the various corps of county Volunteer Force (Great Britain), rifle volunteers were to be designated as volunteer battalions. Each of these regiments was associated by headquarters location and territorial name to its local "Regimental District". The reforms became effective on 1 July. F ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
44th (East Essex) Regiment Of Foot
The 44th Regiment of Foot was an infantry regiment in the British Army, raised in 1741. Under the Childers Reforms it amalgamated with the 56th (West Essex) Regiment of Foot to form the Essex Regiment in 1881. History Early history The regiment was raised by Colonel James Long as James Long's Regiment of Foot in 1741. The regiment saw active service at the Battle of Prestonpans in September 1745 during the Jacobite rising. Ranked as the 55th Regiment of the Line in 1747, the regiment was renamed the 44th Regiment of Foot in 1751. It embarked for North America in January 1755 for service in the French and Indian War and took part in the Battle of the Monongahela where Colonel Sir Peter Halkett was killed while commanding the regiment. The regiment went on to fight at the Battle of Carillon in July 1758, the Battle of Fort Niagara in July 1759 and finally the Montreal Campaign in July to September 1760 before returning home in 1765. The regiment returned to North America landi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |