|
3-manifolds
In mathematics, a 3-manifold is a topological space that locally looks like a three-dimensional Euclidean space. A 3-manifold can be thought of as a possible shape of the universe. Just as a sphere looks like a plane (a tangent plane) to a small and close enough observer, all 3-manifolds look like our universe does to a small enough observer. This is made more precise in the definition below. Principles Definition A topological space M is a 3-manifold if it is a second-countable Hausdorff space and if every point in M has a neighbourhood that is homeomorphic to Euclidean 3-space. Mathematical theory of 3-manifolds The topological, piecewise-linear, and smooth categories are all equivalent in three dimensions, so little distinction is made in whether we are dealing with say, topological 3-manifolds, or smooth 3-manifolds. Phenomena in three dimensions can be strikingly different from phenomena in other dimensions, and so there is a prevalence of very specialized techniques t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
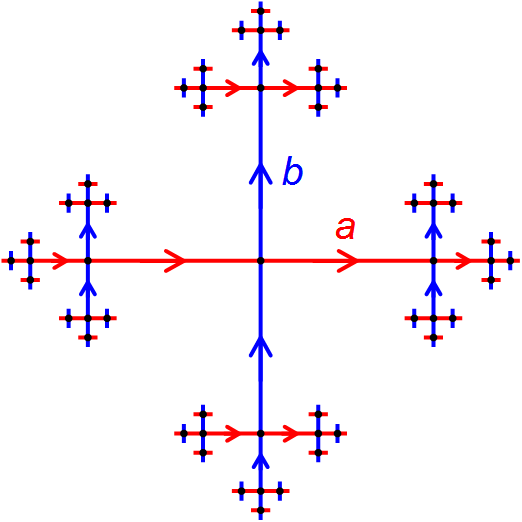
3-Manifold 3-Torus
In mathematics, a 3-manifold is a topological space that locally looks like a three-dimensional Euclidean space. A 3-manifold can be thought of as a possible shape of the universe. Just as a sphere looks like a plane (geometry), plane (a tangent plane) to a small and close enough observer, all 3-manifolds look like our universe does to a small enough observer. This is made more precise in the definition below. Principles Definition A topological space M is a 3-manifold if it is a second-countable Hausdorff space and if every point in M has a neighbourhood (mathematics), neighbourhood that is homeomorphic to Euclidean 3-space. Mathematical theory of 3-manifolds The topological, Piecewise linear manifold, piecewise-linear, and smooth categories are all equivalent in three dimensions, so little distinction is made in whether we are dealing with say, topological 3-manifolds, or smooth 3-manifolds. Phenomena in three dimensions can be strikingly different from phenomena in other dim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Floer Homology
In mathematics, Floer homology is a tool for studying symplectic geometry and low-dimensional topology. Floer homology is an invariant that arises as an infinite-dimensional analogue of finite-dimensional Morse homology. Andreas Floer introduced the first version of Floer homology, now called symplectic Floer homology, in his 1988 proof of the Arnold conjecture in symplectic geometry. Floer also developed a closely related theory for Lagrangian submanifolds of a symplectic manifold. A third construction, also due to Floer, associates homology groups to closed three-dimensional manifolds using the Yang–Mills functional. These constructions and their descendants play a fundamental role in current investigations into the topology of symplectic and contact manifolds as well as (smooth) three- and four-dimensional manifolds. Floer homology is typically defined by associating to the object of interest an infinite-dimensional manifold and a real valued function on it. In the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Thurston
William Paul Thurston (October 30, 1946August 21, 2012) was an American mathematician. He was a pioneer in the field of low-dimensional topology and was awarded the Fields Medal in 1982 for his contributions to the study of 3-manifolds. Thurston was a professor of mathematics at Princeton University, University of California, Davis, and Cornell University. He was also a director of the Mathematical Sciences Research Institute. Early life and education William Thurston was born in Washington, D.C., to Margaret Thurston (), a seamstress, and Paul Thurston, an aeronautical engineer. William Thurston suffered from congenital strabismus as a child, causing issues with depth perception. His mother worked with him as a toddler to reconstruct three-dimensional images from two-dimensional ones. He received his bachelor's degree from New College in 1967 as part of its inaugural class. For his undergraduate thesis, he developed an intuitionist foundation for topology. Following th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Haken Manifold
In mathematics, a Haken manifold is a compact, P²-irreducible 3-manifold that is sufficiently large, meaning that it contains a properly embedded two-sided incompressible surface. Sometimes one considers only orientable Haken manifolds, in which case a Haken manifold is a compact, orientable, irreducible 3-manifold that contains an orientable, incompressible surface. A 3-manifold finitely covered by a Haken manifold is said to be virtually Haken. The Virtually Haken conjecture asserts that every compact, irreducible 3-manifold with infinite fundamental group is virtually Haken. This conjecture was proven by Ian Agol. Haken manifolds were introduced by . proved that Haken manifolds have a hierarchy, where they can be split up into 3-balls along incompressible surfaces. Haken also showed that there was a finite procedure to find an incompressible surface if the 3-manifold had one. gave an algorithm to determine if a 3-manifold was Haken. Normal surfaces are ubiquitous ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heegaard Splitting
In the mathematical field of geometric topology, a Heegaard splitting () is a decomposition of a compact oriented 3-manifold that results from dividing it into two handlebodies. Definitions Let ''V'' and ''W'' be handlebodies of genus ''g'', and let ƒ be an orientation reversing homeomorphism from the boundary of ''V'' to the boundary of ''W''. By gluing ''V'' to ''W'' along ƒ we obtain the compact oriented 3-manifold : M = V \cup_f W. Every closed, orientable three-manifold may be so obtained; this follows from deep results on the triangulability of three-manifolds due to Moise. This contrasts strongly with higher-dimensional manifolds which need not admit smooth or piecewise linear structures. Assuming smoothness the existence of a Heegaard splitting also follows from the work of Smale about handle decompositions from Morse theory. The decomposition of ''M'' into two handlebodies is called a Heegaard splitting, and their common boundary ''H'' is called the Heegaard su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Incompressible Surface
In mathematics, an incompressible surface is a surface properly embedded in a 3-manifold, which, in intuitive terms, is a "nontrivial" surface that cannot be simplified. In non-mathematical terms, the surface of a suitcase is compressible, because we could cut the handle and shrink it into the surface. But a Conway sphere (a sphere with four holes) is incompressible, because there are essential parts of a knot or link both inside and out, so there is no way to move the entire knot or link to one side of the punctured sphere. The mathematical definition is as follows. There are two cases to consider. A sphere is incompressible if both inside and outside the sphere there are some obstructions that prevent the sphere from shrinking to a point and also prevent the sphere from expanding to encompass all of space. A surface other than a sphere is incompressible if any disk with its boundary on the surface spans a disk in the surface."An Introduction to Knot Theory", W. B. Raymond Lickoris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Low-dimensional Topology
In mathematics, low-dimensional topology is the branch of topology that studies manifolds, or more generally topological spaces, of four or fewer dimensions. Representative topics are the theory of 3-manifolds and 4-manifolds, knot theory, and braid groups. This can be regarded as a part of geometric topology. It may also be used to refer to the study of topological spaces of dimension 1, though this is more typically considered part of continuum theory. History A number of advances starting in the 1960s had the effect of emphasising low dimensions in topology. The solution by Stephen Smale, in 1961, of the Poincaré conjecture in five or more dimensions made dimensions three and four seem the hardest; and indeed they required new methods, while the freedom of higher dimensions meant that questions could be reduced to computational methods available in surgery theory. Thurston's geometrization conjecture, formulated in the late 1970s, offered a framework that suggeste ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knot Theory
In topology, knot theory is the study of knot (mathematics), mathematical knots. While inspired by knots which appear in daily life, such as those in shoelaces and rope, a mathematical knot differs in that the ends are joined so it cannot be undone, the simplest knot being a ring (or "unknot"). In mathematical language, a knot is an embedding of a circle in 3-dimensional Euclidean space, \mathbb^3. Two mathematical knots are equivalent if one can be transformed into the other via a deformation of \mathbb^3 upon itself (known as an ambient isotopy); these transformations correspond to manipulations of a knotted string that do not involve cutting it or passing it through itself. Knots can be described in various ways. Using different description methods, there may be more than one description of the same knot. For example, a common method of describing a knot is a planar diagram called a knot diagram, in which any knot can be drawn in many different ways. Therefore, a fundamental p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geometric Group Theory
Geometric group theory is an area in mathematics devoted to the study of finitely generated groups via exploring the connections between algebraic properties of such groups and topological and geometric properties of spaces on which these groups can act non-trivially (that is, when the groups in question are realized as geometric symmetries or continuous transformations of some spaces). Another important idea in geometric group theory is to consider finitely generated groups themselves as geometric objects. This is usually done by studying the Cayley graphs of groups, which, in addition to the graph structure, are endowed with the structure of a metric space, given by the so-called word metric. Geometric group theory, as a distinct area, is relatively new, and became a clearly identifiable branch of mathematics in the late 1980s and early 1990s. Geometric group theory closely interacts with low-dimensional topology, hyperbolic geometry, algebraic topology, computational group ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
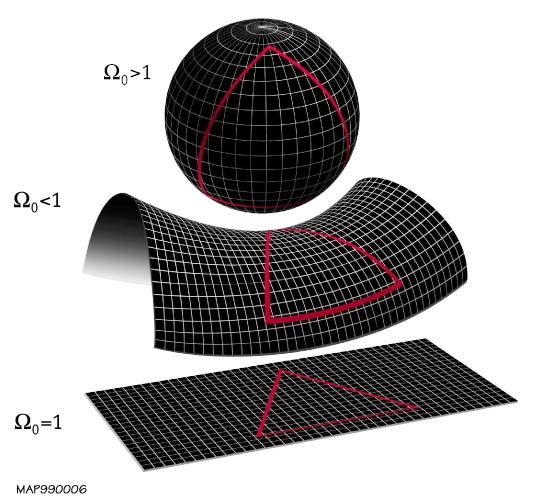
Shape Of The Universe
In physical cosmology, the shape of the universe refers to both its local and global geometry. Local geometry is defined primarily by its curvature, while the global geometry is characterised by its topology (which itself is constrained by curvature). General relativity explains how spatial curvature (local geometry) is constrained by gravity. The global topology of the universe cannot be deduced from measurements of curvature inferred from observations within the family of homogeneous general relativistic models alone, due to the existence of locally indistinguishable spaces with varying global topological characteristics. For example; a multiply connected space like a 3 torus has everywhere zero curvature but is finite in extent, whereas a flat simply connected space is infinite in extent (such as Euclidean space). Current observational evidence ( WMAP, BOOMERanG, and Planck for example) imply that the observable universe is spatially flat to within a 0.4% margin of error o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second-countable
In topology, a second-countable space, also called a completely separable space, is a topological space whose topology has a countable base. More explicitly, a topological space T is second-countable if there exists some countable collection \mathcal = \_^ of open subsets of T such that any open subset of T can be written as a union of elements of some subfamily of \mathcal. A second-countable space is said to satisfy the second axiom of countability. Like other countability axioms, the property of being second-countable restricts the number of open subsets that a space can have. Many "well-behaved" spaces in mathematics are second-countable. For example, Euclidean space (R''n'') with its usual topology is second-countable. Although the usual base of open balls is uncountable, one can restrict this to the collection of all open balls with rational radii and whose centers have rational coordinates. This restricted collection is countable and still forms a basis. Properties ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gauge Theory
In physics, a gauge theory is a type of field theory in which the Lagrangian, and hence the dynamics of the system itself, does not change under local transformations according to certain smooth families of operations (Lie groups). Formally, the Lagrangian is invariant under these transformations. The term "gauge" refers to any specific mathematical formalism to regulate redundant degrees of freedom in the Lagrangian of a physical system. The transformations between possible gauges, called gauge transformations, form a Lie group—referred to as the '' symmetry group'' or the gauge group of the theory. Associated with any Lie group is the Lie algebra of group generators. For each group generator there necessarily arises a corresponding field (usually a vector field) called the gauge field. Gauge fields are included in the Lagrangian to ensure its invariance under the local group transformations (called gauge invariance). When such a theory is quantized, the quanta of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |