|
395 Deaths
__NOTOC__ Year 395 ( CCCXCV) was a common year starting on Monday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Olybrius and Probinus (or, less frequently, year 1148 ''Ab urbe condita''). The denomination 395 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years. Events By place Roman Empire * January 17 – Emperor Theodosius I, age 48, dies of a disease involving severe edema in Milan. The Roman Empire is again divided into an eastern and a western half. The Eastern Roman Empire is centered in Constantinople under Arcadius, son of Theodosius, and the Western Roman Empire in Mediolanum under his brother Honorius. * April 27 – Arcadius marries Aelia Eudoxia, daughter of the Frankish general Flavius Bauto (without the knowledge or consent of Rufinus, Praetorian prefect of the East). His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
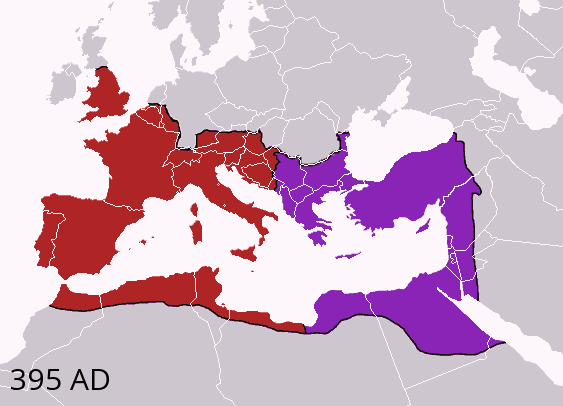
Theodosius I's Empire
Theodosius ( Latinized from the Greek "Θεοδόσιος", Theodosios, "given by god") is a given name. It may take the form Teodósio, Teodosie, Teodosije etc. Theodosia is a feminine version of the name. Emperors of ancient Rome and Byzantium *Theodosius I (347–395; "Theodosius the Great"), son of Count Theodosius *Theodosius II (408–450) *Theodosius III (715–717) *Theodosius (son of Maurice) (583/585–602), eldest son and co-emperor of the Byzantine emperor Maurice Popes of the Coptic Orthodox Church *Pope Theodosius I of Alexandria (d. 566) *Pope Theodosius II of Alexandria (d. 742) *Pope Theodosius III of Alexandria (d. 1300) Patriarchs of Alexandria *Patriarch Theodosius I of Alexandria (535–567) *Patriarch Theodosius II of Alexandria (12th century) Other clergy and monastics In chronological order: *Theodosius, bishop of Philadelphia in Lydia, deposed at the Council of Seleucia, 359 *Theodosius the Cenobiarch (c. 423–529), a monk, abbot, and sa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Honorius (emperor)
Honorius (9 September 384 – 15 August 423) was Roman emperor from 393 to 423. He was the younger son of emperor Theodosius I and his first wife Aelia Flaccilla. After the death of Theodosius, Honorius ruled the western half of the empire while his brother Arcadius ruled the eastern half. In 410, during Honorius's reign over the Western Roman Empire, Rome was sacked for the first time in almost 800 years. Even by the standards of the Western Empire, Honorius's reign was precarious and chaotic. His early reign was supported by his principal general, Stilicho, who was successively Honorius's guardian (during his childhood) and his father-in-law (after the emperor became an adult). Family Honorius was born to Emperor Theodosius I and Empress Aelia Flaccilla on 9 September 384 in Constantinople. He was brother to Arcadius and Pulcheria. In 386, his mother died, and in 387, Theodosius married Galla who had taken a temporary refuge in Thessaloniki with her family, including her ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Foederati
''Foederati'' (, singular: ''foederatus'' ) were peoples and cities bound by a treaty, known as ''foedus'', with Rome. During the Roman Republic, the term identified the ''socii'', but during the Roman Empire, it was used to describe foreign states, client kingdoms or barbarian tribes to which the empire provided benefits in exchange for military assistance. The term was also used, especially under the empire, for groups of "barbarian" mercenaries of various sizes who were typically allowed to settle within the empire. Roman Republic In the early Roman Republic, ''foederati'' were tribes that were bound by a treaty (''foedus'' ) to come to the defence of Rome but were neither Roman colonies nor beneficiaries of Roman citizenship (''civitas''). Members of the Latini tribe were considered blood allies, but the rest were federates or ''socii''. The friction between the treaty obligations without the corresponding benefits of Romanity led to the Social War between the Romans, with a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Visigoths
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is known as the Migration Period. The Visigoths emerged from earlier Gothic groups, including a large group of Thervingi, who had moved into the Roman Empire beginning in 376 and had played a major role in defeating the Romans at the Battle of Adrianople in 378. Relations between the Romans and the Visigoths varied, with the two groups making treaties when convenient, and warring with one another when not. Under their first leader, Alaric I, the Visigoths invaded Italy and sacked Rome in August 410. Afterwards, they began settling down, first in southern Gaul and eventually in Hispania, where they founded the Visigothic Kingdom and maintained a presence from the 5th to the 8th centuries AD. The Visigoths first settled in southern Gaul as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alaric I
Alaric I (; got, 𐌰𐌻𐌰𐍂𐌴𐌹𐌺𐍃, , "ruler of all"; c. 370 – 410 AD) was the first king of the Visigoths, from 395 to 410. He rose to leadership of the Goths who came to occupy Moesia—territory acquired a couple of decades earlier by a combined force of Goths and Alans after the Battle of Adrianople. Alaric began his career under the Gothic soldier Gainas and later joined the Roman army. Once an ally of Rome under the Roman emperor Theodosius, Alaric helped defeat the Franks and other allies of a would-be Roman usurper. Despite losing many thousands of his men, he received little recognition from Rome and left the Roman army disappointed. After the death of Theodosius and the disintegration of the Roman armies in 395, he is described as king of the Visigoths. As the leader of the only effective field force remaining in the Balkans, he sought Roman legitimacy, never quite achieving a position acceptable to himself or to the Roman authorities. He operated m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
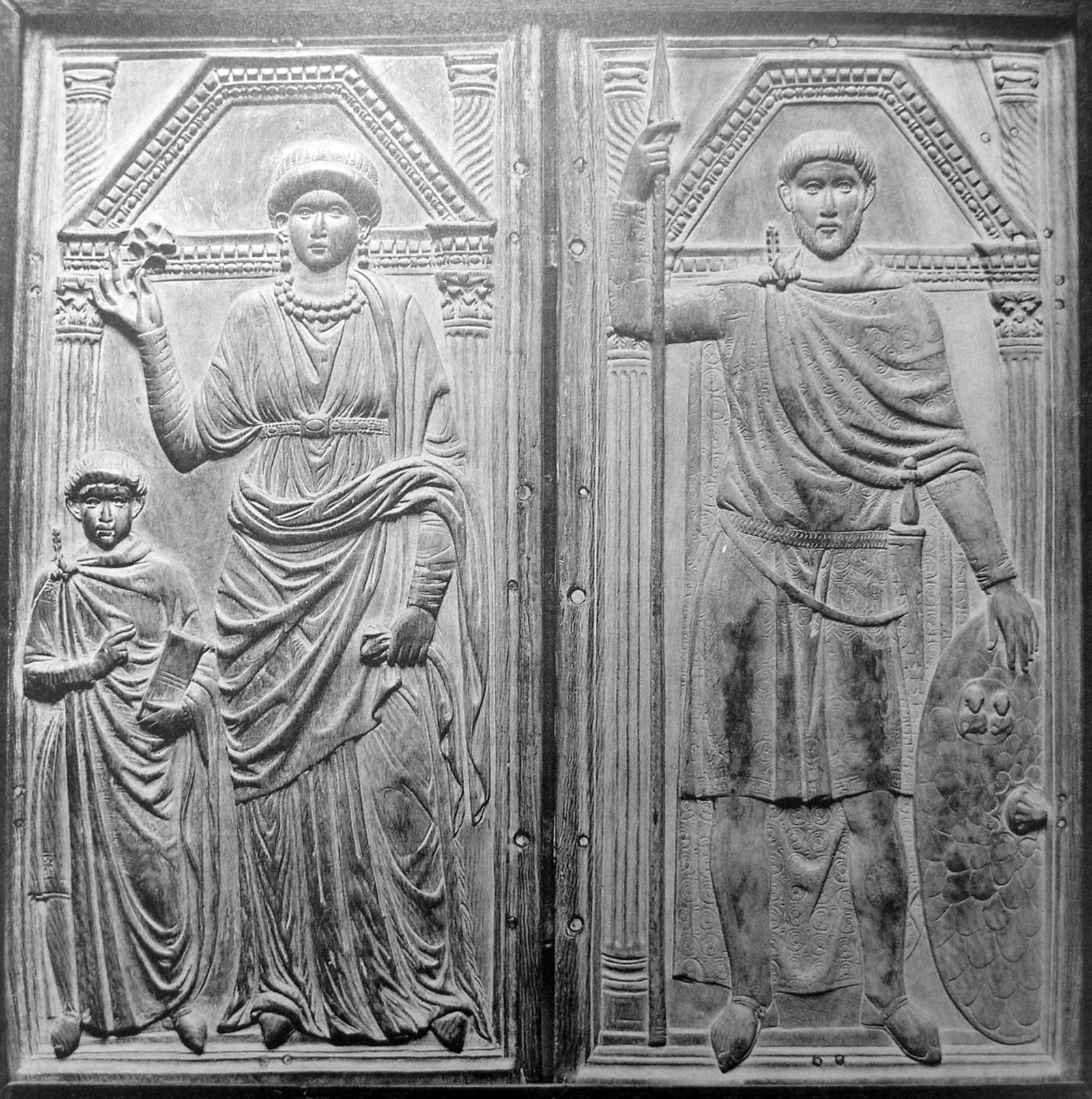
Serena (wife Of Stilicho)
Serena (died 409) was a Theodosian imperial woman, niece of Theodosius I. In 384, Theodosius arranged her marriage to a rising military officer, Stilicho.Stephen Williams & Gerard Friell, ''Theodosius: the Empire at Bay'', (Routledge, 1994): 42, 189 Stilicho's marriage to Serena ensured his loyalty to the House of Theodosius in the years ahead. A resident at the court of her cousin, Honorius, she selected a bride for the court poet, Claudian, and took care of Honorius' half-sister, her cousin Galla Placidia. She and Stilicho had a son, Eucherius, and two daughters, Maria and Thermantia, successively the first and second wives of Honorius. According to the pagan historian Zosimus, Serena took a necklace from a statue of Rhea Silvia and placed it on her own neck, however this was later dismissed; Serena was not a pagan and did not associate with them. Stilicho was executed on Honorius' orders in 408. During the siege of Rome by the Visigoths The Visigoths (; la, Visigoth ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stilicho
Flavius Stilicho (; c. 359 – 22 August 408) was a military commander in the Roman army who, for a time, became the most powerful man in the Western Roman Empire. He was of Vandal origins and married to Serena, the niece of emperor Theodosius I. He became guardian for the underage Honorius. After nine years of struggle against barbarian and Roman enemies, political and military disasters finally allowed his enemies in the court of Honorius to remove him from power. His fall culminated in his arrest and execution in 408. Origins and rise to power Stilicho (Στιλίχων ''Stilíchōn'' in Greek) was the son of a Vandal cavalry officer and a provincial woman of Roman birth. Despite his father's origins there is little to suggest that Stilicho considered himself anything other than a Roman, and his high rank within the empire suggests that he was probably not an Arian like many Germanic Christians but rather a Nicene Christian like his patron Theodosius I, who declared ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rome
, established_title = Founded , established_date = 753 BC , founder = King Romulus (legendary) , image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg , map_caption = The territory of the ''comune'' (''Roma Capitale'', in red) inside the Metropolitan City of Rome (''Città Metropolitana di Roma'', in yellow). The white spot in the centre is Vatican City. , pushpin_map = Italy#Europe , pushpin_map_caption = Location within Italy##Location within Europe , pushpin_relief = yes , coordinates = , coor_pinpoint = , subdivision_type = Country , subdivision_name = Italy , subdivision_type2 = Region , subdivision_name2 = Lazio , subdivision_type3 = Metropolitan city , subdivision_name3 = Rome Capital , government_footnotes= , government_type = Strong Mayor–Council , leader_title2 = Legislature , leader_name2 = Capitoline Assemb ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Galla Placidia
Galla Placidia (388–89/392–93 – 27 November 450), daughter of the Roman emperor Theodosius I, was a mother, tutor, and advisor to emperor Valentinian III, and a major force in Roman politics for most of her life. She was List of Visigothic queens, queen consort to Ataulf, king of the Visigoths from 414 until his death in 415, briefly empress consort to Constantius III in 421, and managed the government administration as a regent during the early reign of Valentinian III, until her death. Family Placidia was the daughter of Theodosius I and his second wife, Galla (wife of Theodosius I), Galla, who was herself daughter of Valentinian I and his second wife, Justina (empress), Justina. Galla Placidia's date of birth is not recorded, but she must have been born either in the period 388-89 or 392–93. Between these dates, her father was in Italy following his campaign against the usurper Magnus Maximus, while her mother remained in Constantinople. A surviving letter from Bisho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Praetorian Prefect Of The East
The praetorian prefecture of the East, or of the Orient ( la, praefectura praetorio Orientis, el, ἐπαρχότης/ὑπαρχία τῶν πραιτωρίων τῆς ἀνατολῆς) was one of four large praetorian prefectures into which the Late Roman Empire was divided. As it comprised the larger part of the Eastern Roman Empire, and its seat was at Constantinople, the praetorian prefect was the second most powerful man in the East, after the Emperor, in essence serving as his first minister. Structure The Prefecture was established after the death of Constantine the Great in 337, when the empire was split up among his sons and Constantius II received the rule of the East, with a praetorian prefect as his chief aide. The part allotted to Constantius encompassed four (later five) dioceses, each in turn comprising several provinces. The authority of the prefecture stretched from the Eastern Balkans, grouped into the Diocese of Thrace, to Asia Minor, divided into the d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rufinus (consul)
Flavius Rufinus ( el, Φλάβιος Ῥουφῖνος; – 27 November 395) was a 4th-century East Roman statesman of Aquitanian extraction who served as Praetorian prefect of the East for the emperor Theodosius I, as well as for his son Arcadius, under whom Rufinus exercised significant influence in the state affairs. He was the subject of the verse invective ''In Rufinum'' by the western court poet Claudian. Life Tall and always in movement, he is described as acute, ambitious, greedy and without principles, but a rigorous Christian. His difficulty with the Greek language is recorded by the sources, as well as his Aquitanian origin. In 388 he was appointed ''magister officiorum''. In 392 he served as Roman consul and in that same year he was appointed as Praetorian prefect of the East. Upon his appointment, he retained the responsibilities of the ''magister officiorum''. In order to become prefect, Rufinus is said to have persuaded the emperor that Eutolmius Tatianus, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flavius Bauto
Flavius Bauto (died c. 385) was a Romanised Frank who served as a ''magister militum'' of the Roman Empire and imperial advisor under Valentinian II. Biography When the usurper Magnus Maximus invaded Italy in an attempt to replace Valentinian II, Bauto led military defence against him. According to bishop Ambrose, Maximus accused Bauto of attacking him with barbarian troops and intending to establish a puppet emperor in the figure of Valentinian II to acquire sovereignty for himself. In matters of religion, Bauto was likely a Christian. He and Rumoridus, who was pagan, were present before Valentinian II when Ambrose successfully convinced the emperor against Quintus Aurelius Symmachus' proposal to restore the pagan Altar of Victory, which had been earlier removed from the Senate of Rome. Afterwards, the two men went along with Valentinian II's decision. He became a consul in 385 but died soon after, likely of natural causes. Afterwards, his daughter Aelia Eudoxia resided in the h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)

