|
277th Rifle Division
The 277th Rifle Division () was an infantry division of the Soviet Union's Red Army and later the Soviet Army, formed twice. First formed in the summer of 1941, the division was destroyed in the Battle of Kiev during September of that year. Reformed in December 1941, the division fought in the Battle of Stalingrad, Operation Bagration, the Vistula–Oder Offensive, and the Soviet invasion of Manchuria. Serving in the Soviet Far East postwar, the division was renumbered in 1955. History First Formation The 277th began forming on 10 July 1941 at Dmitriyev, part of the Orel Military District. Its basic order of battle included the 850th, 852nd, and the 854th Rifle Regiments, as well as the 846th Artillery Regiment. The division was sent into combat while still incomplete and was transferred to the 21st Army's 67th Rifle Corps in the Bryansk Front (later the Central Front) while missing most of its heavy weapons and trucks in early August. The 277th held positions on the sout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen national republics; in practice, both its government and its economy were highly centralized until its final years. It was a one-party state governed by the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, with the city of Moscow serving as its capital as well as that of its largest and most populous republic: the Russian SFSR. Other major cities included Leningrad (Russian SFSR), Kiev (Ukrainian SSR), Minsk ( Byelorussian SSR), Tashkent (Uzbek SSR), Alma-Ata (Kazakh SSR), and Novosibirsk (Russian SFSR). It was the largest country in the world, covering over and spanning eleven time zones. The country's roots lay in the October Revolution of 1917, when the Bolsheviks, under the leadership of Vladimir Lenin, overthrew the Russian Provisional Government ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2nd Panzer Group
The 2nd Panzer Army (german: 2. Panzerarmee) was a German armoured formation during World War II, formed from the 2nd Panzer Group on October 5, 1941. Organisation Panzer Group Guderian (german: Panzergruppe Guderian) was formed on 5 June 1940 and named after its commander, general Heinz Guderian. In early June 1940, after reaching the English Channel following the breakthrough in the Ardennes, the ''Panzergruppe Guderian'' was formed from the XIX Army Corps, and thrust deep into France, cutting off the Maginot Line. In November 1940, it was upgraded into ''Panzergruppe 2''. The 2nd Panzer Group (german: Panzergruppe 2) was formed in November 1940 from Panzer Group Guderian. In October 1941 it was renamed the 2nd Panzer Army. Panzer Group 2 played a significant role in the early stages of the German invasion of the Soviet Union during Operation Barbarossa in 1941 when it was a constituent part of Army Group Centre. Operational history 2nd Panzer Group was part of the Army Grou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western Front (Soviet Union)
The Western Front was a front of the Red Army, one of the Red Army Fronts during World War II. The Western Front was created on 22 June 1941 from the Western Special Military District (which before July 1940 was known as Belorussian Special Military District). The first Front Commander was Dmitry Pavlov (continuing from his position as District Commander since June 1940). The western boundary of the Front in June 1941 was long, from the southern border of Lithuania to the Pripyat River and the town of Włodawa. It connected with the adjacent North-Western Front, which extended from the Lithuanian border to the Baltic Sea, and the Southwestern Front in Ukraine. Operational history Front dispositions 22 June 1941 The 1939 partition of Poland according to the Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact established a new western border with no permanent defense installations, and the army deployment within the Front created weak flanks. At the outbreak of war with Germany, the Western Special ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
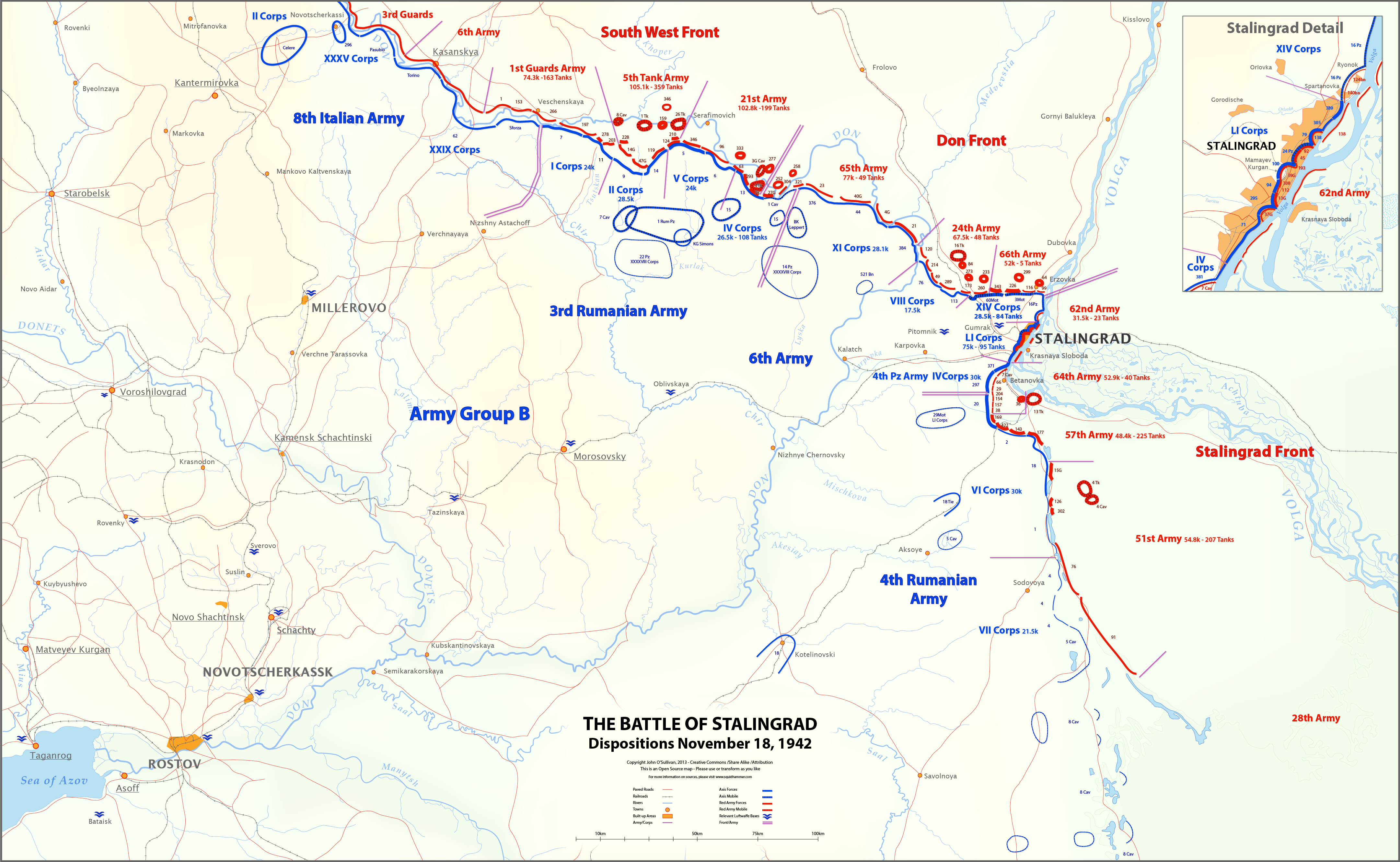
Operation Koltso
Operation Koltso (Operation Ring) was the last part of the Battle of Stalingrad. It resulted in the capitulation of the remaining Axis forces encircled in the city. Initial attack The operation was launched on 10 January 1943 with a mass artillery bombardment of the German positions outside the city, with 7,000 field guns, launchers and mortars, by the seven encircling Soviet armies. On the 10th, it became clear the main goal was the Pitomnik airfield, which was captured on 16 January. "The 44th, 76th and 28th (Motorised) Infantry Divisions were badly hit." The 3rd (Motorised) Infantry Division, deployed on the southwestern corner of the cauldron since the end of Nov. 1942, was ordered to retreat to new defensive positions to avoid encirclement. In the first three days, the Soviets lost 26,000 men and over half their tanks. The western half of the Stalingrad pocket had been lost by 17 January. The fighting then paused for four days while the Soviet forces regrouped and redeploy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Operation Uranus
Operation Uranus (russian: Опера́ция «Ура́н», Operatsiya "Uran") was the codename of the Soviet Red Army's 19–23 November 1942 strategic operation on the Eastern Front of World War II which led to the encirclement of Axis forces in the vicinity of Stalingrad: the German Sixth Army, the Third and Fourth Romanian armies, and portions of the German Fourth Panzer Army. The Red Army carried out the operation at roughly the midpoint of the five-month long Battle of Stalingrad, aiming to destroy German forces in and around Stalingrad. Planning for Operation Uranus had commenced in September 1942, and developed simultaneously with plans to envelop and destroy German Army Group Center (Operation Mars) and German forces in the Caucasus. Due to the length of the front lines created by the German 1942 summer offensive, which had aimed at taking the Caucasus oil fields and the city of Stalingrad, German and other Axis forces were over-extended. The German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10th Reserve Army
The Reserve Armies were a group of armies formed by the Soviet Union's Red Army during World War II. Formed to control the training of newly formed units in the rear areas and provide army level headquarters to reconstitute destroyed armies or to form new armies. The Reserve Armies provided the Soviet High Command with a quickly deployable army headquarters to help stem German breakthroughs in the early part of the war. 1st Reserve Army *Former 24th Army January 1942. *First Formation redesignated 64th Army July 1942. *Second Formation redesignated 2nd Guards Army December 1942. 2nd Reserve Army *First Formation redesignated 1st Guards Army (First Formation) 7 August 1942. *Second Formation redesignated 62nd Army (First Formation) July 1942. *Third Formation redesignated 63rd Army (Second Formation) April 1943. 3rd Reserve Army *First Formation redesignated 60th Army July 1942. *Second Formation redesignated 2nd Tank Army January 1943. *Third Formation redesignated 21st Ar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Case Blue
Case Blue (German: ''Fall Blau'') was the German Armed Forces' plan for the 1942 strategic summer offensive in southern Russia between 28 June and 24 November 1942, during World War II. The objective was to capture the oil fields of the Caucasus for two purposes: to enable the Germans to re-supply their low fuel stock and also to deny their use to the Soviet Union, thereby bringing about the complete collapse of the Soviet war effort. After Operation Barbarossa failed to destroy the Soviet Union as a political and military threat the previous year, Adolf Hitler, the ''Führer'' of Nazi Germany, recognised that Germany was now locked in a war of attrition, and he was also aware that Germany was running low on fuel supply and would not be able to continue attacking deeper into enemy territory without more stock. With this in mind, Hitler ordered for the preparation of offensive plans for summer 1942 to secure the Soviet oil fields in the Caucasus. The operation involved a two-pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Second Battle Of Kharkov
The Second Battle of Kharkov or Operation Fredericus was an Axis counter-offensive in the region around Kharkov against the Red Army Izium bridgehead offensive conducted 12–28 May 1942, on the Eastern Front during World War II. Its objective was to eliminate the Izium bridgehead over Seversky Donets or the "Barvenkovo bulge" (russian: Барвенковский выступ) which was one of the Soviet offensive's staging areas. After a winter counter-offensive that drove German troops away from Moscow but depleted the Red Army's reserves, the Kharkov offensive was a new Soviet attempt to expand upon their strategic initiative, although it failed to secure a significant element of surprise. On 12 May 1942, Soviet forces under the command of Marshal Semyon Timoshenko launched an offensive against the German 6th Army from a salient established during the winter counter-offensive. After a promising start, the offensive was stopped on 15 May by massive airstrikes. Critical S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
