|
2020 In Mammal Paleontology
This mammalogy, paleomammalogy list records new fossil mammal taxa that were binomial nomenclature, described during the year 2020, as well as notes other significant paleomammalogy discoveries and events which occurred during the year. Afrotherians Proboscidea Proboscidea research * A study on dietary differences among Pleistocene proboscideans in North America, and their implications for the knowledge of the causes of extinction of ''Cuvieronius'', is published by Smith & DeSantis (2020). * Evidence of dietary resource partitioning among three proboscidean taxa from the early Pliocene locality of Langebaanweg in South Africa (''Anancus capensis'', ''Mammuthus subplanifrons'' and ''Loxodonta cookei'') is presented by Groenewald ''et al.'' (2020). * A study on the morphology of teeth and mandible of ''"Serridentinus" gobiensis'' and ''Miomastodon tongxinensis'', as well as on the phylogenetic affinities of these taxa, is published by Wang, Zhang & Li (2020), who reestablish ''Mioma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mammalogy
In zoology, mammalogy is the study of mammals – a class of vertebrates with characteristics such as homeothermic metabolism, fur, four-chambered hearts, and complex nervous system In biology, the nervous system is the highly complex part of an animal that coordinates its actions and sensory information by transmitting signals to and from different parts of its body. The nervous system detects environmental changes th ...s. Mammalogy has also been known as "mastology," "theriology," and "therology." The archive of number of mammals on earth is constantly growing, but is currently set at 6,495 different mammal species including recently extinct. There are 5,416 living mammals identified on earth and roughly 1,251 have been newly discovered since 2006. The major branches of mammalogy include natural history, taxonomy and systematics, anatomy and physiology, ethology, ecology, and management and control. The approximate salary of a mammalogist varies from $20,000 to $60,000 a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phylogeography
Phylogeography is the study of the historical processes that may be responsible for the past to present geographic distributions of genealogical lineages. This is accomplished by considering the geographic distribution of individuals in light of genetics, particularly population genetics. This term was introduced to describe geographically structured genetic signals within and among species. An explicit focus on a species' biogeography/biogeographical past sets phylogeography apart from classical population genetics and phylogenetics. Past events that can be inferred include population expansion, population bottlenecks, vicariance, dispersal, and migration. Recently developed approaches integrating coalescent theory or the genealogical history of alleles and distributional information can more accurately address the relative roles of these different historical forces in shaping current patterns. Development The term phylogeography was first used by John Avise in his 1987 work '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ocepeia
''Ocepeia'' is an extinct genus of afrotherian mammal that lived in present-day Morocco during the middle Paleocene epoch, approximately 60 million years ago. First named and described in 2001, the type species is ''O. daouiensis'' from the Selandian stage of Morocco's Ouled Abdoun Basin. A second, larger species, ''O. grandis'', is known from the Thanetian, a slightly younger stage in the same area. In life, the two species are estimated to have weighed about and , respectively, and are believed to have been specialized folivore, leaf-eaters. The fossil skulls of ''Ocepeia'' are the oldest known afrotherian skulls, and the best-known of any Paleocene mammal in Africa. Loosely grouped with the archaic ungulates known as Condylarth, "condylarths", ''Ocepeia'' shares several features with primitive Paenungulata, paenungulates (a group including elephants, hyraxes, and extinct relatives), but some analyses suggest it is more closely related to Afroinsectiphilia (a group containing ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Embrithopoda
Embrithopoda ("heavy-footed") is an order of extinct mammals known from Asia, Africa and Eastern Europe. Most of the embrithopod genera are known exclusively from jaws and teeth dated from the late Paleocene to the late Eocene; however, the order is best known from its terminal member, the elephantine ''Arsinoitherium''. Description While embrithopods bore a superficial resemblance to rhinoceroses, their horns had bony cores covered in keratinized skin. Not all embrithopods possessed horns, either. Despite their appearance, they have been regarded as related to elephants, not perissodactyls. As tethytheres, the Embrithopoda have been believed to be part of the clade Afrotheria. However, a study of the basal arsinoitheriid, ''Palaeoamasia'', suggests that embrithopods are not tethytheres or even paenungulates, and that they need to be better sampled in an analysis of eutherian relationships to clarify if they are even afrotherians.[Erdal et al.'s inclusion of Embrithopoda in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
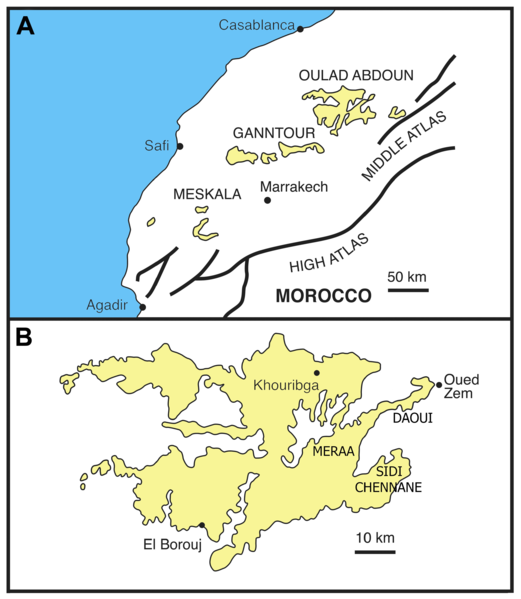
Ouled Abdoun Basin
The Oulad Abdoun Basin (also known as the Ouled Abdoun Basin or Khouribga Basin) is a phosphate sedimentary basin located in Morocco, near the city of Khouribga. It is the largest in Morocco, comprising 44% of Morocco's phosphate reserves, and at least 26.8 billion tons of phosphate. It is also known as an important site for vertebrate fossils, with deposits ranging from the Late Cretaceous (Cenomanian-Turonian) to the Eocene epoch (Ypresian), a period of about 25 million years. Geography The Oulad Abdoun is located west of the Atlas Mountains, near the city of Khouribga. The Oulad Abdoun phosphate deposits encompass some , an area of . The Oulad Abdoun is the largest and northernmost of Morocco's major phosphate basins, which from northeast to southwest, include the Ganntour, Meskala, and Oued Eddahab (Laayoune-Baa) basins. Paleobiota The Oulad Abdoun Basin stretches from late Cretaceous to the Eocene, and contains abundant marine vertebrate fossils, including sharks, bo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ypresian
In the geologic timescale the Ypresian is the oldest age (geology), age or lowest stage (stratigraphy), stratigraphic stage of the Eocene. It spans the time between , is preceded by the Thanetian Age (part of the Paleocene) and is followed by the Eocene Lutetian Age. The Ypresian is consistent with the lower Eocene. Events The Ypresian Age begins during the throes of the Paleocene–Eocene Thermal Maximum (PETM). The Fur Formation in Denmark, the Messel shales in Germany, the Oise amber of France and Cambay amber of India are of this age. The Eocene Okanagan Highlands are an uplands subtropical to temperate series of lakes from the Ypresian. Stratigraphic definition The Ypresian Stage was introduced in scientific literature by Belgium, Belgian geologist André Hubert Dumont in 1850. The Ypresian is named after the Flanders, Flemish city of Ypres in Belgium (spelled ''Ieper'' in Dutch). The definitions of the original stage were totally different from the modern ones. The Ypresi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eocene
The Eocene ( ) Epoch is a geological epoch (geology), epoch that lasted from about 56 to 33.9 million years ago (mya). It is the second epoch of the Paleogene Period (geology), Period in the modern Cenozoic Era (geology), Era. The name ''Eocene'' comes from the Ancient Greek (''ēṓs'', "dawn") and (''kainós'', "new") and refers to the "dawn" of modern ('new') fauna that appeared during the epoch. The Eocene spans the time from the end of the Paleocene Epoch to the beginning of the Oligocene Epoch. The start of the Eocene is marked by a brief period in which the concentration of the carbon isotope Carbon-13, 13C in the atmosphere was exceptionally low in comparison with the more common isotope Carbon-12, 12C. The end is set at a major extinction event called the ''Grande Coupure'' (the "Great Break" in continuity) or the Eocene–Oligocene extinction event, which may be related to the impact of one or more large bolides in Popigai impact structure, Siberia and in what is now ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metaxytherium Lovisati
''Metaxytherium'' is an extinct genus of dugong that lived from the Oligocene until the end of the Pliocene. Fossil remains have been found in Africa, Europe, North America and South America. Generally marine seagrass specialists, they inhabited the warm and shallow waters of the Paratethys, Mediterranean, Caribbean Sea and Pacific coastline. American species of ''Metaxytherium'' are considered to be ancestral to the North Pacific family Hydrodamalinae, which includes the giant Steller's Sea Cow. Discovery and naming The first remains of ''Metaxytherium'' were described in 1822 by Anselme-Gaëtan Demarest as a species of Hippo, ''H. medius'' before the genus name ''Metaxytherium'' was coined in 1840 by De Christol. Although the type species was initially designated to be ''M. cuvieri'', later publications argued that the two species are synonymous and ''M. medium'' thus holds precedence. The grammatical changes of the species name were made to match the rules of the Int ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metaxytherium
''Metaxytherium'' is an extinct genus of dugong that lived from the Oligocene until the end of the Pliocene. Fossil remains have been found in Africa, Europe, North America and South America. Generally marine seagrass specialists, they inhabited the warm and shallow waters of the Paratethys, Mediterranean, Caribbean Sea and Pacific coastline. American species of ''Metaxytherium'' are considered to be ancestral to the North Pacific family Hydrodamalinae, which includes the giant Steller's Sea Cow. Discovery and naming The first remains of ''Metaxytherium'' were described in 1822 by Anselme-Gaëtan Demarest as a species of Hippo, ''H. medius'' before the genus name ''Metaxytherium'' was coined in 1840 by De Christol. Although the type species was initially designated to be ''M. cuvieri'', later publications argued that the two species are synonymous and ''M. medium'' thus holds precedence. The grammatical changes of the species name were made to match the rules of the Internat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; it, Sardegna, label=Italian, Corsican and Tabarchino ; sc, Sardigna , sdc, Sardhigna; french: Sardaigne; sdn, Saldigna; ca, Sardenya, label=Algherese and Catalan) is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, and one of the 20 regions of Italy. It is located west of the Italian Peninsula, north of Tunisia and immediately south of the French island of Corsica. It is one of the five Italian regions with some degree of domestic autonomy being granted by a special statute. Its official name, Autonomous Region of Sardinia, is bilingual in Italian and Sardinian: / . It is divided into four provinces and a metropolitan city. The capital of the region of Sardinia — and its largest city — is Cagliari. Sardinia's indigenous language and Algherese Catalan are referred to by both the regional and national law as two of Italy's twelve officially recognized linguistic minorities, albeit gravely endangered, while the regional law provides ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sobrarbesiren Cardieli
''Sobrarbesiren'' (meaning "siren from Sobrarbe") is a genus of extinct sirenian that lived in the Eocene, about 47 million years ago. The type and only species is ''S. cardieli'', known from a multitude of specimens from the Spanish Pyrenees. ''Sobrarbesiren'' was a medium-sized animal, long and still retaining both pairs of limbs. Although initially thought to be amphibious, later studies instead suggest that they would have been fully aquatic and been selective sea grass browsers. Unlike modern dugongs and manatees, they likely lacked a tail fluke, although it would have appeared horizontally flattened. Discovery and naming ''Sobrarbesiren'' was discovered in the Castejón de Sobrarbe-41 locality (Sobrarbe Formation) in the Spanish Pyrenees, specifically the Huesca province. The locality dates to the Lutetian stage of the Eocene and preserved 300 individual siren fossils thought to belong to at least six individuals of different growth stages. The holotype specimen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.png)


.jpg)
