|
387th Infantry Division (Wehrmacht)
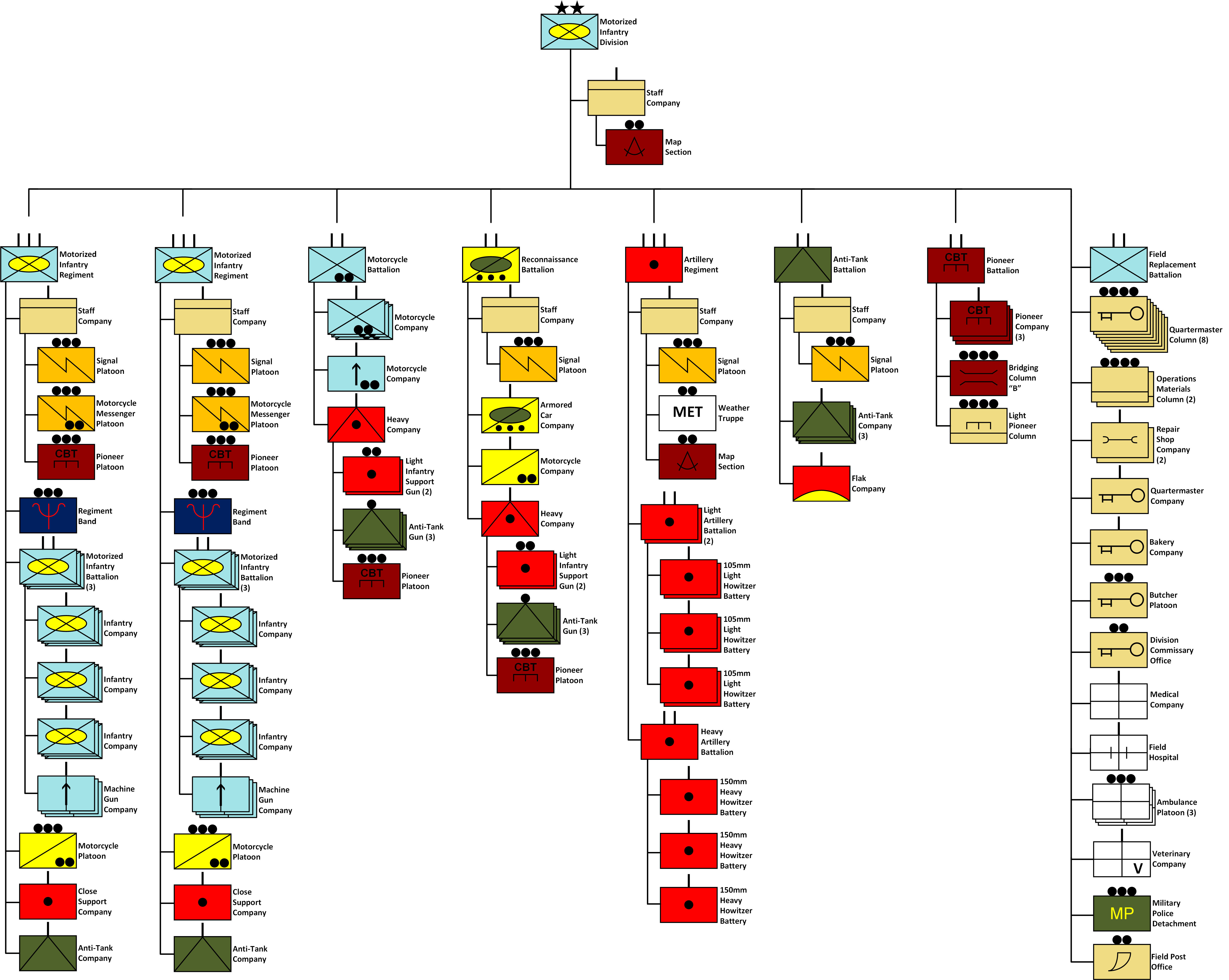
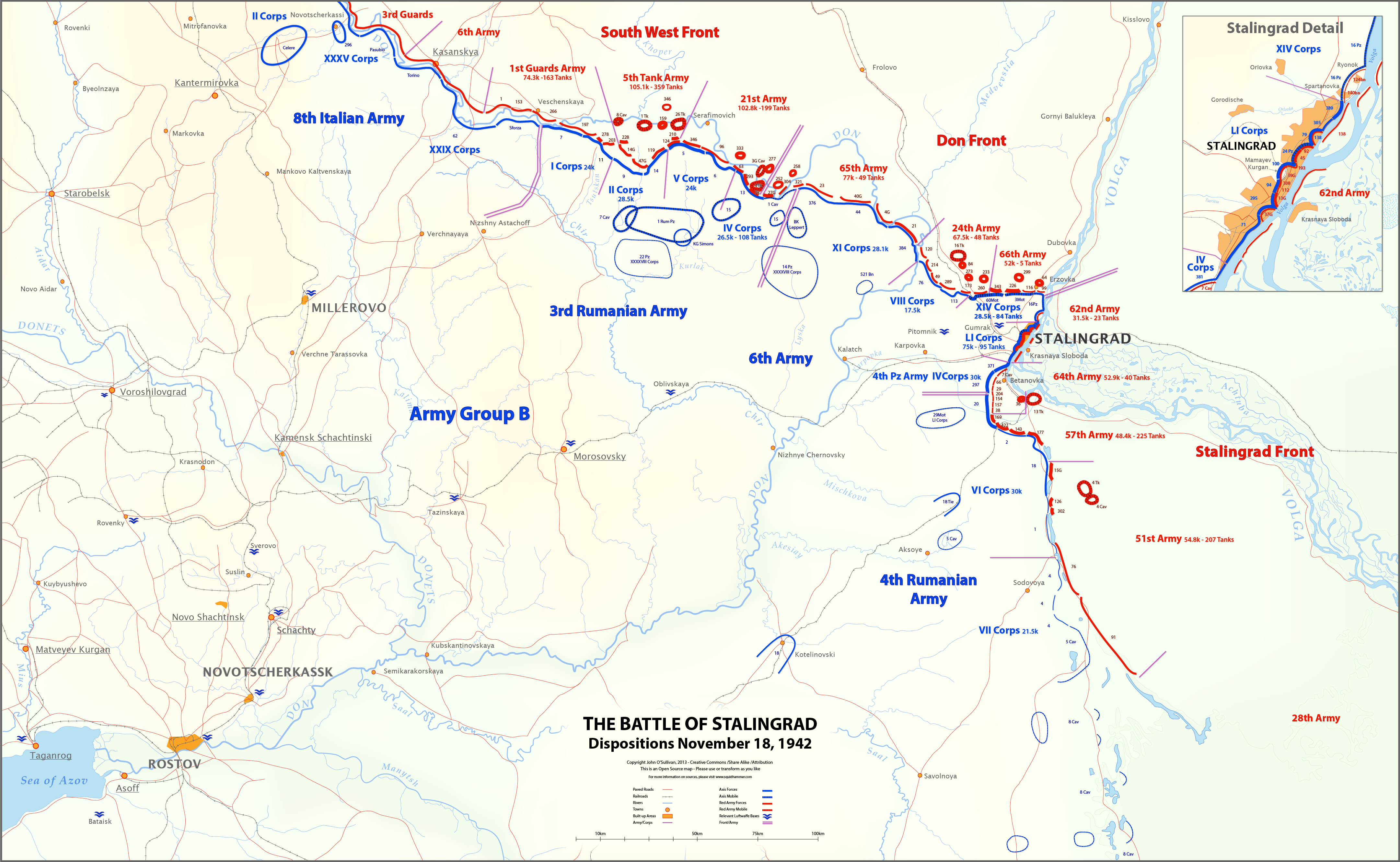
The 387th Infantry Division (german: 387. Infanterie-Division) was an infantry division of the German Army during the Second World War, active from 1942 to 1944. It saw active service on the Eastern Front and was destroyed in fighting in Romania in August 1944. Operational history The 387th Infantry Division was formed in Austria on 1 February 1942 under the command of ''Generalleutnant'' Arno Jahr. The division nominally fell within the responsibility of Wehrkreis VII. At its core were three infantry regiments, one each from Stuttgart, Munich and Salzburg. Dispatched to Russia, the division was soon engaged in the fighting in the southern area of the Eastern Front with Army Group South. From April to June 1942, prior to the commencement of Case Blue, it was active around Kursk. The division was then involved in the Battle of Voronezh. Attached to the Hungarian 2nd Army it fought in the battles around the Don Bend when the Soviet Army launched Operation Uranus and its sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German Army (Wehrmacht)
The German Army (, "army") is the land component of the armed forces of Federal Republic of Germany, Germany. The present-day German Army was founded in 1955 as part of the newly formed West German ''Bundeswehr'' together with the German Navy, ''Marine'' (German Navy) and the German Air Force, ''Luftwaffe'' (German Air Force). , the German Army had a strength of 62,766 soldiers. History Overview A German army equipped, organized, and trained following a single doctrine and permanently unified under one command in 1871 during the unification of Germany under the leadership of Prussia. From 1871 to 1919, the title ''German Army (German Empire), Deutsches Heer'' (German Army) was the official name of the German land forces. Following the German defeat in World War I and the end of the German Empire, the main army was dissolved. From 1921 to 1935 the name of the German land forces was the ''Reichswehr, Reichsheer'' (Army of the Empire) and from 1935 to 1945 the name ''German Army (We ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wehrkreis VII
The military districts, also known in some English-language publications by their German name as Wehrkreise (singular: ''Wehrkreis''), were administrative territorial units in Nazi Germany before and during World War II. The task of military districts was the organization and the handling of reinforcements and resupplies for local military units. The Replacement Army (''Ersatzheer'') managed the districts. Responsibilities such as training, conscription, supply, and equipment were (at least partially) entrusted to the Ersatzheer. History On 30 September 1919, much of the Imperial German Army was dissolved. The Reichswehr (of the Weimar Republic) took its place, and four commands of the type '' Reichswehrgruppenkommando'' were created, as well as seven ''Wehrkreiskommando'' commands, each assigned to one of the seven initial Wehrkreise of the Weimar Republic (numbered I through VII). The ''Reichswehrgruppenkommandos'' (which combined under them several military units across W ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Military Units And Formations Established In 1942
A military, also known collectively as armed forces, is a heavily armed, highly organized force primarily intended for warfare. It is typically authorized and maintained by a sovereign state, with its members identifiable by their distinct military uniform. It may consist of one or more military branches such as an army, navy, air force, space force, marines, or coast guard. The main task of the military is usually defined as defence of the state and its interests against external armed threats. In broad usage, the terms ''armed forces'' and ''military'' are often treated as synonymous, although in technical usage a distinction is sometimes made in which a country's armed forces may include both its military and other paramilitary forces. There are various forms of irregular military forces, not belonging to a recognized state; though they share many attributes with regular military forces, they are less often referred to as simply ''military''. A nation's military may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of German Divisions In World War II
This article lists divisions of the Wehrmacht (German Armed Forces) and Waffen-SS active during World War II, including divisions of the Heer (army), Luftwaffe (air force), and the Kriegsmarine (navy). Upgrades and reorganizations are shown only to identify the variant names for what is notionally a single unit; other upgrades and reorganizations are deferred to the individual articles. Due to the scope of this list, pre-war changes are not shown. Most of these divisions trained in Berlin, which is also where new military technology was kept and tested. German unit designations These designations are normally not translated and used in the German form in the unit name or description. ;''Bodenständige'': A static unit. Normally assigned to units who were deficient in transport and unable to move their own artillery. Many of these were divisions that had been mauled on the Eastern Front and were sent west to serve as coastal defence garrisons until sufficient resources were avail ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erwin Menny
Erwin Menny (18 August 1893 – 6 December 1949) was a German general (Generalleutnant) in the Heer during World War II who commanded several divisions. He was a recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross of Nazi Germany. He was taken prisoner with his 84th Infantry Division in the Falaise Pocket on 21 August 1944. Awards and decorations * Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross on 26 December 1941 as ''Oberst ''Oberst'' () is a senior field officer rank in several German-speaking and Scandinavian countries, equivalent to colonel. It is currently used by both the ground and air forces of Austria, Germany, Switzerland, Denmark, and Norway. The Swedish ...'' and commander of 15. Schützen-BrigadeFellgiebel 2000, p. 252. See also * * * * References Citations Bibliography * {{DEFAULTSORT:Menny, Erwin 1893 births 1949 deaths German Army personnel of World War I German prisoners of war in World War II held by the United States Lieutenant general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brigadier General
Brigadier general or Brigade general is a military rank used in many countries. It is the lowest ranking general officer in some countries. The rank is usually above a colonel, and below a major general or divisional general. When appointed to a field command, a brigadier general is typically in command of a brigade consisting of around 4,000 troops (four battalions). Variants Brigadier general Brigadier general (Brig. Gen.) is a military rank used in many countries. It is the lowest ranking general officer in some countries, usually sitting between the ranks of colonel and major general. When appointed to a field command, a brigadier general is typically in command of a brigade consisting of around 4,000 troops (four battalions). In some countries, this rank is given the name of ''brigadier'', which is usually equivalent to ''brigadier general'' in the armies of nations that use the rank. The rank can be traced back to the militaries of Europe where a "brigadier general ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
98th Infantry Division (Wehrmacht)
The 98th Infantry Division (german: 98. Infanterie-Division) was created on 18 September 1939 in Grafenwöhr. It was destroyed on the Crimea in May 1944 and reformed on 5 June 1944. Commanding officers * Generalleutnant Erich Schröck, 1 September 1939 – 11 April 1940 * Generalleutnant Herbert Stimmel, 11 April 1940 – 10 June 1940 * Generalleutnant Erich Schröck, 10 June 1940 – 31 December 1941 * General der Infanterie Martin Gareis, 31 December 1941 – 1 February 1944 * Generalleutnant Alfred-Hermann Reinhardt, 1 February 1944 – 11 April 1945 * Generalmajor Otto Schiel Otto is a masculine German given name and a surname. It originates as an Old High German short form (variants ''Audo'', ''Odo'', ''Udo'') of Germanic names beginning in ''aud-'', an element meaning "wealth, prosperity". The name is recorded fro ..., 11 April 1945 – 8 May 1945 References ;Citations ;Bibliography Military units and formations established in 1939 0*098 1939 establishmen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
258th Infantry Division (Wehrmacht)
The 258th Infantry Division was an infantry unit of the German Army in World War II. Combat History After formation, the division was moved to southern Poland, where it became the Army Group reserve of Army Group South. At the end of the Polish campaign, the division remained as part of the occupation forces in Poland in December 1939 and moved to the Saarbrücken area, where it remained on the defensive, even during the initial phase of Operation Red, the attack on France.Werner Haupt, Die deutschen Infanterie-Divisionen, p140-141 On 14 June 1940 the Division attacked the Maginot Line and after successfully broke through and advanced in the direction of Nancy. Committed from the opening phases of operation Barbarossa, the 258th division participated in the early encirclement battles at Bialstock, and during the battle of Smolensk was committed to a defensive role, first of the Army Group Center's southern flank, south of Mogilev, and later, after Guderian's wheel to the south ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
385th Infantry Division (Wehrmacht)
The 385th Infantry Division, (German: ''385. Infanterie-Division'') also known as a "Rheingold" Division, was created on 10 January 1942 in Fallingbostel. The division was composed of replacement troops from military districts VI, X and XI. From April 16, 1942, the 385th Infantry Division moved to the Roslavl area and fought in the front lines at the Fomino area. The division was annihilated near the Don River during the Battle of Stalingrad in early 1943 while subordinated to the 8th Italian Army. It was disbanded in the period from February to March 1943 and its survivors joined the 387th Infantry Division. Commanding officers *General der Infanterie Karl Eibl __NOTOC__ Karl Eibl (23 July 1891 – 21 January 1943) was an Austrian general in the Wehrmacht of Nazi Germany during World War II. He was a recipient of the Knight's Cross of the Iron Cross with Oak Leaves and Swords. He also served in World Wa ..., 7 January 1942 – 18 December 1942 (KIA) *Generalmajor Eberhard ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Uranus
Operation Uranus (russian: Опера́ция «Ура́н», Operatsiya "Uran") was the codename of the Soviet Red Army's 19–23 November 1942 strategic operation on the Eastern Front of World War II which led to the encirclement of Axis forces in the vicinity of Stalingrad: the German Sixth Army, the Third and Fourth Romanian armies, and portions of the German Fourth Panzer Army. The Red Army carried out the operation at roughly the midpoint of the five-month long Battle of Stalingrad, aiming to destroy German forces in and around Stalingrad. Planning for Operation Uranus had commenced in September 1942, and developed simultaneously with plans to envelop and destroy German Army Group Center (Operation Mars) and German forces in the Caucasus. Due to the length of the front lines created by the German 1942 summer offensive, which had aimed at taking the Caucasus oil fields and the city of Stalingrad, German and other Axis forces were over-extended. The German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Don River, Russia
The Don ( rus, Дон, p=don) is the fifth-longest river in Europe. Flowing from Central Russia to the Sea of Azov in Southern Russia, it is one of Russia's largest rivers and played an important role for traders from the Byzantine Empire. Its basin is between the Dnieper basin to the west, the lower Volga basin immediately to the east, and the Oka basin (tributary of the Volga) to the north. Native to much of the basin were Slavic nomads. The Don rises in the town of Novomoskovsk southeast of Tula (in turn south of Moscow), and flows 1,870 kilometres to the Sea of Azov. The river's upper half ribbles (meanders subtly) south; however, its lower half consists of a great eastern curve, including Voronezh, making its final stretch, an estuary, run west south-west. The main city on the river is Rostov-on-Don. Its main tributary is the Seversky Donets, centred on the mid-eastern end of Ukraine, thus the other country in the overall basin. To the east of a series of three ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Army (Hungary)
The Hungarian Second Army (''Második Magyar Hadsereg'') was one of three field armies (''hadsereg'') raised by the Kingdom of Hungary (''Magyar Királyság'') which saw action during World War II. All three armies were formed on March 1, 1940. The Second Army was the best-equipped Hungarian formation at the beginning of the war, but was virtually eliminated as an effective fighting unit by overwhelming Soviet force during the Battle of Stalingrad, suffering 84% casualties. Towards the end of the war, a reformed Second Army fought more successfully at the Battle of Debrecen, but, during the ensuing Siege of Budapest, it was destroyed completely and absorbed into the Hungarian Third Army. Commanders The Hungarian Second Army had four commanders from March 1, 1940 - November 13, 1944: * Colonel General Vitéz Gusztáv Jány (vitéz Jány Gusztáv) (March 1, 1940 - August 5, 1943; awarded the German Knight's Cross on March 31, 1943) * Colonel General Géza Lakatos (Lakatos Géz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |