|
5,6-Dibromotryptamine
5,6-Dibromotryptamine is a substituted tryptamine and indolic alkaloid found in some marine sponges such as ''Hyrtios'' sp. found in the South Pacific area. 5,6-Dibromotryptamine is potentially an anti bacterial and anti cancer agent. See also * 5,6-Dibromo-''N''-methyltryptamine *6-Bromotryptamine *5-Bromo-DMT 5-Bromo-DMT (5-bromo-''N'',''N''-dimethyltryptamine) is a psychedelic brominated indole alkaloid found in the sponges ''Smenospongia aurea'' and ''Smenospongia echina'', as well as in ''Verongula rigida'' (0.00142% dry weight) alongside 5,6-Dibr ... References Tryptamine alkaloids Bromoarenes {{alkaloid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Substituted Tryptamine
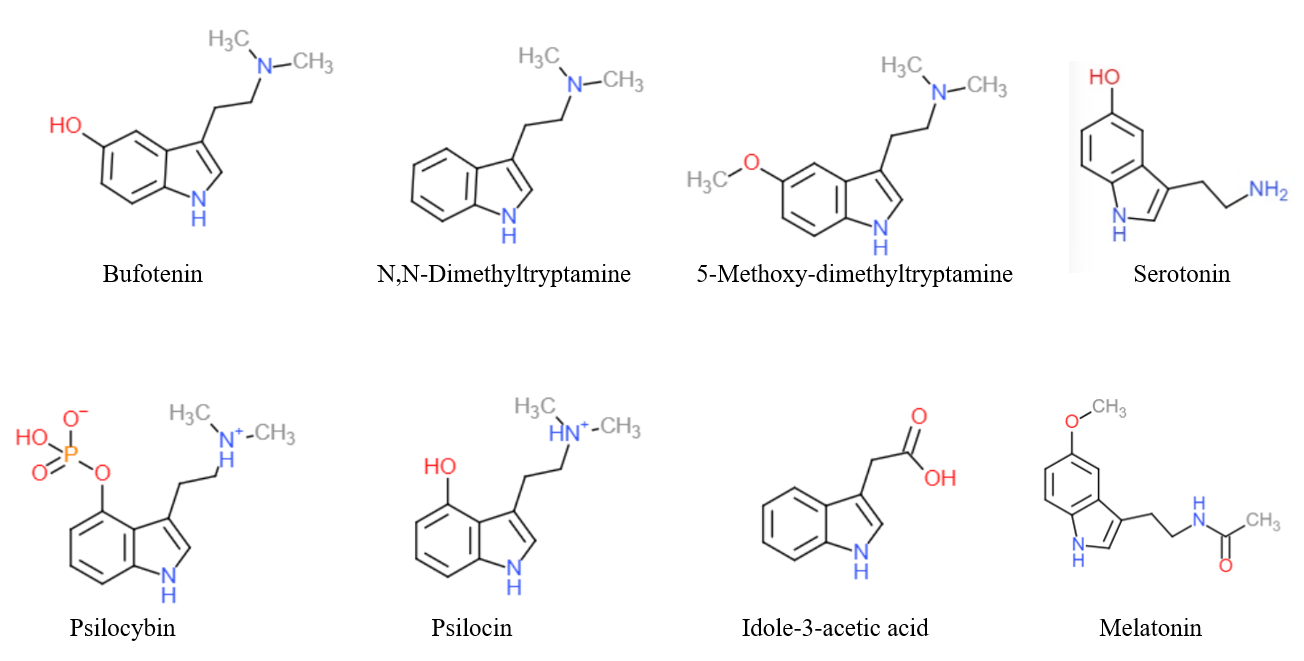
Substituted tryptamines, or serotonin analogues, are organic compounds which may be thought of as being derived from tryptamine itself. The molecular structures of all tryptamines contain an indole ring, joined to an amino group, amino (NH2) group via an ethyl (−CH2–CH2−) side chain, sidechain. In substituted tryptamines, the indole ring, sidechain, and/or amino group are modified by substituting another group for one of the hydrogen (H) atoms. Well-known tryptamines include serotonin, an important neurotransmitter, and melatonin, a hormone involved in regulating the sleep-wake cycle. Tryptamine alkaloids are found in fungi, plants and animals; and sometimes used by humans for the neurological or psychotropic effects of the substance. Prominent examples of tryptamine alkaloids include psilocybin (from "psilocybin mushrooms") and dimethyltryptamine, DMT. In South America, dimethyltryptamine is obtained from numerous plant sources, like chacruna, and it is often used in ayahuas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5,6-Dibromo-N-methyltryptamine
5,6-Dibromo-''N''-methyltryptamine (5,6-Dibromo-NMT) is a substituted tryptamine alkaloid that occurs naturally in marine sponges. See also * 5,6-Dibromotryptamine * 6-Bromotryptamine *5-Bromo-DMT 5-Bromo-DMT (5-bromo-''N'',''N''-dimethyltryptamine) is a psychedelic brominated indole alkaloid found in the sponges ''Smenospongia aurea'' and ''Smenospongia echina'', as well as in ''Verongula rigida'' (0.00142% dry weight) alongside 5,6-Dibr ... References Tryptamine alkaloids Bromoarenes {{alkaloid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
6-Bromotryptamine
6-Bromotryptamine is a substituted tryptamine that is a marine natural product. See also * 5,6-Dibromotryptamine * 5,6-Dibromo-''N''-methyltryptamine *5-Bromo-DMT 5-Bromo-DMT (5-bromo-''N'',''N''-dimethyltryptamine) is a psychedelic brominated indole alkaloid found in the sponges ''Smenospongia aurea'' and ''Smenospongia echina'', as well as in ''Verongula rigida'' (0.00142% dry weight) alongside 5,6-Dibr ... References Tryptamine alkaloids Bromoarenes {{alkaloid-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indolic
Indole is an aromatic heterocyclic organic compound with the formula C8 H7 N. It has a bicyclic structure, consisting of a six-membered benzene ring fused to a five-membered pyrrole ring. Indole is widely distributed in the natural environment and can be produced by a variety of bacteria. As an intercellular signal molecule, indole regulates various aspects of bacterial physiology, including spore formation, plasmid stability, resistance to drugs, biofilm formation, and virulence. The amino acid tryptophan is an indole derivative and the precursor of the neurotransmitter serotonin. General properties and occurrence Indole is a solid at room temperature. It occurs naturally in human feces and has an intense fecal odor. At very low concentrations, however, it has a flowery smell, and is a constituent of many perfumes. It also occurs in coal tar. The corresponding substituent is called indolyl. Indole undergoes electrophilic substitution, mainly at position 3 (see diagram ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaloid
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of similar structure may also be termed alkaloids. In addition to carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen, alkaloids may also contain oxygen, sulfur and, more rarely, other elements such as chlorine, bromine, and phosphorus.Chemical Encyclopedia: alkaloids xumuk.ru Alkaloids are produced by a large variety of organisms including , , Medicinal plant, plants, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sponge
Sponges, the members of the phylum Porifera (; meaning 'pore bearer'), are a basal animal clade as a sister of the diploblasts. They are multicellular organisms that have bodies full of pores and channels allowing water to circulate through them, consisting of jelly-like mesohyl sandwiched between two thin layers of cells. Sponges have unspecialized cells that can transform into other types and that often migrate between the main cell layers and the mesohyl in the process. Sponges do not have nervous, digestive or circulatory systems. Instead, most rely on maintaining a constant water flow through their bodies to obtain food and oxygen and to remove wastes. Sponges were first to branch off the evolutionary tree from the last common ancestor of all animals, making them the sister group of all other animals. Etymology The term ''sponge'' derives from the Ancient Greek word ( 'sponge'). Overview Sponges are similar to other animals in that they are multicellular, he ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South Pacific Area
The South Pacific Area (SOPAC) was a multinational U.S.-led military command active during World War II. It was a part of the U.S. Pacific Ocean Areas under Admiral Chester Nimitz. The delineation and establishment of the Pacific Ocean Areas was negotiated by the Allied governments of the United States, the United Kingdom, Australia, New Zealand, and the Kingdom of the Netherlands in March–April 1942 in response to the Japanese attacks in Southeast Asia and the Pacific. The South Pacific Area was bounded on the west by the Southwest Pacific Area, on the north by the Central Pacific Area, and on the east by the Southeast Pacific Area. It originally encompassed the Ellice, Phoenix, Marquesas, Tuamotu, Samoa, Fiji, and New Hebrides island groups plus New Caledonia and New Zealand. Its western boundary was shifted to just west of Guadalcanal on 1 August 1942 to facilitate operations against that island. Background The assignment orders for Major General Millard Harmon as the Comman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antibiotic
An antibiotic is a type of antimicrobial substance active against bacteria. It is the most important type of antibacterial agent for fighting bacterial infections, and antibiotic medications are widely used in the treatment and prevention of such infections. They may either kill or inhibit the growth of bacteria. A limited number of antibiotics also possess antiprotozoal activity. Antibiotics are not effective against viruses such as the common cold or influenza; drugs which inhibit viruses are termed antiviral drugs or antivirals rather than antibiotics. Sometimes, the term ''antibiotic''—literally "opposing life", from the Greek roots ἀντι ''anti'', "against" and βίος ''bios'', "life"—is broadly used to refer to any substance used against microbes, but in the usual medical usage, antibiotics (such as penicillin) are those produced naturally (by one microorganism fighting another), whereas non-antibiotic antibacterials (such as sulfonamides and antiseptics) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal bleeding, prolonged cough, unexplained weight loss, and a change in bowel movements. While these symptoms may indicate cancer, they can also have other causes. Over 100 types of cancers affect humans. Tobacco use is the cause of about 22% of cancer deaths. Another 10% are due to obesity, poor diet, lack of physical activity or excessive drinking of alcohol. Other factors include certain infections, exposure to ionizing radiation, and environmental pollutants. In the developing world, 15% of cancers are due to infections such as ''Helicobacter pylori'', hepatitis B, hepatitis C, human papillomavirus infection, Epstein–Barr virus and human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). These factors act, at least partly, by changing the genes of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-Bromo-DMT
5-Bromo-DMT (5-bromo-''N'',''N''-dimethyltryptamine) is a psychedelic brominated indole alkaloid found in the sponges ''Smenospongia aurea'' and ''Smenospongia echina'', as well as in ''Verongula rigida'' (0.00142% dry weight) alongside 5,6-Dibromo-DMT (0.35% dry weight) and seven other alkaloids. It is the 5- bromo derivative of DMT, a psychedelic found in many plants and animals. 5-Bromo-DMT has a pEC50 value of 5.51 for the 5-HT2A receptor. Animal studies on 5-Bromo-DMT showed that it produces effects suggestive of sedative and antidepressant activity and caused significant reduction of locomotor activity in the rodent FST model. 5-Bromo-DMT was reported to be psychoactive at 20–50 mg via vaporization with mild psychedelic-like activity. Legality 5-Bromo-DMT is specifically listed as a controlled drug in Singapore. Related compounds * 5-Chloro-αMT * 5-Fluoro-AMT * 5-Fluoro-DMT * Convolutindole A * Desformylflustrabromine * Plakohypaphorine Plakohypaphorines a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tryptamine Alkaloids
Tryptamine is an indolamine metabolite of the essential amino acid, tryptophan. The chemical structure is defined by an indole ─ a fused benzene and pyrrole ring, and a 2-aminoethyl group at the second carbon (third aromatic atom, with the first one being the heterocyclic nitrogen). The structure of tryptamine is a shared feature of certain aminergic neuromodulators including melatonin, serotonin, bufotenin and psychedelic derivatives such as dimethyltryptamine (DMT), psilocybin, psilocin and others. Tryptamine has been shown to activate trace amine-associated receptors expressed in the mammalian brain, and regulates the activity of dopaminergic, serotonergic and glutamatergic systems. In the human gut, symbiotic bacteria convert dietary tryptophan to tryptamine, which activates 5-HT4 receptors and regulates gastrointestinal motility. Multiple tryptamine-derived drugs have been developed to treat migraines, while trace amine-associated receptors are being explored as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |