|
2023 North Indian Ocean Cyclone Season
The 2023 North Indian Ocean cyclone season is an ongoing event in the annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation. The North Indian Ocean cyclone season has no official bounds, but cyclones tend to form between April and December, with the peak from May to November. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northern Indian Ocean. The scope of this article is limited to the Indian Ocean in the Northern Hemisphere, east of the Horn of Africa and west of the Malay Peninsula. There are two main seas in the North Indian Ocean — the Arabian Sea to the west of the Indian subcontinent, abbreviated ''ARB'' by the India Meteorological Department (IMD); and the Bay of Bengal to the east, abbreviated ''BOB'' by the IMD. The official Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre in this basin is the India Meteorological Department (IMD), while the Joint Typhoon Warning Center releases unofficial advisories for interest. On ave ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclone Mocha
Extremely Severe Cyclonic Storm Mocha () was a powerful and deadly tropical cyclone in the North Indian Ocean which affected Myanmar and parts of Bangladesh in May 2023. The second depression and the first cyclonic storm of the 2023 North Indian Ocean cyclone season, Mocha originated from a low-pressure area that was first noted by the India Meteorological Department (IMD) on 8 May. After consolidating into a depression, the storm tracked slowly north-northwestward over the Bay of Bengal, and reached Tropical_cyclone_scales#North_Indian_Ocean, extremely severe cyclonic storm intensity. After undergoing an eyewall replacement cycle, Mocha rapidly strengthened, peaking at Category 5-equivalent intensity on 14 May with winds of , tying with Cyclone Fani as the strongest storm on record in the North Indian Ocean in terms of 1-minute sustained winds. Mocha slightly weakened before making landfall, and its conditions quickly became unfavorable. Mocha rapidly weakened once inland and di ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2019 North Indian Ocean Cyclone Season
The 2019 North Indian Ocean cyclone season was the most active North Indian Ocean cyclone season on record, in terms of cyclonic storms, however the 1992 season was more active according to the Joint Typhoon Warning Center. The season featured 12 depressions, 11 deep depressions, 8 cyclonic storms, 6 severe cyclonic storms, 6 very severe cyclonic storms, 3 extremely severe cyclonic storms, and 1 super cyclonic storm, Kyarr, the first since Cyclone Gonu in 2007. Additionally, it was also the third-costliest season recorded in the North Indian Ocean, only behind the 2020 and 2008 seasons. The season's first named storm, Pabuk, entered the basin on January 4, becoming the earliest-forming cyclonic storm of the North Indian Ocean on record. The second cyclone of the season, Cyclone Fani, was the strongest tropical cyclone in the Bay of Bengal by 3-minute maximum sustained wind speed and minimum barometric pressure since the 1999 Odisha cyclone, while being equal in terms of maximum ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Atmospheric Convection
Atmospheric convection is the result of a parcel-environment instability, or temperature difference layer in the atmosphere. Different lapse rates within dry and moist air masses lead to instability. Mixing of air during the day which expands the height of the planetary boundary layer leads to increased winds, cumulus cloud development, and decreased surface dew points. Moist convection leads to thunderstorm development, which is often responsible for severe weather throughout the world. Special threats from thunderstorms include hail, downbursts, and tornadoes. Overview There are a few general archetypes of atmospheric instability that are used to explain convection (or lack thereof). A necessary (but not sufficient) condition for convection is that the environmental lapse rate (the rate of decrease of temperature with height) is steeper than the lapse rate experienced by a rising parcel of air. When this condition is met, upward-displaced air parcels can become buoyant and th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
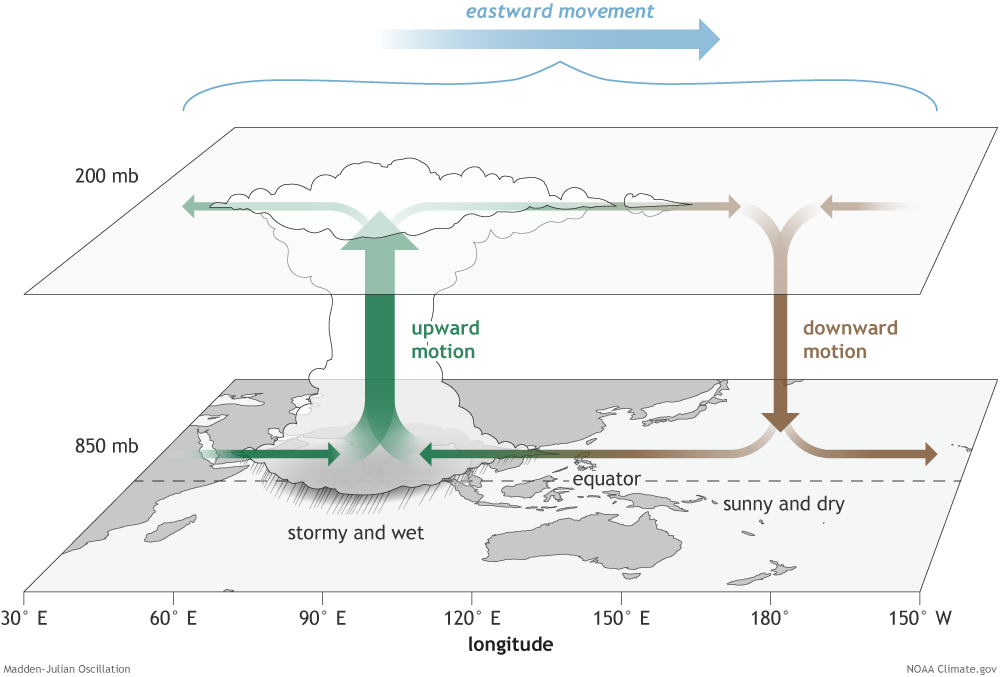
Madden–Julian Oscillation
The Madden–Julian oscillation (MJO) is the largest element of the intraseasonal (30- to 90-day) variability in the tropical atmosphere. It was discovered in 1971 by Roland Madden and Paul Julian of the American National Center for Atmospheric Research (NCAR). It is a large-scale coupling between atmospheric circulation and tropical deep atmospheric convection. Unlike a standing pattern like the El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO), the Madden–Julian oscillation is a traveling pattern that propagates eastward, at approximately , through the atmosphere above the warm parts of the Indian and Pacific oceans. This overall circulation pattern manifests itself most clearly as anomalous rainfall. The Madden–Julian oscillation is characterized by an eastward progression of large regions of both enhanced and suppressed tropical rainfall, observed mainly over the Indian and Pacific Ocean. The anomalous rainfall is usually first evident over the western Indian Ocean, and remains evi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of Mannar
The Gulf of Mannar ( ) is a large shallow bay forming part of the Laccadive Sea in the Indian Ocean with an average depth of .Gulf of Mannar (SE India) Sea-Seek. It lies between the southeastern tip of and the west coast of , in the region. The chain of low islands and reefs known as (aka Adam's Bridge), which includes [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert
A Tropical Cyclone Formation Alert (TCFA) is a bulletin released by the U.S. Navy-operated Joint Typhoon Warning Center in Honolulu, Hawaii or the Fleet Weather Center in Norfolk, Virginia, warning of the possibility of a tropical cyclone forming from a tropical disturbance that has been monitored. Such alerts are generally always issued when it is fairly certain that a tropical cyclone will form and are not always released before cyclone genesis, particularly if the cyclone appears suddenly. The TCFA consists of several different checks that are performed by the on-duty meteorologist of the system and its surroundings. If the condition being checked is met, a certain number of points are given to the system. Parts of the TCFA Section 1 The first section of the TCFA contains information on the area of the alert as well as the estimated center of the circulation. The estimated maximum sustained winds are provided as well. Section 2 The second section generally contains more specif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1989 North Indian Ocean Cyclone Season
The 1989 North Indian Ocean cyclone season was a below-average season in annual cycle of tropical cyclone formation. The season has no official bounds but cyclones tend to form between April and December. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northern Indian Ocean. There are two main seas in the North Indian Ocean—the Bay of Bengal to the east of the Indian subcontinent and the Arabian Sea to the west of India. The official Regional Specialized Meteorological Centre in this basin is the India Meteorological Department (IMD), while the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) releases unofficial advisories. An average of five tropical cyclones form in the North Indian Ocean every season with peaks in May and November. Cyclones occurring between the meridians 45°E and 100°E are included in the season by the IMD. Throughout the season, the IMD monitored ten depressions, three of which became cyclonic storms. The stronges ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Accumulated Cyclone Energy
Accumulated cyclone energy (ACE) is a metric used by various agencies to express the energy released by a tropical cyclone during its lifetime. It is calculating by summing the square of a tropical cyclone's maximum sustained winds, measured every six hours. The resulting total can be divided by 10,000 to make it more manageable, or added to other totals in order to work out a total for a particular group of storms. The calculation was originally created by William Gray and his associates at Colorado State University as the Hurricane Destruction Potential index, which took the square of each hurricane's maximum sustained winds above every six hours. This index was adjusted by the United States National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration in 2000 to include all tropical cyclones, with winds above and renamed accumulated cyclone energy. The index has since been used by various other agencies to calculate a storm's accumulated cyclone energy, including the Australian Bureau of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bangladesh
Bangladesh (}, ), officially the People's Republic of Bangladesh, is a country in South Asia. It is the eighth-most populous country in the world, with a population exceeding 165 million people in an area of . Bangladesh is among the most densely populated countries in the world, and shares land borders with India to the west, north, and east, and Myanmar to the southeast; to the south it has a coastline along the Bay of Bengal. It is narrowly separated from Bhutan and Nepal by the Siliguri Corridor; and from China by the Indian state of Sikkim in the north. Dhaka, the capital and largest city, is the nation's political, financial and cultural centre. Chittagong, the second-largest city, is the busiest port on the Bay of Bengal. The official language is Bengali, one of the easternmost branches of the Indo-European language family. Bangladesh forms the sovereign part of the historic and ethnolinguistic region of Bengal, which was divided during the Partition of India in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yunnan
Yunnan , () is a landlocked Provinces of China, province in Southwest China, the southwest of the People's Republic of China. The province spans approximately and has a population of 48.3 million (as of 2018). The capital of the province is Kunming. The province borders the Chinese provinces of Guizhou, Sichuan, autonomous regions of Guangxi, and Tibet Autonomous Region, Tibet as well as Southeast Asian countries: Vietnam, Laos, and Myanmar. Yunnan is China's fourth least developed province based on disposable income per capita in 2014. Yunnan is situated in a mountainous area, with high elevations in the northwest and low elevations in the southeast. Most of the population lives in the eastern part of the province. In the west, the altitude can vary from the mountain peaks to river valleys by as much as . Yunnan is rich in natural resources and has the largest diversity of plant life in China. Of the approximately 30,000 species of Vascular plant, higher plants in China, Yu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces Of China
The provincial level administrative divisions () are the highest-level administrative divisions of China. There are 34 such divisions claimed by the People's Republic of China, classified as 23 provinces (), five autonomous regions, four municipalities and two special administrative regions. The political status of Taiwan Province along with a small fraction of Fujian Province remain in dispute; those are under separate rule by the Republic of China, which is usually referred to as "Taiwan". Every province on Mainland China (including the island province of Hainan) has a Chinese Communist Party (CCP) provincial committee (), headed by a secretary (). The Committee Secretary is effectively in charge of the province, rather than the governor of the provincial government. The same arrangement exists for the autonomous regions and municipalities. Types of provincial level divisions Province The government of each standard province () is nominally led by a provincial committe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's most populous country, with a population exceeding 1.4 billion, slightly ahead of India. China spans the equivalent of five time zones and borders fourteen countries by land, the most of any country in the world, tied with Russia. Covering an area of approximately , it is the world's third largest country by total land area. The country consists of 22 provinces, five autonomous regions, four municipalities, and two Special Administrative Regions (Hong Kong and Macau). The national capital is Beijing, and the most populous city and financial center is Shanghai. Modern Chinese trace their origins to a cradle of civilization in the fertile basin of the Yellow River in the North China Plain. The semi-legendary Xia dynasty in the 21st century BCE and the well-attested Shang and Zhou dynasties developed a bureaucratic political system to serve hereditary monarchies, or dyna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |