|
354 BC Deaths
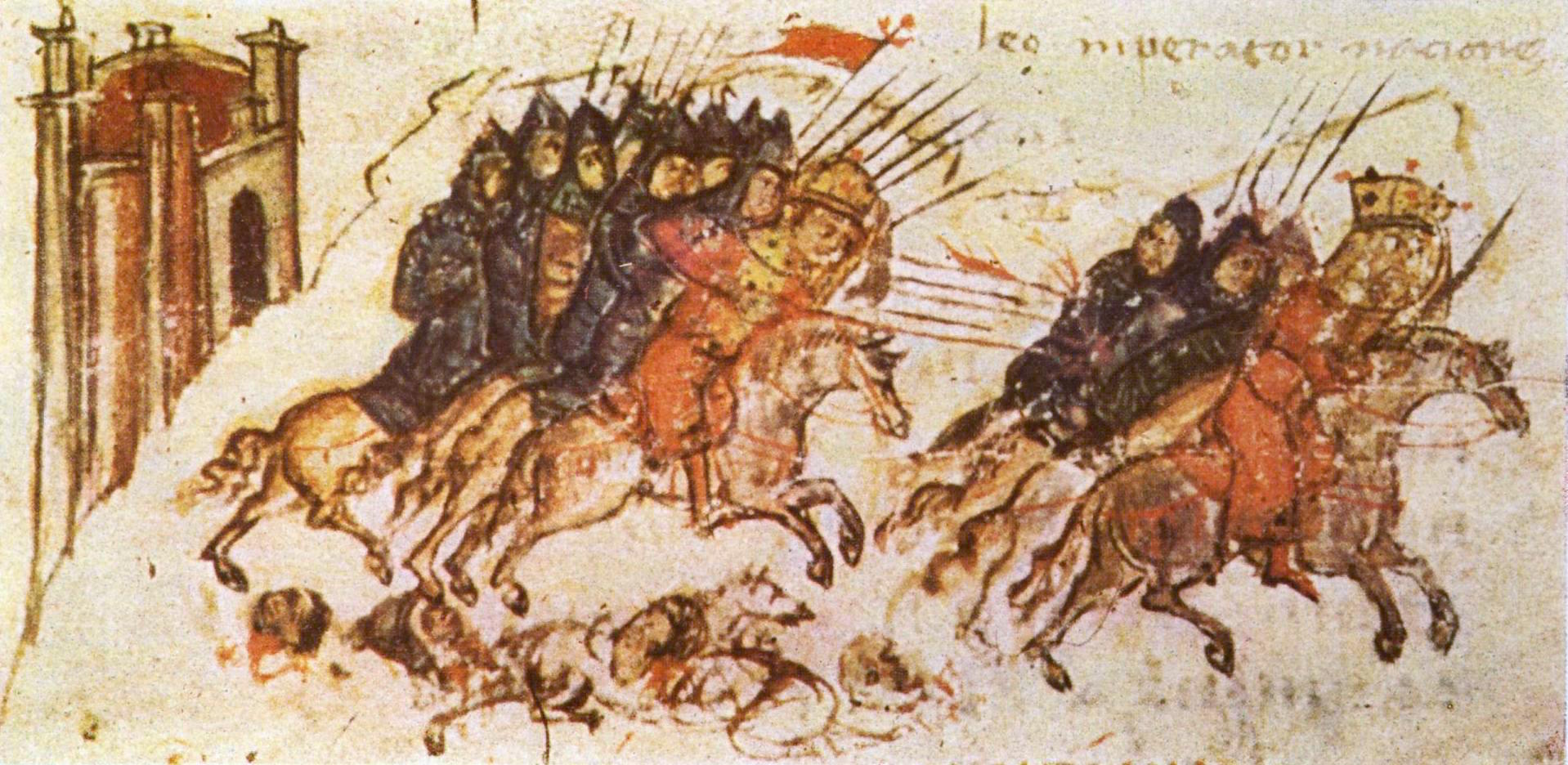
__NOTOC__ Year 354 (Roman numerals, CCCLIV) was a common year starting on Saturday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Constantius and Constantius (or, less frequently, year 1107 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 354 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * Emperor Constantius II recalls his Caesar (title), Caesar (and cousin) Constantius Gallus to Constantinople after hearing unfavorable reports about him. Gallus, Caesar (title), Caesar of the East, has suppressed revolts in Palestine (region), Palestine and central Anatolia. Constantius strips him of his powers and later has him executed in Pula, Pola (Croatia). * The Chronography of 354, Roman Calendar of 354, an illuminated manuscript, is drawn up and becomes the earliest dated codex. Eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
07 Constantius2Chrono354
7 (seven) is the natural number following 6 and preceding 8. It is the only prime number preceding a cube. As an early prime number in the series of positive integers, the number seven has greatly symbolic associations in religion, mythology, superstition and philosophy. The seven Classical planets resulted in seven being the number of days in a week. It is often considered lucky in Western culture and is often seen as highly symbolic. Unlike Western culture, in Vietnamese culture, the number seven is sometimes considered unlucky. It is the first natural number whose pronunciation contains more than one syllable. Evolution of the Arabic digit In the beginning, Indians wrote 7 more or less in one stroke as a curve that looks like an uppercase vertically inverted. The western Ghubar Arabs' main contribution was to make the longer line diagonal rather than straight, though they showed some tendencies to making the digit more rectilinear. The eastern Arabs developed the digit fr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Codex
The codex (plural codices ) was the historical ancestor of the modern book. Instead of being composed of sheets of paper, it used sheets of vellum, papyrus, or other materials. The term ''codex'' is often used for ancient manuscript books, with handwritten contents. A codex, much like the modern book, is bound by stacking the pages and securing one set of edges by a variety of methods over the centuries, yet in a form analogous to modern bookbinding. Modern books are divided into paperback or softback and those bound with stiff boards, called hardbacks. Elaborate historical bindings are called treasure bindings. At least in the Western world, the main alternative to the paged codex format for a long document was the continuous scroll, which was the dominant form of document in the Ancient history, ancient world. Some codices are continuously folded like a concertina, in particular the Maya codices and Aztec codices, which are actually long sheets of paper or animal skin folded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Libanius
Libanius ( grc-gre, Λιβάνιος, Libanios; ) was a teacher of rhetoric of the Sophist school in the Eastern Roman Empire. His prolific writings make him one of the best documented teachers of higher education in the ancient world and a critical source of history of the Greek East during the 4th century AD. During the rise of Christian hegemony in the later Roman Empire, he remained unconverted and in religious matters was a pagan Hellene. Life Libanius was born in Antioch, located near the modern-day city of Antakya, Turkey. He was born into a deeply cultured and once-influential family that had experienced substantial recent decline. In 303 AD, eleven years before his birth, his family had participated in resisting an insurrection by a local army garrison. In the end, Roman Imperial authorities were equally concerned by local aristocrats arming themselves as they were by the rebellious troops. Libanius' family fell out of favor and his grandfather was executed. Libanius' fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and borders fourteen countries by land, the most of any country in the world, tied with Russia. Covering an area of approximately , it is the world's third largest country by total land area. The country consists of 22 provinces, five autonomous regions, four municipalities, and two Special Administrative Regions (Hong Kong and Macau). The national capital is Beijing, and the most populous city and financial center is Shanghai. Modern Chinese trace their origins to a cradle of civilization in the fertile basin of the Yellow River in the North China Plain. The semi-legendary Xia dynasty in the 21st century BCE and the well-attested Shang and Zhou dynasties developed a bureaucratic political system to serve hereditary monarchies, or dyna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Former Qin
The Former Qin, also called Fu Qin (苻秦), (351–394) was a dynastic state of the Sixteen Kingdoms in Chinese history ruled by the Di ethnicity. Founded by Fu Jian (posthumously Emperor Jingming) who originally served under the Later Zhao dynasty, it completed the unification of northern China in 376. Its capital was Xi'an up to the death of the Emperor Xuanzhao in 385. Despite its name, the Former Qin was much later and less powerful than the Qin dynasty which had ruled all of China proper during the 3rd century BC. The adjectival prefix "former" is used to distinguish it from the "Later Qin dynasty" (384-417). In 383, the severe defeat of the Former Qin by the Jin dynasty at the Battle of Fei River encouraged uprisings, splitting Former Qin territory into two noncontiguous pieces after the death of Fu Jian. One fragment, at present-day Taiyuan, Shanxi was soon overwhelmed in 386 by the Xianbei under the Later Yan and the Dingling. The other struggled in greatly ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fu Sheng (Former Qin)
Fu Sheng (; 335–357), originally named Pu Sheng (蒲生), courtesy name Changsheng (長生), formally Prince Li of Yue (越厲王), was an emperor of the Di-led Former Qin dynasty of China. He was the son of Former Qin's founding emperor Fu Jiàn, and was a violent, arbitrary, and cruel ruler, and after ruling for only two years was overthrown by his cousin Fu Jiān (note different tone than his father) in a coup and executed, and therefore was not posthumously recognized as an emperor during the remainder of Former Qin's rule. Before reign Pu Sheng was born to Pu Jiàn in 335, as his third son, by his wife, the later Empress Qiang. At that time, both Pu Jiàn and his father Pu Hong (蒲洪) were generals for Later Zhao. Pu Sheng was born blind in one eye (though some accounts said that he lost his eye to an eagle while trying to get eagles' eggs). Once, his grandfather Pu Hong teased him, "I heard that you, my blind boy, only shed tears from one eye; is that true?" Pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chronicle
A chronicle ( la, chronica, from Greek ''chroniká'', from , ''chrónos'' – "time") is a historical account of events arranged in chronological order, as in a timeline. Typically, equal weight is given for historically important events and local events, the purpose being the recording of events that occurred, seen from the perspective of the chronicler. A chronicle which traces world history is a universal chronicle. This is in contrast to a narrative or history, in which an author chooses events to interpret and analyze and excludes those the author does not consider important or relevant. The information sources for chronicles vary. Some are written from the chronicler's direct knowledge, others from witnesses or participants in events, still others are accounts passed down from generation to generation by oral tradition.Elisabeth M. C. Van Houts, ''Memory and Gender in Medieval Europe: 900–1200'' (Toronto; Buffalo : University of Toronto Press, 1999), pp. 19–20. Some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bulgars
The Bulgars (also Bulghars, Bulgari, Bolgars, Bolghars, Bolgari, Proto-Bulgarians) were Turkic semi-nomadic warrior tribes that flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region during the 7th century. They became known as nomadic equestrians in the Volga-Ural region, but some researchers say that their ethnic roots can be traced to Central Asia. During their westward migration across the Eurasian steppe, the Bulgar tribes absorbed other tribal groups and cultural influences in a process of ethnogenesis, including Iranian, Finnic and Hunnic tribes. Modern genetic research on Central Asian Turkic people and ethnic groups related to the Bulgars points to an affiliation with Western Eurasian populations. The Bulgars spoke a Turkic language, i.e. Bulgar language of Oghuric branch. They preserved the military titles, organization and customs of Eurasian steppes, as well as pagan shamanism and belief in the sky deity Tangra. The Bulgars became semi-sedentary durin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Helvetians
The Helvetii ( , Gaulish: *''Heluētī''), anglicized as Helvetians, were a Celtic tribe or tribal confederation occupying most of the Swiss plateau at the time of their contact with the Roman Republic in the 1st century BC. According to Julius Caesar, the Helvetians were divided into four subgroups or '' pagi.'' Of these, Caesar names only the Verbigeni and the Tigurini, while Posidonius mentions the Tigurini and the Tougeni (). They feature prominently in the ''Commentaries on the Gallic War,'' with their failed migration attempt to southwestern Gaul (58 BC) serving as a catalyst for Caesar's conquest of Gaul. The Helvetians were subjugated after 52 BC, and under Augustus, Celtic oppida, such as Vindonissa or Basilea, were re-purposed as garrisons. In AD 68, a Helvetian uprising was crushed by Aulus Caecina Alienus. The Swiss plateau was at first incorporated into the Roman province of Gallia Belgica (22 BC), later into Germania Superior (AD 83). The Helvetians, like the rest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during Republican era, Cisalpina was annexed in 42 BC to Roman Italy), and Germany west of the Rhine. It covered an area of . According to Julius Caesar, Gaul was divided into three parts: Gallia Celtica, Belgica, and Aquitania. Archaeologically, the Gauls were bearers of the La Tène culture, which extended across all of Gaul, as well as east to Raetia, Noricum, Pannonia, and southwestern Germania during the 5th to 1st centuries BC. During the 2nd and 1st centuries BC, Gaul fell under Roman rule: Gallia Cisalpina was conquered in 204 BC and Gallia Narbonensis in 123 BC. Gaul was invaded after 120 BC by the Cimbri and the Teutons, who were in turn defeated by the Romans by 103 BC. Julius Caesar finally subdued the remaining parts of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland , source1_coordinates= , source1_elevation = , source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein , source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland , source2_coordinates= , source2_elevation = , source_confluence = Reichenau , source_confluence_location = Tamins, Graubünden, Switzerland , source_confluence_coordinates= , source_confluence_elevation = , mouth = North Sea , mouth_location = Netherlands , mouth_coordinates = , mouth_elevation = , progression = , river_system = , basin_size = , tributaries_left = , tributaries_right = , custom_label = , custom_data = , extra = The Rhine ; french: Rhin ; nl, Rijn ; wa, Rén ; li, Rien; rm, label= Sursilvan, Rein, rm, label= Sutsilvan and Surmiran, Ragn, rm, label=Rumantsch Grischun, Vallader and Puter, Rain; it, Reno ; gsw, Rhi(n), inclu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alemanni
The Alemanni or Alamanni, were a confederation of Germanic tribes * * * on the Upper Rhine River. First mentioned by Cassius Dio in the context of the campaign of Caracalla of 213, the Alemanni captured the in 260, and later expanded into present-day Alsace, and northern Switzerland, leading to the establishment of the Old High German language in those regions, by the eighth century named '' Alamannia''. In 496, the Alemanni were conquered by Frankish leader Clovis and incorporated into his dominions. Mentioned as still pagan allies of the Christian Franks, the Alemanni were gradually Christianized during the seventh century. The is a record of their customary law during this period. Until the eighth century, Frankish suzerainty over Alemannia was mostly nominal. After an uprising by Theudebald, Duke of Alamannia, though, Carloman executed the Alamannic nobility and installed Frankish dukes. During the later and weaker years of the Carolingian Empire, the Alemannic co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)



