Multidimensional Signal Processing on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In
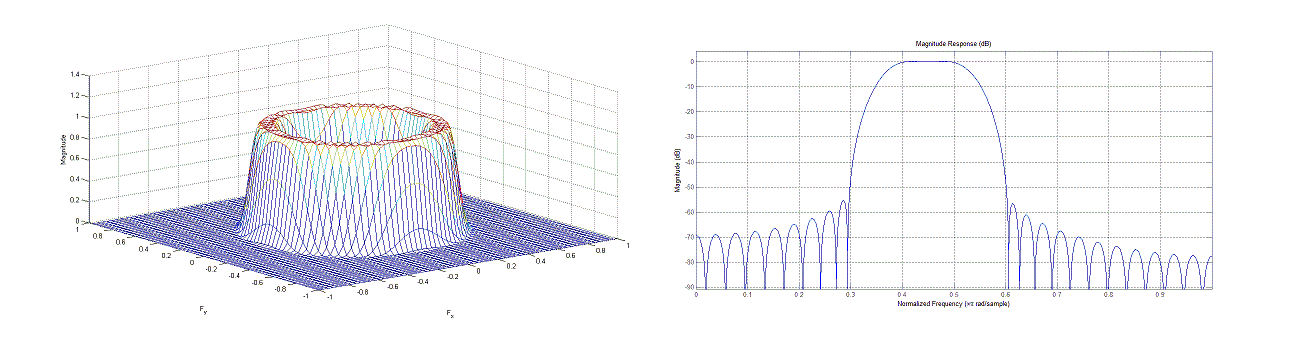 Filtering is an important part of any signal processing application. Similar to typical single dimension signal processing applications, there are varying degrees of complexity within filter design for a given system. M-D systems utilize
Filtering is an important part of any signal processing application. Similar to typical single dimension signal processing applications, there are varying degrees of complexity within filter design for a given system. M-D systems utilize
signal processing
Signal processing is an electrical engineering subfield that focuses on analyzing, modifying and synthesizing '' signals'', such as sound, images, and scientific measurements. Signal processing techniques are used to optimize transmissions, ...
, multidimensional signal processing covers all signal processing done using multidimensional signals and systems. While multidimensional signal processing is a subset of signal processing, it is unique in the sense that it deals specifically with data that can only be adequately detailed using more than one dimension. In m-D digital signal processing, useful data is sampled in more than one dimension. Examples of this are image processing
An image is a visual representation of something. It can be two-dimensional, three-dimensional, or somehow otherwise feed into the visual system to convey information. An image can be an artifact, such as a photograph or other two-dimension ...
and multi-sensor radar detection. Both of these examples use multiple sensors to sample signals and form images based on the manipulation of these multiple signals.
Processing in multi-dimension (m-D) requires more complex algorithms, compared to the 1-D case, to handle calculations such as the fast Fourier transform
A fast Fourier transform (FFT) is an algorithm that computes the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) of a sequence, or its inverse (IDFT). Fourier analysis converts a signal from its original domain (often time or space) to a representation in t ...
due to more degrees of freedom.D. Dudgeon and R. Mersereau, Multidimensional Digital Signal Processing, Prentice-Hall, First Edition, pp. 2, 1983. In some cases, m-D signals and systems can be simplified into single dimension signal processing methods, if the considered systems are separable.
Typically, multidimensional signal processing is directly associated with digital signal processing
Digital signal processing (DSP) is the use of digital processing, such as by computers or more specialized digital signal processors, to perform a wide variety of signal processing operations. The digital signals processed in this manner ar ...
because its complexity warrants the use of computer modelling and computation. A multidimensional signal is similar to a single dimensional signal as far as manipulations that can be performed, such as sampling, Fourier analysis, and filtering
Filter, filtering or filters may refer to:
Science and technology
Computing
* Filter (higher-order function), in functional programming
* Filter (software), a computer program to process a data stream
* Filter (video), a software component th ...
. The actual computations of these manipulations grow with the number of dimensions.
Sampling
Multidimensional sampling requires different analysis than typical 1-D sampling. Single dimension sampling is executed by selecting points along a continuous line and storing the values of this data stream. In the case of multidimensional sampling, the data is selected utilizing a lattice, which is a "pattern" based on the sampling vectors of the m-D data set.Mersereau, R.; Speake, T., "The processing of periodically sampled multidimensional signals," Acoustics, IEEE Transactions on Speech and Signal Processing, vol.31, no.1, pp.188-194, Feb 1983. These vectors can be single dimensional or multidimensional depending on the data and the application. Multidimensional sampling is similar to classical sampling as it must adhere to theNyquist–Shannon sampling theorem
The Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem is a theorem in the field of signal processing which serves as a fundamental bridge between continuous-time signals and discrete-time signals. It establishes a sufficient condition for a sample rate that per ...
. It is affected by aliasing
In signal processing and related disciplines, aliasing is an effect that causes different signals to become indistinguishable (or ''aliases'' of one another) when sampled. It also often refers to the distortion or artifact that results when ...
and considerations must be made for eventual Multidimensional Signal Reconstruction.
Fourier Analysis
A multidimensional signal can be represented in terms of sinusoidal components. This is typically done with a type ofFourier transform
A Fourier transform (FT) is a mathematical transform that decomposes functions into frequency components, which are represented by the output of the transform as a function of frequency. Most commonly functions of time or space are transformed, ...
. The m-D Fourier transform
A Fourier transform (FT) is a mathematical transform that decomposes functions into frequency components, which are represented by the output of the transform as a function of frequency. Most commonly functions of time or space are transformed, ...
transforms a signal from a signal domain representation to a frequency domain
In physics, electronics, control systems engineering, and statistics, the frequency domain refers to the analysis of mathematical functions or signals with respect to frequency, rather than time. Put simply, a time-domain graph shows how a ...
representation of the signal. In the case of digital processing, a discrete Fourier Transform (DFT) is utilized to transform a sampled signal domain representation into a frequency domain representation:
:
where ''X'' stands for the multidimensional discrete Fourier transform, ''x'' stands for the sampled time/space domain signal, ''m'' stands for the number of dimensions in the system, ''n'' are sample indices and ''k'' are frequency samples.D. Dudgeon and R. Mersereau, Multidimensional Digital Signal Processing, Prentice-Hall, First Edition, pp. 61,112, 1983.
Computational complexity is usually the main concern when implementing any Fourier transform. For multidimensional signals, the complexity can be reduced by a number of different methods. The computation may be simplified if there is independence
Independence is a condition of a person, nation, country, or state in which residents and population, or some portion thereof, exercise self-government, and usually sovereignty, over its territory. The opposite of independence is the s ...
between variables of the multidimensional signal. In general, fast Fourier transform
A fast Fourier transform (FFT) is an algorithm that computes the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) of a sequence, or its inverse (IDFT). Fourier analysis converts a signal from its original domain (often time or space) to a representation in t ...
s (FFTs), reduce the number of computations by a substantial factor. While there are a number of different implementations of this algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for performing ...
for m-D signals, two often used variations are the vector-radix FFT and the row-column FFT.
Filtering
 Filtering is an important part of any signal processing application. Similar to typical single dimension signal processing applications, there are varying degrees of complexity within filter design for a given system. M-D systems utilize
Filtering is an important part of any signal processing application. Similar to typical single dimension signal processing applications, there are varying degrees of complexity within filter design for a given system. M-D systems utilize digital filters
In signal processing, a digital filter is a system that performs mathematical operations on a sampled, discrete-time signal to reduce or enhance certain aspects of that signal. This is in contrast to the other major type of electronic filte ...
in many different applications. The actual implementation of these m-D filters can pose a design problem depending on whether the multidimensional polynomial is factorable. Typically, a prototype filter is designed in a single dimension and that filter is extrapolate
In mathematics, extrapolation is a type of estimation, beyond the original observation range, of the value of a variable on the basis of its relationship with another variable. It is similar to interpolation, which produces estimates between kno ...
d to m-D using a mapping function. One of the original mapping functions from 1-D to 2-D was the McClellan Transform.Mersereau, R.M.; Mecklenbrauker, W.; Quatieri, T., Jr., "McClellan transformations for two-dimensional digital filtering-Part I: Design," IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems, vol.23, no.7, pp.405-414, Jul 1976. Both FIR
Firs (''Abies'') are a genus of 48–56 species of evergreen coniferous trees in the family Pinaceae. They are found on mountains throughout much of North and Central America, Europe, Asia, and North Africa. The genus is most closely related to ...
and IIR filters can be transformed to m-D, depending on the application and the mapping function.
Applicable Fields
*Audio signal processing
Audio signal processing is a subfield of signal processing that is concerned with the electronic manipulation of audio signals. Audio signals are electronic representations of sound waves— longitudinal waves which travel through air, consist ...
* Image processing
An image is a visual representation of something. It can be two-dimensional, three-dimensional, or somehow otherwise feed into the visual system to convey information. An image can be an artifact, such as a photograph or other two-dimension ...
* Towed array sonar
A towed array sonar is a system of hydrophones towed behind a submarine or a surface ship on a cable. Trailing the hydrophones behind the vessel, on a cable that can be kilometers long, keeps the array's sensors away from the ship's own noise sou ...
* X-ray computed tomography
X-rays (or rarely, ''X-radiation'') are a form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. In many languages, it is referred to as Röntgen radiation, after the German scientist Wilhelm Conrad Röntgen, who discovered it in 1895 and named it ' ...
References
External links
*{{Commonscat-inline Signal processing