|
416 BC Deaths
__NOTOC__ Year 416 ( CDXVI) was a leap year starting on Saturday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Theodosius and Palladius (or, less frequently, year 1169 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 416 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Priscus Attalus, Roman usurper, is forced to participate in a triumph celebrated by Emperor Honorius, in the streets of Rome. After the festivities, he is exiled to the Lipari Islands (north of Sicily). Europe * The Visigoths continue their invasion of Hispania, and take control of Tarraconensis. King Wallia occupies the gold mines at Las Médulas, and forces Jewish citizens to convert to Christianity. Asia * Reports of the eruption of Krakatoa are recorded in a Javanese historical chronicle called the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wallia
Wallia or Walha (Spanish: ''Walia'', Portuguese ''Vália''), ( 385 – 418) was king of the Visigoths from 415 to 418, earning a reputation as a great warrior and prudent ruler. He was elected to the throne after Athaulf and then Sigeric were assassinated in 415. Biography Early on, Wallia made peace with Emperor Honorius and accepted a treaty with the Roman Empire. He also returned Honorius' sister Galla Placidia to him. As gains from these arrangements, Wallia was granted Aquitaine in 417 as a region where the Visigoths would be based as official allies or ''foederati''. He established his court in Toulouse, which became the Visigothic capital for the rest of the fifth century. In 418 he honored the alliance by invading Hispania, where his army destroyed the Siling Vandals and so reduced the numbers of Alans living there that the survivors placed themselves under the rule of Gunderic, king of the Asding Vandals. Some historical sources say that he was related to Alaric only ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lü Long
Lü Long (; died 416), courtesy name Yongji (永基), was the last emperor of the Di-led Chinese Later Liang dynasty. He was the nephew of the founding emperor Lü Guang (Emperor Yiwu), and he took the throne after his brother Lü Chao (呂超) assassinated the emperor Lü Zuan (Emperor Ling) in 401 and offered the throne to him. During his reign, Later Liang was under constant attacks by Northern Liang and Southern Liang and reduced largely to its capital Guzang (姑臧, in modern Wuwei, Gansu). In 403, Lü Long decided to end the state by surrendering Guzang to Later Qin's emperor Yao Xing. He became a Later Qin official, but after aligning himself with Yao Xing's son Yao Bi (姚弼), who made unsuccessful attempts to seize the crown prince position from Yao Hong, was executed by Yao Hong after Yao Xing's death in 416. Early life Not much is known about Lü Long's early life, and his birthdate is not known, and virtually nothing is known about his father Lü Bao. He was des ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Donglin Temple (Jiangxi)
Donglin Temple () is a Buddhist monastery approximately from Jiujiang, in the north of Jiangxi province, China. Built in 386 CE at the foot of Mountain Lu by Huiyuan, founder of the Pure Land Sect of Buddhism, it is well known for how long it has stood without collapsing. In the Tang dynasty, Jianzhen made several trips to Japan for the mission of preaching Buddhism. As a result, Huiyuan and the doctrine of Donglin Temple began to spread in Japan. Donglin Temple made contributions to improve cultural exchanges and friendly visits between China and Nepal, India, Japan. The monastery reached its peak of influence during the Tang Dynasty (618–907 CE), but was severely damaged during the Taiping Rebellion and was almost destroyed during the Republican period (1912–1949) of Chinese history. History Eastern Jin dynasty Donglin Temple was originally built as "Longquan Jingshe" () in 386 by a prominent Buddhist monk named Huiyuan, founder of the Pure Land Sect of Buddhis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Buddhism
Chinese Buddhism or Han Buddhism ( zh, s=汉传佛教, t=漢傳佛教, p=Hànchuán Fójiào) is a Chinese form of Mahayana Buddhism which has shaped Chinese culture in a wide variety of areas including art, politics, literature, philosophy, medicine and material culture. Chinese Buddhism is the largest institutionalized religion in Mainland China.Cook, Sarah (2017). The Battle for China's Spirit: Religious Revival, Repression, and Resistance under Xi Jinping.' Freedom House Report. Rowman & Littlefield. Currently, there are an estimated 185 to 250 million Chinese Buddhists in the People's Republic of China. It is also a major religion in Taiwan, Singapore, and Malaysia, as well as among the Chinese Diaspora. Buddhism was first introduced to China during the Han Dynasty (202 BCE–220 CE). The translation of a large body of Indian Buddhist scriptures into Chinese and the inclusion of these translations (along with Taoist and Confucian works) into a Chinese Buddhist canon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
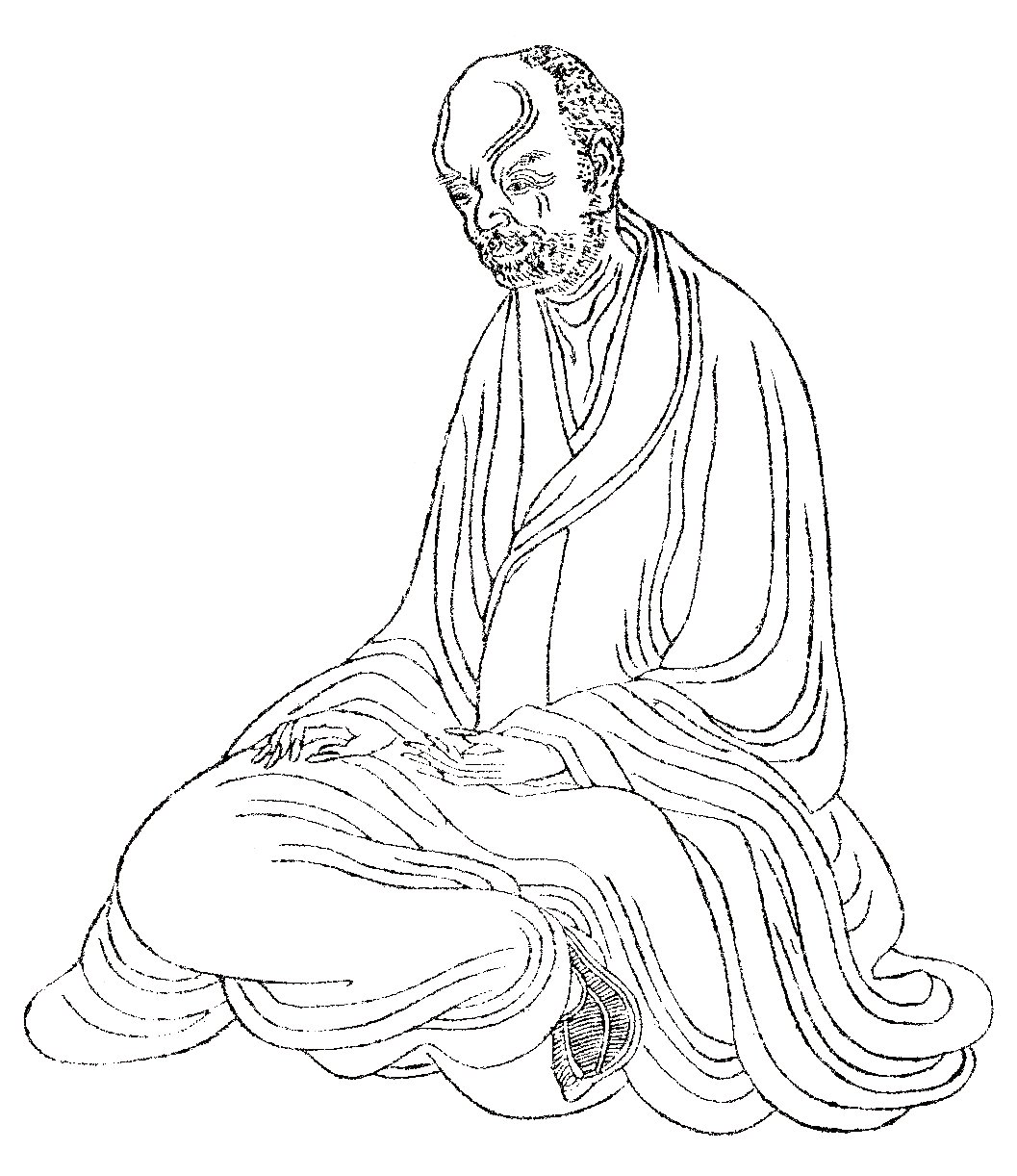
Huiyuan (Buddhist)
Huiyuan (; 334–416 AD) was a Chinese Buddhist teacher who founded Donglin Temple on Mount Lushan in Jiangxi province and wrote the text ''On Why Monks Do Not Bow Down Before Kings'' in 404 AD. He was born in Shanxi province but after a long life of Buddhist teaching he wound up in Jiangxi province, where he died in 416. Although he was born in the north, he moved south to live within the bounds of the Eastern Jin Dynasty. Huiyuan was posthumously named First Patriarch of the Pure Land School of Buddhism. His disciples included Huiguan (慧觀), Sengji (僧濟), and Faan (法安). Life Huiyuan began studying the ''Zhuangzi'' and '' Laozi'' at a young age, as well as the teachings of Confucius. However, at the age of 21 he was converted in Hebei Province by the Buddhist Dao An, who was a Chinese disciple of a Kuchan missionary. Hearing the sermons of Dao An convinced Huiyuan to "leave the family" and embark on a life of Buddhist teachings.Ebrey, Cambridge Illustrated Histor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during Republican era, Cisalpina was annexed in 42 BC to Roman Italy), and Germany west of the Rhine. It covered an area of . According to Julius Caesar, Gaul was divided into three parts: Gallia Celtica, Belgica, and Aquitania. Archaeologically, the Gauls were bearers of the La Tène culture, which extended across all of Gaul, as well as east to Raetia, Noricum, Pannonia, and southwestern Germania during the 5th to 1st centuries BC. During the 2nd and 1st centuries BC, Gaul fell under Roman rule: Gallia Cisalpina was conquered in 204 BC and Gallia Narbonensis in 123 BC. Gaul was invaded after 120 BC by the Cimbri and the Teutons, who were in turn defeated by the Romans by 103 BC. Julius Caesar finally subdued the remaining parts of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rutilius Claudius Namatianus
Rutilius Claudius Namatianus (fl. 5th century) was a Roman Imperial poet, best known for his Latin poem, ''De reditu suo'', in elegiac metre, describing a coastal voyage from Rome to Gaul in 416. The poem was in two books; the exordium of the first and the greater part of the second have been lost. What remains consists of about seven hundred lines. Whether Rutilius had converted to Christianity (the state church of the Roman Empire during his time) has been a matter of scholarly debate, but in the early 21st century, editors of his work concluded that he had not. Alan Cameron, a leading scholar of Late Antiquity, agrees that he "probably" remained unconverted from Rome's traditional religious practices, but that his hostility was not to Christianity as it was practiced by the vast majority of citizens of the Empire, but rather against the total renunciation of public life advocated by the ascetics. Life Origins Rutilius was a native of southern Gaul (Toulouse or perhaps Poit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pararaton
The Pararaton (''Book of Kings''), also known as the Katuturanira Ken Angrok (''Story of Ken Angrok''), is a Javanese historical chronicle written in Kawi (Old Javanese). The comparatively short text of 32 folio-size pages (1126 lines) contains the history of the kings of Singhasari and Majapahit in eastern Java. Pararaton opens with a formal incarnation of the founder of Singhasari kingdom (1222–1292), Ken Arok (or Ken Angrok). Almost half of the manuscript is the story of Ken Arok's career before his accession to the throne in 1222. This part is clearly mythical in character. There then follow a number of shorter narrative fragments in chronological order. Many of the events recorded here are dated. Towards the end the pieces of history become shorter and shorter and are mixed with genealogical information concerning the members of the royal family of the Majapahit empire. Since the oldest colophon in the manuscripts contains the date 1522 Saka (1600 AD), the final part o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
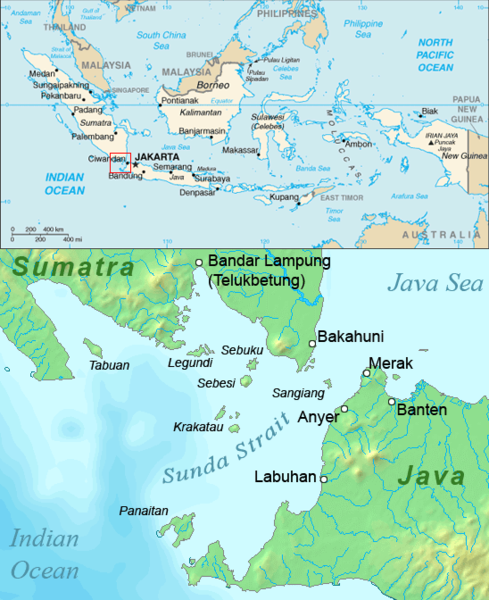
Krakatoa
Krakatoa (), also transcribed (), is a caldera in the Sunda Strait between the islands of Java and Sumatra in the Indonesian province of Lampung. The caldera is part of a volcanic island group (Krakatoa archipelago) comprising four islands. Two, Lang and Verlaten, are remnants of a previous volcanic edifice destroyed in eruptions long before the famous 1883 eruption; another, Rakata, is the remnant of a much larger island destroyed in the 1883 eruption. In 1927, a fourth island, Anak Krakatoa, or "Child of Krakatoa", emerged from the caldera formed in 1883. There has been new eruptive activity since the late 20th century, with a large collapse causing a deadly tsunami in December 2018. Historical significance The most notable eruptions of Krakatoa culminated in a series of massive explosions over 26–27 August 1883, which were among the most violent volcanic events in recorded history. With an estimated Volcanic Explosivity Index (VEI) of 6, the eruption was equivalen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eruption
Several types of volcanic eruptions—during which lava, tephra (ash, lapilli, volcanic bombs and volcanic blocks), and assorted gases are expelled from a volcanic vent or fissure—have been distinguished by volcanologists. These are often named after famous volcanoes where that type of behavior has been observed. Some volcanoes may exhibit only one characteristic type of eruption during a period of activity, while others may display an entire sequence of types all in one eruptive series. There are three different types of eruptions: * Magmatic eruptions are the most well-observed type of eruption. They involve the decompression of gas within magma that propels it forward. * Phreatic eruptions are driven by the superheating of steam due to the close proximity of magma. This type exhibits no magmatic release, instead causing the granulation of existing rock. * Phreatomagmatic eruptions are driven by the direct interaction of magma and water, as opposed to phreatic erupti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global population. Its adherents, known as Christians, are estimated to make up a majority of the population in 157 countries and territories, and believe that Jesus is the Son of God, whose coming as the messiah was prophesied in the Hebrew Bible (called the Old Testament in Christianity) and chronicled in the New Testament. Christianity began as a Second Temple Judaic sect in the 1st century Hellenistic Judaism in the Roman province of Judea. Jesus' apostles and their followers spread around the Levant, Europe, Anatolia, Mesopotamia, the South Caucasus, Ancient Carthage, Egypt, and Ethiopia, despite significant initial persecution. It soon attracted gentile God-fearers, which led to a departure from Jewish customs, and, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |