|
4-Hydroxyphenylacetaldehyde
4-Hydroxyphenylacetaldehyde, also known as ''p''-hydroxyphenylacetaldehyde, is a natural product with the formula HOC6H4CH2CHO. It is a derivative of phenylacetaldehyde and occurs as a white solid at room temperature. Synthesis 4-Hydroxyphenylacetaldehyde can be synthesized from a parsley tyrosine -Tyrosine or tyrosine (symbol Tyr or Y) or 4-hydroxyphenylalanine is one of the 20 standard amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a non-essential amino acid with a polar side group. The word "tyrosine" is from the Gr ... decarboxylase (L-Tyrosine, L-tyrosine). Occurrence 4-Hydroxyphenylacetaldehyde is produced from the metabolism of tyramine by monoamine oxidase (MAO) enzymes in humans and the primary amine oxidase, tyramine oxidase (tynA) enzyme in ''Escherichia coli''. In both species, it is subsequently metabolized into 4-hydroxyphenylacetate by aldehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH) enzymes in humans and the phenylacetaldehyde dehydrogenase (feaB) enzyme in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Berberine
Berberine is a quaternary ammonium salt from the protoberberine group of benzylisoquinoline alkaloids found in such plants as ''Berberis vulgaris'' (barberry), ''Berberis aristata'' (tree turmeric), ''Mahonia aquifolium'' (Oregon grape), ''Hydrastis canadensis'' (goldenseal), ''Xanthorhiza simplicissima'' (yellowroot), ''Phellodendron amurense'' (Amur cork tree), ''Coptis chinensis'' (Chinese goldthread), ''Tinospora cordifolia'', ''Argemone mexicana'' (prickly poppy), and ''Eschscholzia californica'' (Californian poppy). Berberine is usually found in the roots, rhizomes, stems, and bark. Due to its yellow color, ''Berberis'' species were used to dye wool, leather, and wood. Under ultraviolet light, berberine shows a strong yellow fluorescence, making it useful in histology for staining heparin in mast cells. As a natural dye, berberine has a color index of 75160. Research and adverse effects The safety of using berberine for any condition is not adequately defined by high-qua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
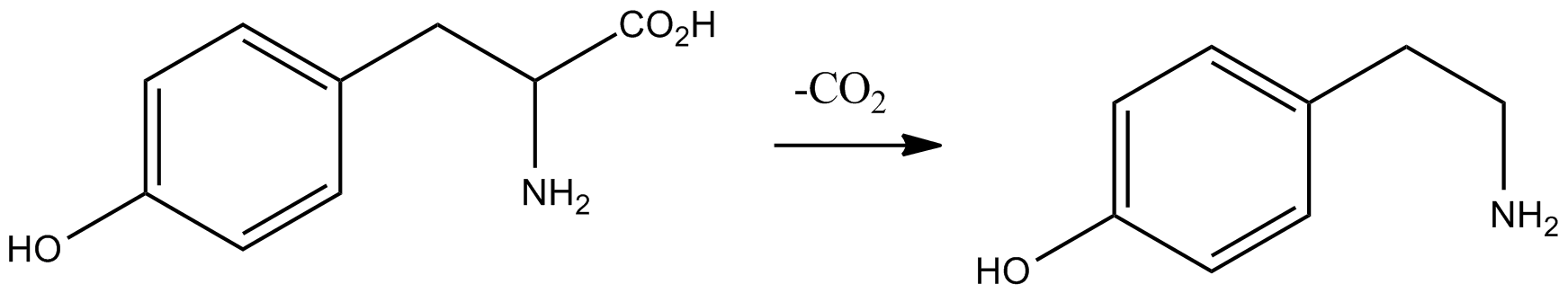
Tyramine
Tyramine ( ) (also spelled tyramin), also known under several other names, is a naturally occurring trace amine derived from the amino acid tyrosine. Tyramine acts as a catecholamine releasing agent. Notably, it is unable to cross the blood-brain barrier, resulting in only non-psychoactive peripheral sympathomimetic effects following ingestion. A hypertensive crisis can result, however, from ingestion of tyramine-rich foods in conjunction with the use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs). Occurrence Tyramine occurs widely in plants and animals, and is metabolized by various enzymes, including monoamine oxidases. In foods, it often is produced by the decarboxylation of tyrosine during fermentation or decay. Foods that are fermented, cured, pickled, aged, or spoiled have high amounts of tyramine. Tyramine levels go up when foods are at room temperature or go past their freshness date. Specific foods containing considerable amounts of tyramine include: * strong or ag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benzylisoquinoline
Substitution of the heterocycle isoquinoline at the C1 position by a benzyl group provides 1‑benzylisoquinoline, the most widely examined of the numerous benzylisoquinoline structural isomers. The 1-benzylisoquinoline moiety can be identified within numerous compounds of pharmaceutical interest, such as moxaverine; but most notably it is found within the structures of a wide variety of plant natural products, collectively referred to as benzylisoquinoline alkaloids. This class is exemplified in part by the following compounds: papaverine, noscapine, codeine, morphine, apomorphine, berberine, tubocurarine. Biosynthesis (''S'')-Norcoclaurine (higenamine) has been identified as the central 1-benzyl-tetrahydro-isoquinoline precursor from which numerous complex biosynthetic pathways eventually emerge. These pathways collectively lead to the structurally disparate compounds comprising the broad classification of plant natural products referred to as benzylisoquinoline alkaloids (BIA), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Product
A natural product is a natural compound or substance produced by a living organism—that is, found in nature. In the broadest sense, natural products include any substance produced by life. Natural products can also be prepared by chemical synthesis (both semisynthesis and total synthesis) and have played a central role in the development of the field of organic chemistry by providing challenging synthetic targets. The term natural product has also been extended for commercial purposes to refer to cosmetics, dietary supplements, and foods produced from natural sources without added artificial ingredients. Within the field of organic chemistry, the definition of natural products is usually restricted to organic compounds isolated from natural sources that are produced by the pathways of primary or secondary metabolism. Within the field of medicinal chemistry, the definition is often further restricted to secondary metabolites. Secondary metabolites (or specialized metabolites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aldehyde Dehydrogenase
Aldehyde dehydrogenases () are a group of enzymes that catalyse the oxidation of aldehydes. They convert aldehydes (R–C(=O)) to carboxylic acids (R–C(=O)). The oxygen comes from a water molecule. To date, nineteen ALDH genes have been identified within the human genome. These genes participate in a wide variety of biological processes including the detoxification of exogenously and endogenously generated aldehydes. Function Aldehyde dehydrogenase is a polymorphic enzyme responsible for the oxidation of aldehydes to carboxylic acids, which leave the liver and are metabolized by the body’s muscle and heart. There are three different classes of these enzymes in mammals: class 1 (low ''K''m, cytosolic), class 2 (low ''K''m, mitochondrial), and class 3 (high ''K''m, such as those expressed in tumors, stomach, and cornea). In all three classes, constitutive and inducible forms exist. ALDH1 and ALDH2 are the most important enzymes for aldehyde oxidation, and both a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenols
In organic chemistry, phenols, sometimes called phenolics, are a class of chemical compounds consisting of one or more hydroxyl groups (— O H) bonded directly to an aromatic hydrocarbon group. The simplest is phenol, . Phenolic compounds are classified as simple phenols or polyphenols based on the number of phenol units in the molecule. Phenols are both synthesized industrially and produced by plants and microorganisms. Properties Acidity Phenols are more acidic than typical alcohols. The acidity of the hydroxyl group in phenols is commonly intermediate between that of aliphatic alcohols and carboxylic acids (their pKa is usually between 10 and 12). Deprotonation of a phenol forms a corresponding negative phenolate ion or phenoxide ion, and the corresponding salts are called phenolates or phenoxides (aryloxides according to the IUPAC Gold Book). Condensation with aldehydes and ketones Phenols are susceptible to Electrophilic aromatic substitutions. Condensation with formald ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Morphine
Morphine is a strong opiate that is found naturally in opium, a dark brown resin in poppies (''Papaver somniferum''). It is mainly used as a analgesic, pain medication, and is also commonly used recreational drug, recreationally, or to make other illicit drug, illicit opioids. There are numerous methods used to administer morphine: oral; sublingual administration, sublingual; via inhalation; intramuscular, injection into a muscle; by Subcutaneous injection, injection under the skin; intravenously; Intrathecally, injection into the space around the spinal cord; transdermal; or via rectal administration, rectal suppository. It acts directly on the central nervous system (CNS) to induce analgesia and alter perception and emotional response to pain. Physical and psychological dependence and tolerance may develop with repeated administration. It can be taken for both acute pain and chronic pain and is frequently used for pain from myocardial infarction, kidney stones, and during Ch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alkaloid
Alkaloids are a class of basic, naturally occurring organic compounds that contain at least one nitrogen atom. This group also includes some related compounds with neutral and even weakly acidic properties. Some synthetic compounds of similar structure may also be termed alkaloids. In addition to carbon, hydrogen and nitrogen, alkaloids may also contain oxygen, sulfur and, more rarely, other elements such as chlorine, bromine, and phosphorus.Chemical Encyclopedia: alkaloids xumuk.ru Alkaloids are produced by a large variety of organisms including , , Medicinal plant, plants, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dopamine
Dopamine (DA, a contraction of 3,4-dihydroxyphenethylamine) is a neuromodulatory molecule that plays several important roles in cells. It is an organic compound, organic chemical of the catecholamine and phenethylamine families. Dopamine constitutes about 80% of the catecholamine content in the brain. It is an amine synthesized by removing a carboxyl group from a molecule of its precursor (chemistry), precursor chemical, L-DOPA, which is biosynthesis, synthesized in the brain and kidneys. Dopamine is also synthesized in plants and most animals. In the brain, dopamine functions as a neurotransmitter—a chemical released by neurons (nerve cells) to send signals to other nerve cells. Neurotransmitters are synthesized in specific regions of the brain, but affect many regions systemically. The brain includes several distinct dopaminergic pathway, dopamine pathways, one of which plays a major role in the motivational component of reward system, reward-motivated behavior. The anticipa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phenylacetaldehyde Dehydrogenase
In enzymology, a phenylacetaldehyde dehydrogenase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction :phenylacetaldehyde + NAD+ + H2O \rightleftharpoons phenylacetate + NADH + 2 H+ The 3 substrates of this enzyme are phenylacetaldehyde, NAD+, and H2O, whereas its 3 products are phenylacetate, NADH, and H+. This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductases, specifically those acting on the aldehyde or oxo group of donor with NAD+ or NADP+ as acceptor. The systematic name of this enzyme class is phenylacetaldehyde:NAD+ oxidoreductase. This enzyme participates in phenylalanine metabolism and styrene degradation Styrene () is an organic compound with the chemical formula C6H5CH=CH2. This derivative of benzene is a colorless oily liquid, although aged samples can appear yellowish. The compound evaporates easily and has a sweet smell, although high concen .... References * EC 1.2.1 NADH-dependent enzymes Enzymes of unknown structure {{1.2-enzyme-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Escherichia Coli
''Escherichia coli'' (),Wells, J. C. (2000) Longman Pronunciation Dictionary. Harlow ngland Pearson Education Ltd. also known as ''E. coli'' (), is a Gram-negative, facultative anaerobic, rod-shaped, coliform bacterium of the genus ''Escherichia'' that is commonly found in the lower intestine of warm-blooded organisms. Most ''E. coli'' strains are harmless, but some serotypes ( EPEC, ETEC etc.) can cause serious food poisoning in their hosts, and are occasionally responsible for food contamination incidents that prompt product recalls. Most strains do not cause disease in humans and are part of the normal microbiota of the gut; such strains are harmless or even beneficial to humans (although these strains tend to be less studied than the pathogenic ones). For example, some strains of ''E. coli'' benefit their hosts by producing vitamin K2 or by preventing the colonization of the intestine by pathogenic bacteria. These mutually beneficial relationships between ''E. col ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4-hydroxyphenylacetate
4-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid is a chemical compound found in olive oil and beer. Synthesis 4-Hydroxyphenylacetic acid is obtained by reducing 4-hydroxymandelic acid with elemental phosphorus and iodine. Uses In industry, 4-hydroxyphenylacetic acid is an intermediate used to synthesize atenolol, 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid, and coclaurine Coclaurine is a nicotinic acetylcholine receptor antagonist which has been isolated from a variety of plant sources including ''Nelumbo nucifera'', '' Sarcopetalum harveyanum'', '' Ocotea duckei'', and others. It belongs to the class of tetrahydr .... References {{DEFAULTSORT:Hydroxyphenylacetic Acid, 4- Phenols Acetic acids Hydroxy acids ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |