|
39 Pattern Webbing
The 1939 pattern webbing was an item of military load-carrying equipment used in the Second World War. It was a leather variant of the 1937 pattern web equipment. History In 1939, at the beginning of the Second World War, the number of troops in the British Army stood at roughly 200,000. This number rose to 2,000,000 with the introduction of National Service and the activation of reservists. The rapid increase resulted in a lack of proper equipment. Manufacturers of the webbing product—at the time a treated cotton variant, pattern 37—could not keep up with demand. This led the British government to commission the leather industry to design an alternative. The British army had faced the same problem in the First World War, when troops were deployed with the 1908 pattern webbing. The issue was resolved by introducing the 1914 pattern web. The difference between 1937- and 1939 pattern webbing, besides materials used in manufacturing, came down to the latter not being issued wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing military alliances: the Allies and the Axis powers. World War II was a total war that directly involved more than 100 million personnel from more than 30 countries. The major participants in the war threw their entire economic, industrial, and scientific capabilities behind the war effort, blurring the distinction between civilian and military resources. Aircraft played a major role in the conflict, enabling the strategic bombing of population centres and deploying the only two nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II was by far the deadliest conflict in human history; it resulted in 70 to 85 million fatalities, mostly among civilians. Tens of millions died due to genocides (including the Holocaust), starvation, ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Home Guard (United Kingdom)
The Home Guard (initially Local Defence Volunteers or LDV) was an armed citizen militia supporting the British Army during the Second World War. Operational from 1940 to 1944, the Home Guard had 1.5 million local volunteers otherwise ineligible for military service, such as those who were too young or too old to join the regular armed services (regular military service was restricted to those aged 18 to 41) and those in reserved occupations. Excluding those already in the armed services, the civilian police or civil defence, approximately one in five men were volunteers. Their role was to act as a secondary defence force in case of invasion by the forces of Nazi Germany. The Home Guard were to try to slow down the advance of the enemy even by a few hours to give the regular troops time to regroup. They were also to defend key communication points and factories in rear areas against possible capture by paratroops or fifth columnists. A key purpose was to maintain control of the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Army Equipment
This is a list of equipment of the British Army currently in use. It includes small arms, combat vehicles, aircraft, watercraft, artillery and transport vehicles. The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of British Armed Forces. Since the end of the Cold War, the British Army has been deployed to a number of conflict zones, often as part of an expeditionary force, a coalition force or part of a United Nations peacekeeping operation. To meet its commitments, the equipment of the Army is periodically updated and modified. Programs exist to ensure the Army is suitably equipped for both current conflicts and expected future conflicts, with any shortcomings in equipment addressed as Urgent Operational Requirements (UOR), which supplements planned equipment programmes. Infantry section equipment The British infantry section consists of eight soldiers who are normally organised into two four-soldier infantry fireteams. While equipmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
58 Pattern Webbing
1958 Pattern Web Equipment was a modular personal equipment system issued to the British Armed Forces from 1959 up until the mid 90s. It replaced the 1937 Pattern Web Equipment that had served the UK's Armed Forces through the Second World War and the first decade of the Cold War and also the 1944 pattern Webbing which was used in jungle conditions starting from the mid-1960s. It was in turn gradually replaced in the 1990s by 90 and 95 Pattern Personal Load Carrying Equipment (PLCE), though usage in Ministry of Defence-sponsored Community and Combined Cadet Forces persisted into the 2000s. Although replaced, the belt in particular seems to survive as an unofficial form of dress (replacing the general issue Working Belt) by older soldiers when worn with Combat Soldier 95 clothing. Components A standard set of 1958 Pattern webbing as issued to most British personnel consisted of a belt, a yoke that supported the attachment of a shovel or pick, two ammunition pouches to carry m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populous member state of the European Union. Warsaw is the nation's capital and largest metropolis. Other major cities include Kraków, Wrocław, Łódź, Poznań, Gdańsk, and Szczecin. Poland has a temperate transitional climate and its territory traverses the Central European Plain, extending from Baltic Sea in the north to Sudeten and Carpathian Mountains in the south. The longest Polish river is the Vistula, and Poland's highest point is Mount Rysy, situated in the Tatra mountain range of the Carpathians. The country is bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukraine to the east, Slovakia and the Czech Republic to the south, and Germany to the west. It also shares maritime boundaries with Denmark and Sweden. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Czechoslovakia
, rue, Чеськословеньско, , yi, טשעכאסלאוואקיי, , common_name = Czechoslovakia , life_span = 1918–19391945–1992 , p1 = Austria-Hungary , image_p1 = , s1 = Czech Republic , flag_s1 = Flag of the Czech Republic.svg , s2 = Slovakia , flag_s2 = Flag of Slovakia.svg , image_flag = Flag of Czechoslovakia.svg , flag = Flag of Czechoslovakia , flag_type = Flag(1920–1992) , flag_border = Flag of Czechoslovakia , image_coat = Middle coat of arms of Czechoslovakia.svg , symbol_type = Middle coat of arms(1918–1938 and 1945–1961) , image_map = Czechoslovakia location map.svg , image_map_caption = Czechoslovakia during the interwar period and the Cold War , national_motto = , anthems = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Netherlands
) , anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau") , image_map = , map_caption = , subdivision_type = Sovereign state , subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands , established_title = Before independence , established_date = Spanish Netherlands , established_title2 = Act of Abjuration , established_date2 = 26 July 1581 , established_title3 = Peace of Münster , established_date3 = 30 January 1648 , established_title4 = Kingdom established , established_date4 = 16 March 1815 , established_title5 = Liberation Day (Netherlands), Liberation Day , established_date5 = 5 May 1945 , established_title6 = Charter for the Kingdom of the Netherlands, Kingdom Charter , established_date6 = 15 December 1954 , established_title7 = Dissolution of the Netherlands Antilles, Caribbean reorganisation , established_date7 = 10 October 2010 , official_languages = Dutch language, Dutch , languages_type = Regional languages , languages_sub = yes , languages = , languages2_type = Reco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Belgians
Belgians ( nl, Belgen; french: Belges; german: Belgier) are people identified with the Kingdom of Belgium, a federal state in Western Europe. As Belgium is a multinational state, this connection may be residential, legal, historical, or cultural rather than ethnic. The majority of Belgians, however, belong to two distinct ethnic groups or ''communities'' ( nl, gemeenschap, links=no; french: communauté, links=no) native to the country, i.e. its historical regions: Flemings in Flanders, who speak Dutch; and Walloons in Wallonia, who speak French or Walloon. There is also a substantial Belgian diaspora, which has settled primarily in the United States, Canada, France, and the Netherlands. Etymology The 1830 revolution led to the establishment of an independent country under a provisional government and a national congress. The name "Belgium" was adopted for the country, the word being derived from ''Gallia Belgica'', a Roman province in the northernmost part of Gaul that, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fighting occurring throughout Europe, the Middle East, Africa, the Pacific, and parts of Asia. An estimated 9 million soldiers were killed in combat, plus another 23 million wounded, while 5 million civilians died as a result of military action, hunger, and disease. Millions more died in genocides within the Ottoman Empire and in the 1918 influenza pandemic, which was exacerbated by the movement of combatants during the war. Prior to 1914, the European great powers were divided between the Triple Entente (comprising France, Russia, and Britain) and the Triple Alliance (containing Germany, Austria-Hungary, and Italy). Tensions in the Balkans came to a head on 28 June 1914, following the assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
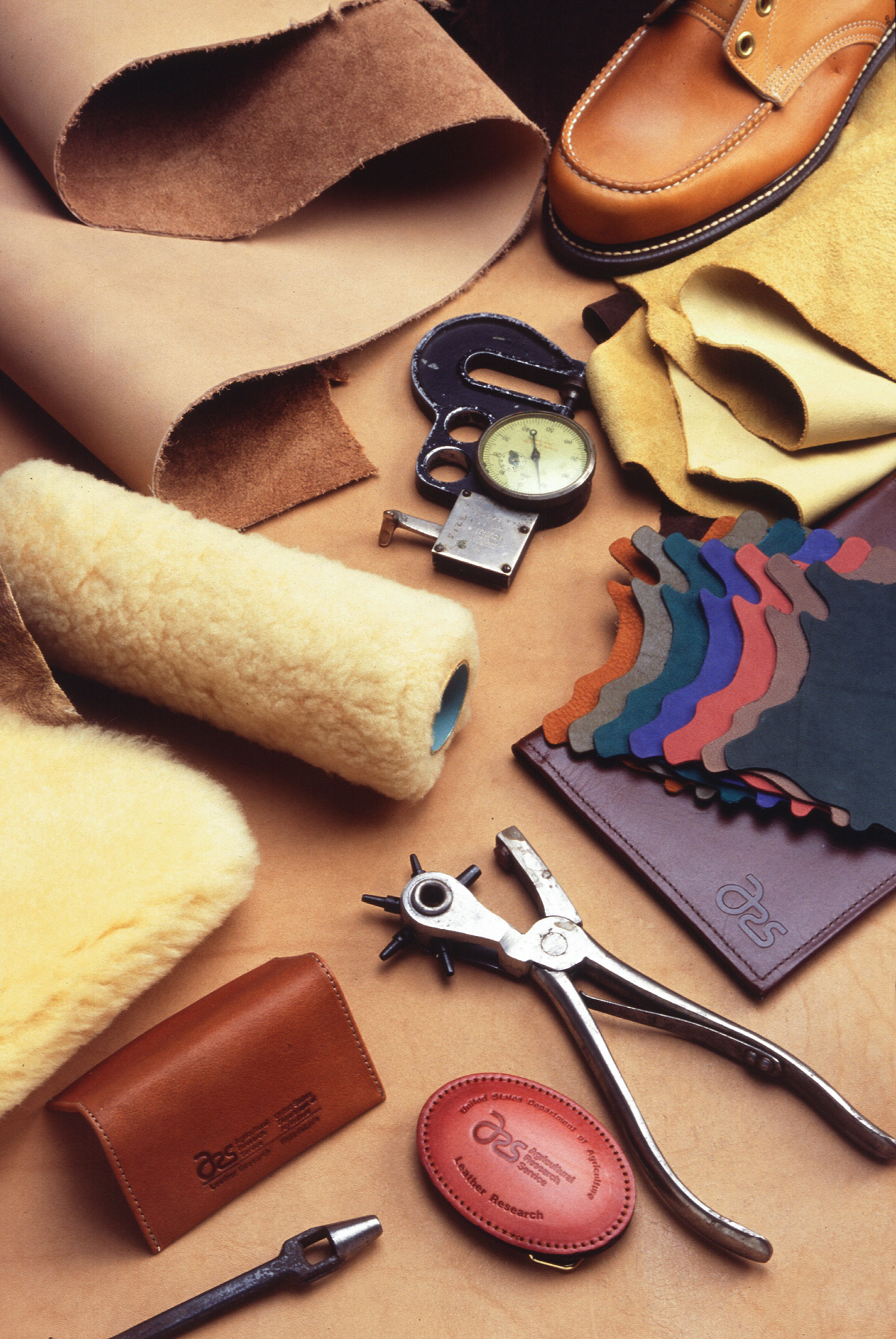
Leather
Leather is a strong, flexible and durable material obtained from the tanning, or chemical treatment, of animal skins and hides to prevent decay. The most common leathers come from cattle, sheep, goats, equine animals, buffalo, pigs and hogs, and aquatic animals such as seals and alligators. Leather can be used to make a variety of items, including clothing, footwear, handbags, furniture, tools and sports equipment, and lasts for decades. Leather making has been practiced for more than 7,000 years and the leading producers of leather today are China and India. Animal rights groups claim that modern commercial leather making and the consumption of its products is unethically killing animals. According to the life-cycle assessment (LCA) report for the United Nations Industrial Development Organization, 99% of the raw hides and skins used in the production of leather derive from animals raised for meat and/or dairy production. Critics of tanneries claim that they engage in uns ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1914 Pattern Webbing
The British Army used a variety of standardized battle uniforms and weapons during World War I. According to the British official historian Brigadier James E. Edmonds writing in 1925, " The British Army of 1914 was the best trained best equipped and best organized British Army ever sent to war". They were the only army to wear any form of a camouflage uniform; the value of drab clothing was quickly recognised by the British Army, who introduced Khaki drill for Indian and colonial warfare from the mid-19th century on. As part of a series of reforms following the Second Boer War, a darker khaki serge was adopted in 1902, for service dress in Britain itself. The British military authorities showed more foresight than their French counterparts, who retained highly visible blue coats and red trousers for active service until the final units received a new uniform over a year into World War I. The soldier was issued with the 1908 Pattern Webbing for carrying personal equipment, and he wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1908 Pattern Webbing
The 1908 Pattern Web Infantry Equipment was an innovative type of webbing equipment adopted by the British Army before World War I. Origins During the Second Boer War of 1899–1902, the standard British Army set of personal equipment, comprising a belt, haversack and ammunition pouches, was the leather Slade-Wallace Equipment, which had been introduced in 1888. It proved unsuitable for holding modern ammunition, which was carried in stripper clips instead of as individual rounds, and its buffalo-hide leather tended to deteriorate during long periods in the field. A review of British shortcomings during the war was conducted by the 1903 Royal Commission on the War in South Africa, which heard evidence that the Slade-Wallace equipment was "an absurdity" and "cumbersome, heavy and badly balanced". As a stop-gap measure, the leather 1903 Bandolier Equipment, based on that used by the Boer Commandos, was issued, but it quickly proved to be unsuitable for infantry use.Chappell, Mike ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

_after_a_Church_Parade_at_Llandyssil_Parish_Church_(1501745)2.jpg)




.jpg)