|
2D Z-transform
The 2D Z-transform, similar to the Z-transform, is used in Multidimensional signal processing to relate a two-dimensional discrete-time signal to the complex frequency domain in which the 2D surface in 4D space that the Fourier Transform lies on is known as the unit surface or unit bicircle.Siamak Khatibi, “Multidimensional Signal Processing: Lecture 11”, BLEKINGE INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY, PowerPoint Presentation. The 2D Z-transform is defined by :X_z(z_1,z_2) = \sum_^\sum_^ x(n_1,n_2) z_1^ z_2^ where n_1,n_2 are integers and z_1,z_2 are represented by the complex numbers: :z_1 = Ae^ = A(\cos+j\sin)\, :z_2 = Be^ = B(\cos+j\sin)\, The 2D Z-transform is a generalized version of the 2D Fourier transform. It converges for a much wider class of sequences, and is a helpful tool in allowing one to draw conclusions on system characteristics such as BIBO stability. It is also used to determine the connection between the input and output of a linear Shift-invariant system, such as mani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Z-transform
In mathematics and signal processing, the Z-transform converts a discrete-time signal, which is a sequence of real or complex numbers, into a complex frequency-domain (z-domain or z-plane) representation. It can be considered as a discrete-time equivalent of the Laplace transform (s-domain). This similarity is explored in the theory of time-scale calculus. Whereas the continuous-time Fourier transform is evaluated on the Laplace s-domain's imaginary line, the discrete-time Fourier transform is evaluated over the unit circle of the z-domain. What is roughly the s-domain's left half-plane, is now the inside of the complex unit circle; what is the z-domain's outside of the unit circle, roughly corresponds to the right half-plane of the s-domain. One of the means of designing digital filters is to take analog designs, subject them to a bilinear transform which maps them from the s-domain to the z-domain, and then produce the digital filter by inspection, manipulation, or nume ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
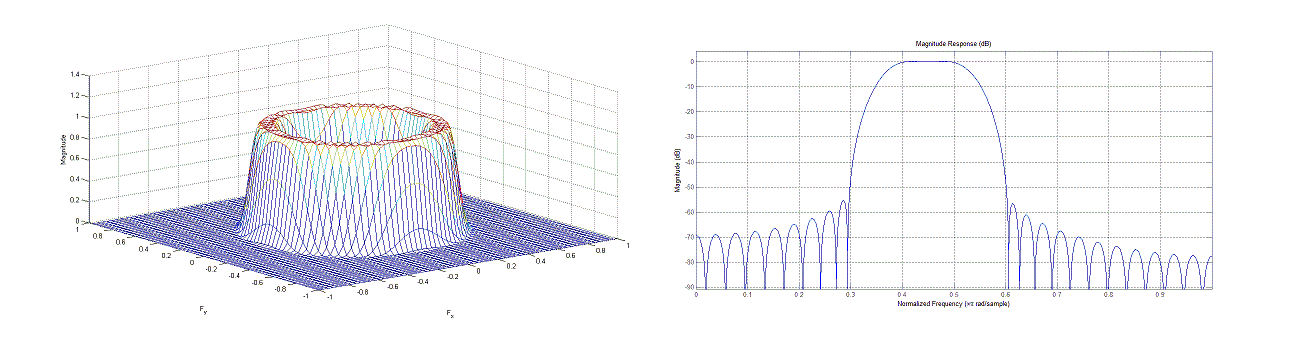
Multidimensional Signal Processing
In signal processing, multidimensional signal processing covers all signal processing done using multidimensional signals and systems. While multidimensional signal processing is a subset of signal processing, it is unique in the sense that it deals specifically with data that can only be adequately detailed using more than one dimension. In m-D digital signal processing, useful data is sampled in more than one dimension. Examples of this are image processing and multi-sensor radar detection. Both of these examples use multiple sensors to sample signals and form images based on the manipulation of these multiple signals. Processing in multi-dimension (m-D) requires more complex algorithms, compared to the 1-D case, to handle calculations such as the fast Fourier transform due to more degrees of freedom.D. Dudgeon and R. Mersereau, Multidimensional Digital Signal Processing, Prentice-Hall, First Edition, pp. 2, 1983. In some cases, m-D signals and systems can be simplified into single ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Discrete-time Signal
In mathematical dynamics, discrete time and continuous time are two alternative frameworks within which variables that evolve over time are modeled. Discrete time Discrete time views values of variables as occurring at distinct, separate "points in time", or equivalently as being unchanged throughout each non-zero region of time ("time period")—that is, time is viewed as a discrete variable. Thus a non-time variable jumps from one value to another as time moves from one time period to the next. This view of time corresponds to a digital clock that gives a fixed reading of 10:37 for a while, and then jumps to a new fixed reading of 10:38, etc. In this framework, each variable of interest is measured once at each time period. The number of measurements between any two time periods is finite. Measurements are typically made at sequential integer values of the variable "time". A discrete signal or discrete-time signal is a time series consisting of a sequence of quantities. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fourier Transform
A Fourier transform (FT) is a mathematical transform that decomposes functions into frequency components, which are represented by the output of the transform as a function of frequency. Most commonly functions of time or space are transformed, which will output a function depending on temporal frequency or spatial frequency respectively. That process is also called ''analysis''. An example application would be decomposing the waveform of a musical chord into terms of the intensity of its constituent pitches. The term ''Fourier transform'' refers to both the frequency domain representation and the mathematical operation that associates the frequency domain representation to a function of space or time. The Fourier transform of a function is a complex-valued function representing the complex sinusoids that comprise the original function. For each frequency, the magnitude ( absolute value) of the complex value represents the amplitude of a constituent complex sinusoid wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BIBO Stability
In signal processing, specifically control theory, bounded-input, bounded-output (BIBO) stability is a form of stability for signals and systems that take inputs. If a system is BIBO stable, then the output will be bounded for every input to the system that is bounded. A signal is bounded if there is a finite value B > 0 such that the signal magnitude never exceeds B, that is :For discrete-time signals: \ , y \leq B \quad \text n \in \mathbb. :For continuous-time signals: \ , y(t), \leq B \quad \text t \in \mathbb. Time-domain condition for linear time-invariant systems Continuous-time necessary and sufficient condition For a continuous time linear time-invariant (LTI) system, the condition for BIBO stability is that the impulse response, h(t) , be absolutely integrable, i.e., its L1 norm exists. : \int_^\infty \left, h(t)\\,\mathordt = \, h \, _1 and the output \ y /math> is :\ y = h * x /math> where * denotes convolution. Then it follows by the definition of conv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shift-invariant System
A shift invariant system is the discrete equivalent of a time-invariant system, defined such that if y(n) is the response of the system to x(n), then y(n-k) is the response of the system to x(n-k).Oppenheim, Schafer, 12 That is, in a shift-invariant system the contemporaneous response of the output variable to a given value of the input variable does not depend on when the input occurs; time shifts are irrelevant in this regard. Applications Because digital systems need not be causal, some operations can be implemented in the digital domain that cannot be implemented using discrete analog components. Digital filters that require finite numbers of future values can be implemented while the analog counterparts cannot. Notes References * Oppenheim, Schafer, ''Digital Signal Processing'', Prentice Hall, 1975, See also * LTI system theory LTI can refer to: * '' LTI – Lingua Tertii Imperii'', a book by Victor Klemperer * Language Technologies Institute, a division of Carnegie Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transfer Function
In engineering, a transfer function (also known as system function or network function) of a system, sub-system, or component is a mathematical function that theoretically models the system's output for each possible input. They are widely used in electronics and control systems. In some simple cases, this function is a two-dimensional graph of an independent scalar input versus the dependent scalar output, called a transfer curve or characteristic curve. Transfer functions for components are used to design and analyze systems assembled from components, particularly using the block diagram technique, in electronics and control theory. The dimensions and units of the transfer function model the output response of the device for a range of possible inputs. For example, the transfer function of a two-port electronic circuit like an amplifier might be a two-dimensional graph of the scalar voltage at the output as a function of the scalar voltage applied to the input; the transfer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Annulus (mathematics)
In mathematics, an annulus (plural annuli or annuluses) is the region between two concentric circles. Informally, it is shaped like a ring or a hardware washer. The word "annulus" is borrowed from the Latin word ''anulus'' or ''annulus'' meaning 'little ring'. The adjectival form is annular (as in annular eclipse). The open annulus is topologically equivalent to both the open cylinder and the punctured plane. Area The area of an annulus is the difference in the areas of the larger circle of radius and the smaller one of radius : :A = \pi R^2 - \pi r^2 = \pi\left(R^2 - r^2\right). The area of an annulus is determined by the length of the longest line segment within the annulus, which is the chord tangent to the inner circle, in the accompanying diagram. That can be shown using the Pythagorean theorem since this line is tangent to the smaller circle and perpendicular to its radius at that point, so and are sides of a right-angled triangle with hypotenuse , and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reinhardt Domain
The theory of functions of several complex variables is the branch of mathematics dealing with complex-valued functions. The name of the field dealing with the properties of function of several complex variables is called several complex variables (and analytic space), that has become a common name for that whole field of study and Mathematics Subject Classification has, as a top-level heading. A function f:(z_1,z_2, \ldots, z_n) \rightarrow f(z_1,z_2, \ldots, z_n) is -tuples of complex numbers, classically studied on the complex coordinate space \Complex^n. As in complex analysis of functions of one variable, which is the case , the functions studied are ''holomorphic'' or ''complex analytic'' so that, locally, they are power series in the variables . Equivalently, they are locally uniform limits of polynomials; or locally square-integrable solutions to the -dimensional Cauchy–Riemann equations. For one complex variable, every domainThat is an open connected subset. (D \sub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Support (mathematics)
In mathematics, the support of a real-valued function f is the subset of the function domain containing the elements which are not mapped to zero. If the domain of f is a topological space, then the support of f is instead defined as the smallest closed set containing all points not mapped to zero. This concept is used very widely in mathematical analysis. Formulation Suppose that f : X \to \R is a real-valued function whose domain is an arbitrary set X. The of f, written \operatorname(f), is the set of points in X where f is non-zero: \operatorname(f) = \. The support of f is the smallest subset of X with the property that f is zero on the subset's complement. If f(x) = 0 for all but a finite number of points x \in X, then f is said to have . If the set X has an additional structure (for example, a topology), then the support of f is defined in an analogous way as the smallest subset of X of an appropriate type such that f vanishes in an appropriate sense on its compleme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wedge ROC
A wedge is a triangular shaped tool, and is a portable inclined plane, and one of the six simple machines. It can be used to separate two objects or portions of an object, lift up an object, or hold an object in place. It functions by converting a force applied to its blunt end into forces perpendicular (normal) to its inclined surfaces. The mechanical advantage of a wedge is given by the ratio of the length of its slope to its width..''McGraw-Hill Concise Encyclopedia of Science & Technology'', Third Ed., Sybil P. Parker, ed., McGraw-Hill, Inc., 1992, p. 2041. Although a short wedge with a wide angle may do a job faster, it requires more force than a long wedge with a narrow angle. The force is applied on a flat, broad surface. This energy is transported to the pointy, sharp end of the wedge, hence the force is transported. The wedge simply transports energy in the form of friction and collects it to the pointy end, consequently breaking the item. History Wedges have exi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |