|
3mm Finescale
3 mm scale, also known as 3 mm finescale, is a model railway scale of 3 mm: 1 ft used for British prototypes. Introduced as British TT gauge, it sits approximately halfway between British N gauge and OO gauge, but is not as popular as either and there is no longer any mass manufacturer ready-to-run support. When TT gauge model railways were developed for British prototypes, in order to fit the small British prototypes, the scale was enlarged but without altering the 12mm gauge. The result, British TT gauge, is too narrow. This led to the development of gauge 3mm finescale. Thus two finescale standards were developed. By far the more common of these is 14.2 mm gauge track, which is accurate. Some modellers choose to use slightly narrower 13.5 mm track due to the necessary oversize motion of outside-cylindered steam locomotives. British TT, also known as TT3, was pioneered by Triang Railways as ready-to-run models. Other gauges are also used to mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brunel gauge
Isambard Kingdom Brunel (; 9 April 1806 – 15 September 1859) was a British civil engineer who is considered "one of the most ingenious and prolific figures in engineering history," "one of the 19th-century engineering giants," and "one of the greatest figures of the Industrial Revolution, hochanged the face of the English landscape with his groundbreaking designs and ingenious constructions." Brunel built dockyards, the Great Western Railway (GWR), a series of steamships including the first propeller-driven transatlantic steamship, and numerous important bridges and tunnels. His designs revolutionised public transport and modern engineering. Though Brunel's projects were not always successful, they often contained innovative solutions to long-standing engineering problems. During his career, Brunel achieved many engineering firsts, including assisting in the building of the first tunnel under a navigable river (the River Thames) and the development of the , the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
TT Gauge
TT scale is a model railroading scale, whose name stands for ''table top''. Its 1:120 scale (from a common engineering scale where one inch equals ten feet) and gauge are roughly halfway between HO scale (1:87) and N scale (1:160). Its original purpose, like the name suggests, was to make a train set small enough to assemble and operate on a tabletop. The scale originated in the USA, but is today widespread mainly in Central Europe, thanks to "Berliner Bahnen", a defunct East German manufacturer of train sets in TT. It is the second-most popular scale in Central Europe and Russia, after HO, and adherents to TT maintain it is the smallest practical scale, especially for those who like to build models from scratch. In other parts of the world it is less spread, and can be described as a niche scale in the United States and the United Kingdom. In wargaming, the TT scale equals the 15 mm scale where the height of "standard" soldier height is . For British 3mm-scale, see 3 m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Standard Gauge
A standard-gauge railway is a railway with a track gauge of . The standard gauge is also called Stephenson gauge (after George Stephenson), International gauge, UIC gauge, uniform gauge, normal gauge and European gauge in Europe, and SGR in East Africa. It is the most widely used track gauge around the world, with approximately 55% of the lines in the world using it. All high-speed rail lines use standard gauge except those in Russia, Finland, and Uzbekistan. The distance between the inside edges of the rails is defined to be 1435 mm except in the United States and on some heritage British lines, where it is defined in U.S. customary/Imperial units as exactly "four feet eight and one half inches" which is equivalent to 1435.1mm. History As railways developed and expanded, one of the key issues was the track gauge (the distance, or width, between the inner sides of the rails) to be used. Different railways used different gauges, and where rails of different gauge met – ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
N Gauge
N scale is a popular model railway scale. Depending upon the manufacturer (or country), the scale ranges from 1:148 to 1:160. In all cases, the ''gauge'' (the distance between the rails) is . The term N ''gauge'' refers to the track dimensions, but in the United Kingdom in particular British N gauge refers to a 1:148 scale with 1:160 () track gauge modelling. The terms N scale and N gauge are often inaccurately used interchangeably, as scale is defined as ratio or proportion of the model, and gauge only as a distance between rails. The scale 1:148 defines the rail-to-rail gauge equal to 9 mm exactly (at the cost of scale exactness), so when calculating the rail or track use 1:160 and for engines and car wheel base use 1:148. All rails are spaced 9 mm apart but the height can differ. Rail height (in thousandths of an inch) is expressed as a "code": thus, Code 55 rails are high while Code 80 rails have a height of . Common real railroad rails are at least tall and can b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
OO Gauge
OO gauge or OO scale (also, 00 gauge and 00 scale) is the most popular standard-gauge model railway standard in the United Kingdom, outside of which it is virtually unknown. OO gauge is one of several 4 mm-scale standards (4 mm to 1 foot, or 1:76.2), and the only one to be marketed by major manufacturers. The OO track gauge of (same as H0 scale) corresponds to prototypical gauge of , rather than standard gauge. However, since the 1960s, other gauges in the same scale have arisen—18.2 mm (EM) and 18.83 mm (Scalefour)—to reflect the desire of some modellers for greater scale accuracy. Origin Double-0 scale model railways were launched by Bing in 1921 as "The Table Railway", running on track and scaled at 4 mm-to-the-foot. In 1922, the first models of British prototypes appeared. Initially all locomotives were powered by clockwork, but the first electric power appeared in autumn 1923. OO describes models with a scale of 4 mm = 1 foot (1:76) runnin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British TT Gauge
3 mm scale, also known as 3 mm finescale, is a model railway scale of 3 mm: 1 ft used for British prototypes. Introduced as British TT gauge, it sits approximately halfway between British N gauge and OO gauge, but is not as popular as either and there is no longer any mass manufacturer ready-to-run support. When TT gauge model railways were developed for British prototypes, in order to fit the small British prototypes, the scale was enlarged but without altering the TT gauge, 12mm gauge. The result, British TT gauge, is too narrow. This led to the development of gauge 3mm finescale. Thus two finescale standards were developed. By far the more common of these is 14.2 mm gauge track, which is accurate. Some modellers choose to use slightly narrower 13.5 mm track due to the necessary oversize motion of outside-Cylinder (locomotive), cylindered steam locomotives. British TT, also known as TT3, was pioneered by Triang Railways as ready-to-run models. Oth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
3mm Finescale
3 mm scale, also known as 3 mm finescale, is a model railway scale of 3 mm: 1 ft used for British prototypes. Introduced as British TT gauge, it sits approximately halfway between British N gauge and OO gauge, but is not as popular as either and there is no longer any mass manufacturer ready-to-run support. When TT gauge model railways were developed for British prototypes, in order to fit the small British prototypes, the scale was enlarged but without altering the 12mm gauge. The result, British TT gauge, is too narrow. This led to the development of gauge 3mm finescale. Thus two finescale standards were developed. By far the more common of these is 14.2 mm gauge track, which is accurate. Some modellers choose to use slightly narrower 13.5 mm track due to the necessary oversize motion of outside-cylindered steam locomotives. British TT, also known as TT3, was pioneered by Triang Railways as ready-to-run models. Other gauges are also used to mode ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finescale
Finescale standards or Fine Standards are model railway standards that aim to be close to the prototype dimensions. Reduction in toylike, overscale flanges, pointwork, etc. In Britain it is particularly used because small British prototypes meant that track gauge is underscale. Modelling to finescale standards requires skill, so modellers usually start with the coarse standards applied to ready-to-run models suitable as toys. Standards are set by modellers' societies. Finescale model railway standards * ScaleSeven (7 mm scale, O gauge) * EM gauge ( 4 mm scale, 18.2 mm gauge) * P4 (4 mm scale, 18.83 mm gauge) * Proto:48 (1/4 inch scale) * Proto:87 (H0 scale) * 3 mm finescale * 2 mm finescale * O14 O14 is a set of model railway standards for accurately modelling narrow-gauge railways in 1:43.5 (7 mm scale) using gauge track. The first published O14 standards appeared in ''Model Railway Constructor'' magazine, September 1951. The article ... (7 mm scale, 14 mm gauge - t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
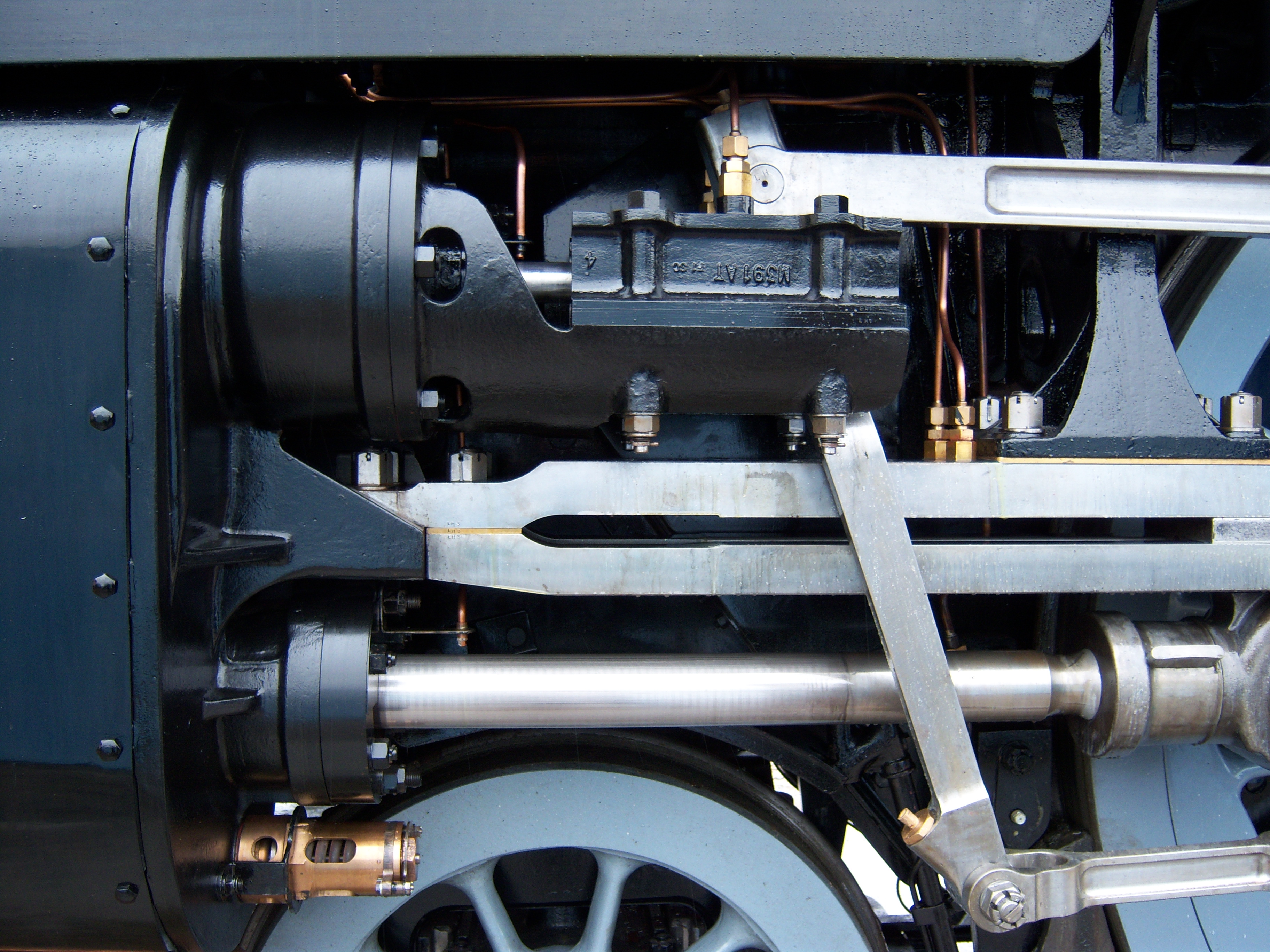
Cylinder (locomotive)
The cylinder is the power-producing element of the steam engine powering a steam locomotive. The cylinder is made pressure-tight with end covers and a piston; a valve distributes the steam to the ends of the cylinder. Cylinders were cast in iron and later made of steel. The cylinder casting includes other features such as (in the case of the early Rocket locomotive) valve ports and mounting feet. The last big American locomotives incorporated the cylinders as part of huge one-piece steel castings that were the main frame of the locomotive. Renewable wearing surfaces were needed inside the cylinders and provided by cast-iron bushings. The way the valve controlled the steam entering and leaving the cylinder was known as steam distribution and shown by the shape of the indicator diagram. What happened to the steam inside the cylinder was assessed separately from what happened in the boiler and how much friction the moving machinery had to cope with. This assessment was known as "e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Irish Gauge
Railways with a track gauge of fall within the category of broad gauge railways. , they were extant in Australia, Brazil and Ireland. History 600 BC :The Diolkos (Δίολκος) across the Isthmus of Corinth in Greece – a grooved paved trackway – was constructed with an average gauge of . 1840 : The Grand Duchy of Baden State Railway was constructed in 1840-1851 to gauge before being converted to in 1854–1855. 1843 : The Board of Trade of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, after investigating a dispute caused by diverse gauges, recommended the use of in Ireland. 1846 : The Regulating the Gauge of Railways Act 1846 made mandatory throughout all of Ireland. 1847 : The Swiss Northern Railway was opened as a line and converted to in 1854. 1854 : The first Australian railway to operate steam-powered freight and passenger services, Melbourne and Hobson's Bay Railway Company, was built as a line. 1858 : The first Brazilian railway was opened: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brunel Gauge
Isambard Kingdom Brunel (; 9 April 1806 – 15 September 1859) was a British civil engineer who is considered "one of the most ingenious and prolific figures in engineering history," "one of the 19th-century engineering giants," and "one of the greatest figures of the Industrial Revolution, hochanged the face of the English landscape with his groundbreaking designs and ingenious constructions." Brunel built dockyards, the Great Western Railway (GWR), a series of steamships including the first propeller-driven transatlantic steamship, and numerous important bridges and tunnels. His designs revolutionised public transport and modern engineering. Though Brunel's projects were not always successful, they often contained innovative solutions to long-standing engineering problems. During his career, Brunel achieved many engineering firsts, including assisting in the building of the first tunnel under a navigable river (the River Thames) and the development of the , the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Z Gauge
Z (or z) is the 26th and last Letter (alphabet), letter of the Latin alphabet, used in the English alphabet, modern English alphabet, the alphabets of other western European languages and others worldwide. Its usual names in English are English alphabet#Letter names, ''zed'' () and English alphabet#Letter names, ''zee'' (), with an occasional archaic variant ''izzard'' ()."Z", ''Oxford English Dictionary,'' 2nd edition (1989); ''Merriam-Webster's Third New International Dictionary of the English Language, Unabridged'' (1993); "zee", ''op. cit''. Name and pronunciation In most English-speaking countries, including Australia, Canada, India, Ireland, New Zealand and the United Kingdom, the letter's name is ''zed'' , reflecting its derivation from the Greek alphabet, Greek ''zeta'' (this dates to Latin, which borrowed Y and Z from Greek), but in American English its name is ''zee'' , analogous to the names for B, C, D, etc., and deriving from a late 17th-century English dialectal fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