38th Army (Soviet Union)
The 38th Red Banner Army was a field army of the Soviet Union that existed between 1941 and 1991. August 1941 to January 1942 The 38th Army was formed on 4 August 1941 after a large Soviet force had been surrounded by Axis forces in the area of Uman in the western Ukraine. Under the command of Lieutenant-General Dmitry Ryabyshev, 38th Army was based on the forces and headquarters of the 8th Mechanised Corps and incorporated other Soviet units then in the Cherkassy area. The army was subordinated to the Soviet Southwestern Front command, and Riabyshev's task was to defend the line of the Dnepr upriver from Kremenchuk, a task that became more urgent after the Soviet forces at Uman surrendered on 12 August and German forces began to close up to the Dnepr. On 30 August Riabyshev was assigned to command Soviet forces further south and Major-General Nikolay Feklenko was appointed to the command of 38th Army. By then 38th Army (based on seven rifle divisions, four cavalry divisions a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
28th Army (Soviet Union)
The 28th Army was a field army of the Red Army and the Soviet Ground Forces, formed three times in 1941–42 and active during the postwar period for many years in the Belorussian Military District. Initial formation The army was formed first in June 1941 from the Arkhangelsk Military District. It included the 30th and 33rd Rifle Corps, 69th Motorised Division, artillery and several other units. The Army Commander was Lieutenant General Vladimir Kachalov (previously commander of the Arkhangelsk Military District). Members of the army's Military Council were Brigade Commissioner Vasily T. Kolesnikov, and Army Chief of Staff Major General Pavel G. Egorov. On 14 July 1941, the order creating the Reserve Front gave the 28th Army's composition as nine divisions, one gun, one howitzer, and four corps artillery regiments, and four anti-tank artillery regiments. It participated in the Battle of Smolensk. The army was encircled in the Smolensk Pocket and destroyed. Army headquar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reserve Of The Supreme High Command
The Reserve of the Supreme High Command (Russian: Резерв Верховного Главнокомандования; also known as the '' Stavka'' Reserve or RVGK ( ru , РВГК)) comprises reserve military formations and units; the Stavka Reserve acted as the principal military reserve of the Soviet Red Army during World War II, and the RVGK now operate as part of the Russian Armed Forces under the control of the Supreme Commander-in-Chief of the Russian Armed Forces ( ru , Верховный главнокомандующий) - the President of the Russian Federation. History World War II Forces from the Reserve were assigned by the '' Stavka'' (Supreme High Command) to individual '' fronts'' (army groups) that were conducting major operations. These formations were designed to support any forms of operations but especially penetrations and exploitations in accordance with the Soviet deep battle doctrine. Beginning in 1943, the formations and units in the Rese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stalingrad
Volgograd ( rus, Волгогра́д, a=ru-Volgograd.ogg, p=vəɫɡɐˈɡrat), geographical renaming, formerly Tsaritsyn (russian: Цари́цын, Tsarítsyn, label=none; ) (1589–1925), and Stalingrad (russian: Сталингра́д, Stalingrád, label=none; ) (1925–1961), is the largest city and the administrative centre of Volgograd Oblast, Russia. The city lies on the western bank of the Volga, covering an area of , with a population of slightly over 1 million residents. Volgograd is the List of cities and towns in Russia by population, sixteenth-largest city by population size in Russia, the second-largest city of the Southern Federal District, and the Volga#Biggest cities on the shores of the Volga, fourth-largest city on the Volga. The city was founded as the fortress of ''Tsaritsyn'' in 1589. By the nineteenth century, Tsaritsyn had become an important river-port and commercial centre, leading to its population to grow rapidly. In November 1917, at the start of th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)



_(1857).png)