|
3rd Century In Lebanon
This article lists historical events that occurred between 201–300 in modern-day Lebanon or regarding its people. Administration Tyre was the capital of Phoenice, but the Roman emperor Elagabalus (r. 218–222) raised his native Emesa (modern-day Homs) to co-capital, leading to a rivalry between the two cities as the head of the province. Propraetorial Imperial Legates of Phoenicia Events 200s * Domitius Leo Procillianus is Propraetorial Imperial Legate of Phoenicia . * Roman Emperor Marcus Aurelius Severus Alexander, known simply as Severus Alexander, is born in 1 October 208, Arqa, in modern-day Lebanon. 210s * The Phoenician-born Papinian, a celebrated Roman jurist, '' magister libellorum'', attorney general (''advocatus fisci'') and, praetorian prefect is murdered in 212 AD. * D. Pius Cassius is Propraetorial Imperial Legate of Phoenicia, 213 AD. * Septimius Severus' wife Julia Domna and son Caracalla tour in Baalbek, 215 AD. * Marcus Julius Gessius M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
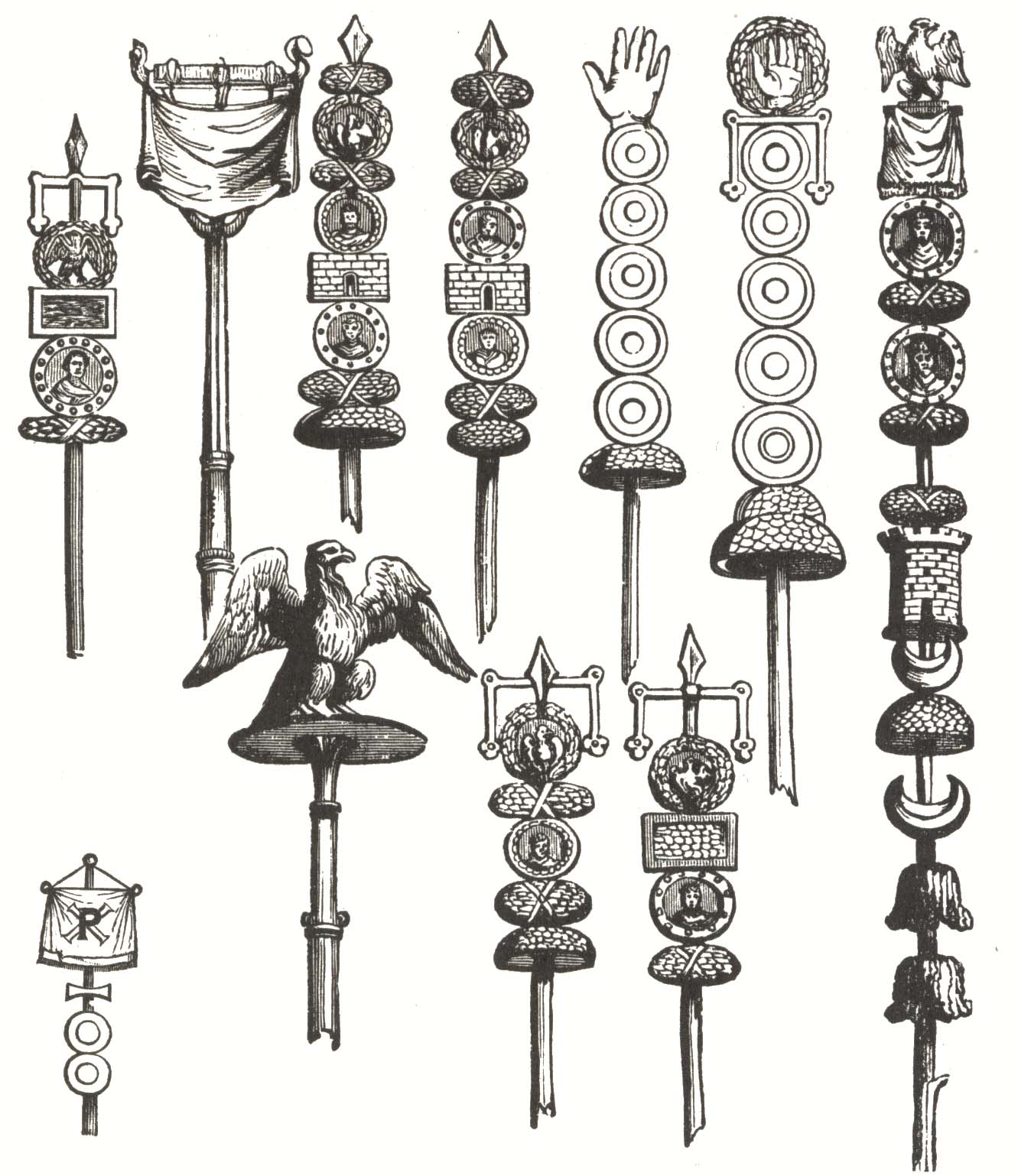
Vexilloid Of The Roman Empire
A vexilloid is any flag-like (vexillary) object used by countries, organisations, or individuals as a form of representation other than flags. American vexillologist Whitney Smith coined the term ''vexilloid'' in 1958, defining it as This includes vexillum, vexilla, banderoles, pennons, streamers, heraldic flag, heraldic flags, standards, and gonfalons. Examples include the Sassanid battle standard Derafsh Kaviani, and the standards of the Roman legion, Roman legions such as the Aquila (Roman), eagle of Augustus Caesar's Legio X Fretensis, Xth legion and the Draconarius, dragon standard of the Sarmatians; the latter was allowed to fly freely in the wind, carried by a horseman, but depictions suggest that it bore more similarity to an elongated dragon kite than to a simple flag. The use of flags replaced the use of vexilloids for general purposes during late medieval times between about 1100 to about 1400. However, vexilloids still remain in use for specialised purposes, such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronograph Of 354
The ''Chronograph of 354'' (or "Chronography"), also known as the ''Calendar of 354'', is a compilation of chronological and calendrical texts produced in 354 AD for a wealthy Roman Christian named Valentinus by the calligrapher and illustrator Furius Dionysius Filocalus. The original illustrated manuscript is lost, but several copies have survived. It is the earliest dated codex to have full page illustrations. The term ''Calendar of Filocalus'' is sometimes used to describe the whole collection, and sometimes just the sixth part, which is the Calendar itself. Other versions of the names ("Philocalus", "Codex-Calendar of 354", "Chronography of 354") are occasionally used. The text and illustrations are available online. Amongst other historically significant information, the work contains the earliest reference to the celebration of Christmas as an annual holiday or feast, on , although unique historical dates had been mentioned much earlier by Hippolytus of Rome during 2 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the Roman Republic it became the dominant language in the Italian region and subsequently throughout the Roman Empire. Even after the fall of Western Rome, Latin remained the common language of international communication, science, scholarship and academia in Europe until well into the 18th century, when other regional vernaculars (including its own descendants, the Romance languages) supplanted it in common academic and political usage, and it eventually became a dead language in the modern linguistic definition. Latin is a highly inflected language, with three distinct genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), six or seven noun cases (nominative, accusative, genitive, dative, ablative, and vocative), five declensions, four verb conjuga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marcus Julius Gessius Marcianus
Marcus Julius Gessius Marcianus also known as Gessius MarcianusBirley, ''Septimius Severus: The African Emperor'', p. 222 (flourished second half of the 2nd century and first half of the 3rd century, died 218) was a Syrian Roman aristocrat. He was the second husband of Julia Avita Mamaea and step-father of the future emperor Severus Alexander. Early life Little is known about the origins of Marcianus. He originally came from Arca Caesarea (modern Arqa, Lebanon). He was an Equestrian officer who became a Promagistrate. No further details are known of the political career of Marcianus. Family Cassius Dio mentions a daughter that was married in 218 AD, thus probably a child from a previous marriage than the one to Mamaea. Marcianus married the Roman Syrian noblewoman Julia Avita Mamaea, as her second husband. Mamaea was the second daughter of the powerful Roman Syrian nobles Julia Maesa and Julius Avitus. Her maternal aunt was the Roman empress Julia Domna (wife of emperor Septimius ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baalbek
Baalbek (; ar, بَعْلَبَكّ, Baʿlabakk, Syriac-Aramaic: ܒܥܠܒܟ) is a city located east of the Litani River in Lebanon's Beqaa Valley, about northeast of Beirut. It is the capital of Baalbek-Hermel Governorate. In Greek and Roman times Baalbek was also known as Heliopolis (, Greek for "Sun City"). In 1998 Baalbek had a population of 82,608, mostly Shia Muslims, followed by Sunni Muslims and Christians. It is home to the Baalbek temple complex which includes two of the largest and grandest Roman temple ruins: the Temple of Bacchus and the Temple of Jupiter. It was inscribed in 1984 as an UNESCO World Heritage site. Name A few miles from the swamp from which the Litani (the classical Leontes) and the Asi (the upper Orontes) flow, Baalbek may be the same as the ''manbaa al-nahrayn'' ("Source of the Two Rivers"), the abode of El in the Ugaritic Baal Cycle discovered in the 1920s and a separate serpent incantation. Baalbek was called Heliopolis during the Roma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caracalla
Marcus Aurelius Antoninus (born Lucius Septimius Bassianus, 4 April 188 – 8 April 217), better known by his nickname "Caracalla" () was Roman emperor from 198 to 217. He was a member of the Severan dynasty, the elder son of Emperor Septimius Severus and Empress Julia Domna. Proclaimed co-ruler by his father in 198, he reigned jointly with his brother Geta, co-emperor from 209, after their father's death in 211. His brother was murdered by the Praetorian Guard later that year, under orders from Caracalla himself, who then reigned afterwards as sole ruler of the Roman Empire. Caracalla found administration to be mundane, leaving those responsibilities to his mother. Caracalla's reign featured domestic instability and external invasions by the Germanic peoples. Caracalla's reign became notable for the Antonine Constitution ( la, Constitutio Antoniniana), also known as the Edict of Caracalla, which granted Roman citizenship to all free men throughout the Roman Empire. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Julia Domna
Julia Domna (; – 217 AD) was Roman empress from 193 to 211 as the wife of Emperor Septimius Severus. She was the first empress of the Severan dynasty. Domna was born in Emesa (present-day Homs) in Roman Syria to an Arab family of priests of the deity Elagabalus. In 187, she married Severus, who at the time was governor of the Roman province of Gallia Lugdunensis. They had two sons, Caracalla and Geta. A civil war over the Roman throne broke out in 193, and shortly afterwards Severus declared himself emperor. The war ended in 197 with the defeat of the last of Severus's opponents. As empress, Domna was famous for her political, social, and philosophical influence. She received titles such as "Mother of the Invincible Camps".; la, Mater invictorum castrorum. After the elder of her sons, Caracalla, started ruling with his father, she was briefly co-empress with Caracalla's wife, Fulvia Plautilla, until the latter fell into disgrace. Following the death of Severus in 211, Domn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Septimius Severus
Lucius Septimius Severus (; 11 April 145 – 4 February 211) was Roman emperor from 193 to 211. He was born in Leptis Magna (present-day Al-Khums, Libya) in the Roman province of Africa (Roman province), Africa. As a young man he advanced through cursus honorum, the customary succession of offices under the reigns of Marcus Aurelius and Commodus. Severus seized power after the death of the emperor Pertinax in 193 during the Year of the Five Emperors. After deposing and killing the incumbent emperor Didius Julianus, Severus fought his rival claimants, the Roman generals Pescennius Niger and Clodius Albinus. Niger was defeated in 194 at the Battle of Issus (194), Battle of Issus in Roman Cilicia, Cilicia. Later that year Severus waged a short punitive campaign beyond the eastern frontier, annexing the Osroene, Kingdom of Osroene as a new province. Severus defeated Albinus three years later at the Battle of Lugdunum in Roman Gaul, Gaul. Following the consolidation of his rule over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praetorian Prefect
The praetorian prefect ( la, praefectus praetorio, el, ) was a high office in the Roman Empire. Originating as the commander of the Praetorian Guard, the office gradually acquired extensive legal and administrative functions, with its holders becoming the Emperor's chief aides. Under Constantine I, the office was much reduced in power and transformed into a purely civilian administrative post, while under his successors, territorially-defined praetorian prefectures emerged as the highest-level administrative division of the Empire. The prefects again functioned as the chief ministers of the state, with many laws addressed to them by name. In this role, praetorian prefects continued to be appointed by the Eastern Roman Empire (and the Ostrogothic Kingdom) until the reign of Heraclius in the 7th century AD, when wide-ranging reforms reduced their power and converted them to mere overseers of provincial administration. The last traces of the prefecture disappeared in the Byzantine Em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Attorney General
In most common law jurisdictions, the attorney general or attorney-general (sometimes abbreviated AG or Atty.-Gen) is the main legal advisor to the government. The plural is attorneys general. In some jurisdictions, attorneys general also have executive responsibility for law enforcement, prosecutions or even responsibility for legal affairs generally. In practice, the extent to which the attorney general personally provides legal advice to the government varies between jurisdictions, and even between individual office-holders within the same jurisdiction, often depending on the level and nature of the office-holder's prior legal experience. Where the attorney general has ministerial responsibility for legal affairs in general (as is the case, for example, with the United States Attorney General or the Attorney-General for Australia, and the respective attorneys general of the states in each country), the ministerial portfolio is largely equivalent to that of a Minister of Justice ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Master Of Requests
Master of Requests, from the Latin Requestarum Magister, is an office that developed in several European systems of law and government in the late Middle Ages and the early modern period. Holders of the title had the responsibility of presenting petitions, requests and appeals for clemency to a higher court of law, a royal council, or directly to a monarch or other ruler. In origin they were not clearly separate from royal secretaries, carrying out the presentation of petitions as part of the administration of the royal household but gaining influence through their ability to provide access to the ruler. In several jurisdictions they came to have an important legal role as assessors or arbiters of requests, attached to specific executive or judicial bodies, and in France even exercised royal oversight over the law courts.Gwilym Dodd and Sophie Petit-Renaud, "Grace and Favour: The Petition and its Mechanisms", in ''Government and Political Life in England and France, c. 1300–c. 1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |