|
44,100 Hz
In digital audio, 44,100 Hz (alternately represented as 44.1 kHz) is a common sampling frequency. Analog audio is often recorded by sampling it 44,100 times per second, and then these samples are used to reconstruct the audio signal when playing it back. The 44.1 kHz audio sampling rate is widely used due to the compact disc (CD) format, dating back to its use by Sony from 1979. History The 44.1 kHz sampling rate originated in the late 1970s with PCM adaptors, which recorded digital audio on video cassettes,Specifically U-matic cassettes notably the Sony PCM-1600 introduced in 1979 and carried forward in subsequent models in this series. This then became the basis for Compact Disc Digital Audio (CD-DA), defined in the Red Book standard in 1980. Its use has continued as an option in 1990s standards such as the DVD, and in 2000s, standards such as HDMI. This sampling frequency is commonly used for MP3 and other consumer audio file formats which were ori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Digital Audio
Digital audio is a representation of sound recorded in, or converted into, digital form. In digital audio, the sound wave of the audio signal is typically encoded as numerical samples in a continuous sequence. For example, in CD audio, samples are taken 44,100 times per second, each with 16-bit sample depth. Digital audio is also the name for the entire technology of sound recording and reproduction using audio signals that have been encoded in digital form. Following significant advances in digital audio technology during the 1970s and 1980s, it gradually replaced analog audio technology in many areas of audio engineering, record production and telecommunications in the 1990s and 2000s In a digital audio system, an analog electrical signal representing the sound is converted with an analog-to-digital converter (ADC) into a digital signal, typically using pulse-code modulation (PCM). This digital signal can then be recorded, edited, modified, and copied using compu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
De Facto
''De facto'' ( ; , "in fact") describes practices that exist in reality, whether or not they are officially recognized by laws or other formal norms. It is commonly used to refer to what happens in practice, in contrast with '' de jure'' ("by law"), which refers to things that happen according to official law, regardless of whether the practice exists in reality. History In jurisprudence, it mainly means "practiced, but not necessarily defined by law" or "practiced or is valid, but not officially established". Basically, this expression is opposed to the concept of "de jure" (which means "as defined by law") when it comes to law, management or technology (such as standards) in the case of creation, development or application of "without" or "against" instructions, but in accordance with "with practice". When legal situations are discussed, "de jure" means "expressed by law", while "de facto" means action or what is practiced. Similar expressions: "essentially", "unofficial", " ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
EIAJ
Founded in 1948, the Electronic Industries Association of Japan (EIAJ) was one of two Japanese electronics trade organizations that were merged into the Japan Electronics and Information Technology Industries Association (JEITA). Prior to the merger, EIAJ created a number of electronics industry standards that have had some use outside Japan, including: *The EIAJ connectors used for DC power (EIAJ RC-5320A, EIAJ RC-5321, and EIAJ RC-5322 *The D-Terminal connector (RC-5237), used instead of three RCA plugs for component video connections. *The TOSLINK (EIAJ Optical, RC-5720C) optical S/PDIF audio connector. *The EIAJ-1 videotape format, the first standardized format for industrial/non-broadcast video tape recording, released in 1969. Another standard is the multi-channel TV sound system used with the NTSC-J analog TV system. It is often referred to simply as EIAJ, or sometimes as FM-FM audio. Transistor nomenclature The Japanese technical standard JIS-C-7102 provides a meth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
FM Stereo
FM broadcasting is a method of radio broadcasting using frequency modulation (FM). Invented in 1933 by American engineer Edwin Armstrong, wide-band FM is used worldwide to provide high fidelity sound over broadcast radio. FM broadcasting is capable of higher fidelity—that is, more accurate reproduction of the original program sound—than other broadcasting technologies, such as AM broadcasting. It is also less susceptible to common forms of interference, reducing static and popping sounds often heard on AM. Therefore, FM is used for most broadcasts of music or general audio (in the audio spectrum). FM radio stations use the very high frequency range of radio frequencies. Broadcast bands Throughout the world, the FM broadcast band falls within the VHF part of the radio spectrum. Usually 87.5 to 108.0 MHz is used, or some portion thereof, with few exceptions: * In the former Soviet republics, and some former Eastern Bloc countries, the older 65.8–74 MHz band ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soundstream
Soundstream Inc. was the first United States audiophile digital audio recording company, providing commercial services for recording and computer-based editing.Robert Easton, ''Soundstream, the first Digital Studio'', Recording Engineer/Producer, April 1976 Company Soundstream was founded in 1975 in Salt Lake City, Utah by Dr. Thomas G. Stockham, Jr. The company provided worldwide on-location recording services to Telarc, Delos, RCA, Philips, Vanguard, Varèse Sarabande, Angel, Warner Brothers, CBS, Decca, Chalfont, and other labels. They manufactured a total of 18 digital recorders, of which seven were sold and the rest leased out. Although most recordings were of classical music, the range included country, rock, jazz, pop, and avant-garde. The first US live digital recording was made in 1976 by Soundstream's prototype 37 kHz, 16-bit, two channel recorder. New World Records recorded the Santa Fe Opera's performance of Virgil Thomson's ''The Mother of Us All'', an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DVD-Audio
DVD-Audio (commonly abbreviated as DVD-A) is a digital format for delivering high-fidelity audio content on a DVD. DVD-Audio uses most of the storage on the disc for high-quality audio and is not intended to be a video delivery format. The standard was published in March 1999 and the first discs entered the marketplace in 2000. DVD-Audio was in a format war with Super Audio CD (SACD), and along with consumers' tastes tending towards downloadable music, these factors meant that neither high-quality disc achieved considerable market penetration; DVD-Audio has been described as "extinct" by 2007. DVD-Audio remains a niche market but some independent online labels offer a wider choice of titles. Audio specifications DVD-Audio offers many possible configurations of audio channels, ranging from single-channel mono to 5.1-channel surround sound, at various sampling frequencies and sample rates. (The ".1" denotes a low-frequency effects channel (LFE) for bass and/or special audio e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Integer Factors
In number theory, integer factorization is the decomposition of a composite number into a product of smaller integers. If these factors are further restricted to prime numbers, the process is called prime factorization. When the numbers are sufficiently large, no efficient non-quantum integer factorization algorithm is known. However, it has not been proven that such an algorithm does not exist. The presumed difficulty of this problem is important for the algorithms used in cryptography such as RSA public-key encryption and the RSA digital signature. Many areas of mathematics and computer science have been brought to bear on the problem, including elliptic curves, algebraic number theory, and quantum computing. In 2019, Fabrice Boudot, Pierrick Gaudry, Aurore Guillevic, Nadia Heninger, Emmanuel Thomé and Paul Zimmermann factored a 240-digit (795-bit) number ( RSA-240) utilizing approximately 900 core-years of computing power. The researchers estimated that a 1024- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NTSC
The first American standard for analog television broadcast was developed by National Television System Committee (NTSC)National Television System Committee (1951–1953), Report and Reports of Panel No. 11, 11-A, 12–19, with Some supplementary references cited in the Reports, and the Petition for adoption of transmission standards for color television before the Federal Communications Commission, n.p., 1953], 17 v. illus., diagrs., tables. 28 cm. LC Control No.:5402138Library of Congress Online Catalog/ref> in 1941. In 1961, it was assigned the designation CCIR System M, System M. In 1953, a second NTSC standard was adopted, which allowed for color television broadcast compatible with the existing stock of black-and-white receivers. It is one of three major color formats for analog television, the others being PAL and SECAM. NTSC color is usually associated with the System M. The only other broadcast television system to use NTSC color was the System J. Since the intr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transport (recording)
A transport is a device that handles a particular physical storage medium (such as magnetic tape, audio CD, CD-R, or other type of recordable media) itself, and extracts or records the information to and from the medium, to (and from) an outboard set of processing electronics that the transport is connected to. A transport houses no electronics itself for encoding and decoding the information recorded to and from a certain format of media. It only extracts and records information to the media, as well as handling mechanical operations for accessing the media itself, such as playing or rewinding a tape, or accessing the tracks on a disc. An example of a transport for a storage medium would be an audiophile-grade audio CD transport, which houses no D/A converter, unlike most ordinary audio CD players. Instead, the audio CD transport is connected to an external D/A converter via a coaxial ( SPDIF) or optical (Toslink) digital audio connection to convert the digital audio informat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
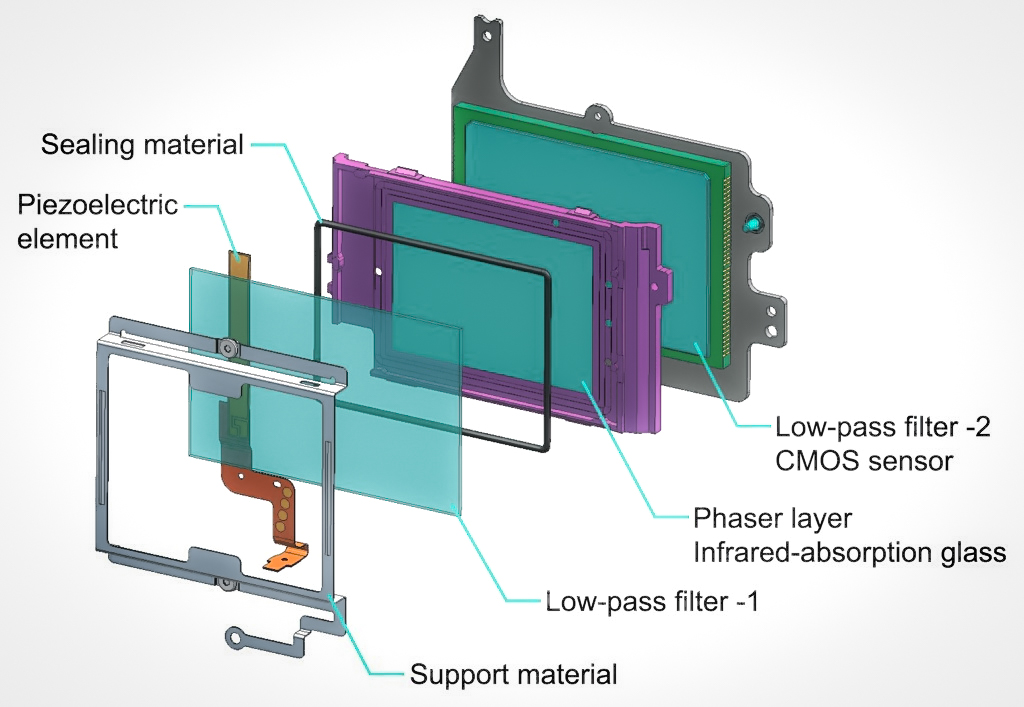
Anti-aliasing Filter
An anti-aliasing filter (AAF) is a filter used before a signal sampler to restrict the bandwidth of a signal to satisfy the Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem over the band of interest. Since the theorem states that unambiguous reconstruction of the signal from its samples is possible when the power of frequencies above the Nyquist frequency is zero, a brick wall filter is an idealized but impractical AAF. A practical AAF makes a trade off between reduced bandwidth and increased aliasing. A practical anti-aliasing filter will typically permit some aliasing to occur or attenuate or otherwise distort some in-band frequencies close to the Nyquist limit. For this reason, many practical systems sample higher than would be theoretically required by a perfect AAF in order to ensure that all frequencies of interest can be reconstructed, a practice called oversampling. Optical applications The Pentax K-3 from Ricoh introduced a unique sensor-based anti-aliasing filter. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transition Band
The transition band, also called the skirt, is a range of frequencies that allows a transition between a passband and a stopband of a signal processing filter. The transition band is defined by a passband and a stopband cutoff frequency or corner frequency. This is the area between where a filter "turns the corner" and where it "hits the bottom". An example of this can be taken from a low-pass filter, commonly used in audio systems to allow the bass signal to pass through to a subwoofer, and cut out all unwanted frequencies above a defined point. If the cutoff point for such a filter is defined as 200 Hz, then in a perfect system, all frequencies above 200 Hz will be stopped and all frequencies below 200 Hz will be allowed to pass through. The transition band can be implemented to allow for a smooth fall off to avoid introducing audible peaks in amplitude. If the transition band of the example 200 Hz filter is 20 Hz, then the signal should start attenuati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Causal System
In control theory, a causal system (also known as a physical or nonanticipative system) is a system where the output depends on past and current inputs but not future inputs—i.e., the output y(t_) depends only on the input x(t) for values of t \le t_. The idea that the output of a function at any time depends only on past and present values of input is defined by the property commonly referred to as causality. A system that has ''some'' dependence on input values from the future (in addition to possible dependence on past or current input values) is termed a non-causal or acausal system, and a system that depends ''solely'' on future input values is an anticausal system. Note that some authors have defined an anticausal system as one that depends solely on future ''and present'' input values or, more simply, as a system that does not depend on past input values. Classically, nature or physical reality has been considered to be a causal system. Physics involving special rela ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |