|
2016 Ecuador Earthquake
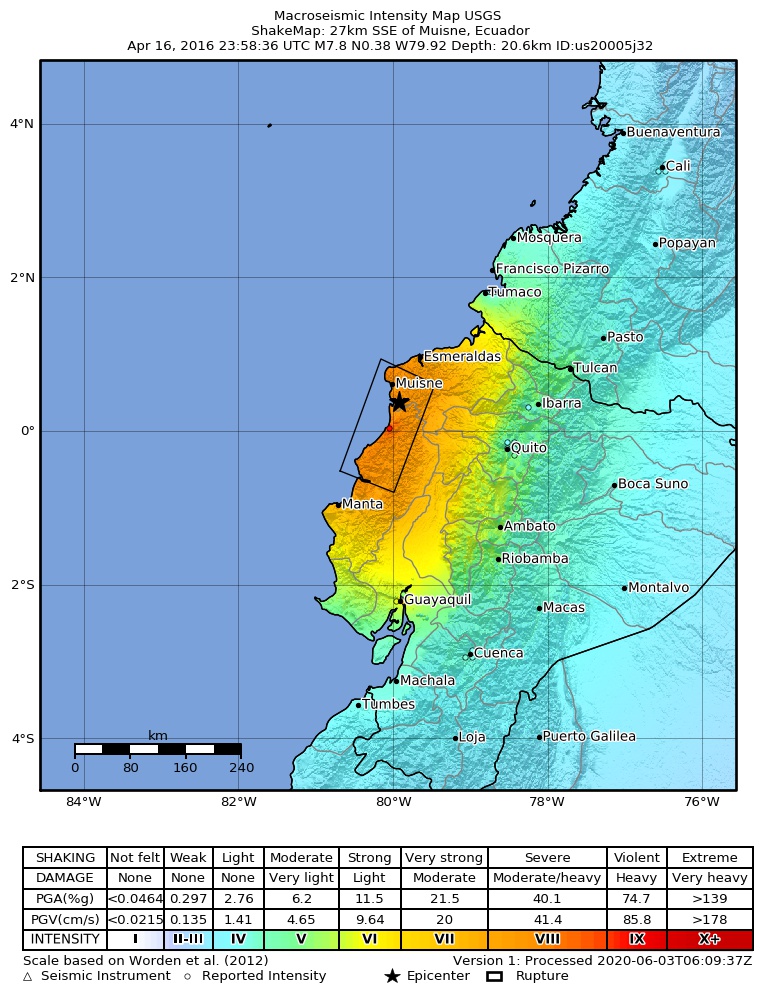
The 2016 Ecuador earthquake occurred on April 16 at with a moment magnitude of 7.8 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (''Severe''). The very large thrust earthquake was centered approximately from the towns of Muisne and Pedernales in a sparsely populated part of the country, and from the capital Quito, where it was felt strongly. Regions of Manta, Pedernales and Portoviejo accounted for over 75 percent of total casualties. Manta's central commercial shopping district, Tarqui, was completely destroyed. Widespread damage was caused across Manabí Province, with structures hundreds of kilometres from the epicenter collapsing. At least 676 people were killed and 16,600 people injured. President Rafael Correa declared a state of emergency; 13,500 military personnel and police officers were dispatched for recovery operations. Geology Ecuador lies above the destructive plate boundary where the Nazca Plate is subducting beneath the South American Plate. The co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecuador Time
Ecuador Time (ECT), as named by the IANA time zone database, is the time observed in mainland Ecuador since 1931. Ecuador Time is at UTC-05:00Time zone: Ecuador at timeanddate.com and has no , except for a brief period in the 1990s during the government of president . This means Ecuador without , which observed Ecuador Time until 1986, when it switched to |
List Of Heads Of State Of Ecuador
The president of Ecuador ( es, Presidente del Ecuador), officially called the Constitutional President of the Republic of Ecuador ( es, Presidente Constitucional de la República del Ecuador), serves as both the head of state and head of government of Ecuador. It is the highest political office in the country as the head of the executive branch of government. Per the current constitution, the President can serve two four-year terms. Prior to that, the president could only serve one four-year term. The current President of Ecuador is Guillermo Lasso, who succeeded Lenín Moreno on 24 May 2021. He was elected in 2021. History The presidency of Ecuador has been marked by periods of instability, causing the office to change presidents frequently throughout the history of the country. At least five times, the duties of the president have been charged to a provisional government or a military junta. Often, the office has been left to an interim or acting president, many of whom wou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shakemap Ecuador April 2016
In seismology, strong ground motion is the strong earthquake shaking that occurs close to (less than about 50 km from) a causative fault. The strength of the shaking involved in strong ground motion usually overwhelms a seismometer, forcing the use of accelerographs (or strong ground motion accelerometers) for recording. The science of strong ground motion also deals with the variations of fault rupture, both in total displacement, energy released, and rupture velocity. As seismic instruments (and accelerometers in particular) become more common, it becomes necessary to correlate expected damage with instrument-readings. The old Modified Mercalli intensity scale (MM), a relic of the pre-instrument days, remains useful in the sense that each intensity-level provides an observable difference in seismic damage. After many years of trying every possible manipulation of accelerometer-time histories, it turns out that the extremely simple peak ground velocity (PGV) provides th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1958 Ecuador–Colombia Earthquake
The 1958 Ecuador–Colombia earthquake struck the coastal regions of Ecuador and Colombia on January 19 with a surface wave magnitude of 7.6 at 9:07 local time. Approximately 30 percent of Esmeraldas (Ecuador) was destroyed, including the children's department of the hospital, where three children died. In all, 111 persons died and 45 were injured as a result of the earthquake. Water mains were broken and power transmission lines were damaged. The Esmeraldas- Quito highway collapsed at many places. Many other roads of the country were made impassable by cracks and fallen trees. According to press reports, a landslide from the slopes of the Andes at Panado village buried a hundred people. The earthquake was destructive in the cities on the northern coast of the country and was strong from Latacunga to Quito, Ibarra and Tulcán. It was felt at Guayaquil. Tectonic setting Ecuador and Colombia lie above a convergent boundary where the Nazca Plate is being subducted beneath the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1979 Tumaco Earthquake
The 1979 Tumaco earthquake occurred at on 12 December with a moment magnitude of 8.2 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of IX (''Violent''). The epicenter was just offshore from the border between Ecuador and Colombia, near the port city of Tumaco. It triggered a major tsunami, which was responsible for most of the estimated 300–600 deaths. The hardest hit area was Colombia's Nariño Department. Tectonic setting Coastal parts of Ecuador and southern Colombia lie above the convergent boundary where the Malpelo Plate subducts beneath the South American Plate along the Colombia–Ecuador Trench. At this location the Malpelo Plate, the microplate northeast of the Nazca Plate, is moving to the east relative to South America at a rate of 58 mm per year. North of the Carnegie Ridge, the subduction interface has four recognisable segments, from south to north, the Esmeraldas, Manglares, Tumaco and Patia segments. This plate boundary has been the location of several great histori ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1942 Ecuador Earthquake
The 1942 Ecuador earthquake or the Guayaquil earthquake occurred on 13 May at 9:06 or 9:13 pm local time with a moment magnitude of 7.9. The temblor struck the coastal ( Esmeraldas) region of Manabí Province, Ecuador. It caused damage mainly to cities like Guayaquil, Portoviejo and Guaranda. More than 300 people were killed and the total cost of damage was about US$2.5 million (1942 rate). Ecuador's largest city Guayaquil was the most affected despite the significant distantce from the epicenter. Many reinforced concrete structures in a particular area in the city were completely destroyed, contributing to fatalities. Tectonic setting The Nazca Plate dives beneath the South American Plate along a convergent plate boundary stretching from Colombia to Chile in a process known as subduction. This plate boundary occasionally produces large megathrust earthquakes along the west coast of South America. The Ecuador–Colombia subduction zone occupies part of this plate boundary, wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earthquake Rupture
In seismology, an earthquake rupture is the extent of slip that occurs during an earthquake in the Earth's crust. Earthquakes occur for many reasons that include: landslides, movement of magma in a volcano, the formation of a new fault, or, most commonly of all, a slip on an existing fault. Nucleation A tectonic earthquake begins by an initial rupture at a point on the fault surface, a process known as nucleation. The scale of the nucleation zone is uncertain, with some evidence, such as the rupture dimensions of the smallest earthquakes, suggesting that it is smaller than 100 m while other evidence, such as a slow component revealed by low-frequency spectra of some earthquakes, suggest that it is larger. The possibility that the nucleation involves some sort of preparation process is supported by the observation that about 40% of earthquakes are preceded by foreshocks. However, some large earthquakes, such as the M8.6 1950 India - China earthquake., have no foreshocks and it re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1906 Ecuador–Colombia Earthquake
The 1906 Ecuador–Colombia earthquake occurred at 10:36:10 (UTC+5) on Wednesday January 31, 1906 off the coast of Ecuador, near Esmeraldas. The earthquake had a moment magnitude of 8.8 and triggered a destructive tsunami that caused at least 500 casualties on the coast of Colombia. Tectonic setting The earthquake occurred along the boundary between the Malpelo Plate, formerly considered the northeastern part of the Nazca Plate, and the North Andes Plate. The earthquake is likely to be a result of thrust-faulting, caused by the subduction of the Coiba, Malpelo and Nazca Plates beneath the North Andes and South American Plates. The coastal parts of Ecuador and Colombia have a history of strong megathrust earthquakes originating from this Malpelo-North Andes plate boundary. Damage The greatest damage from the tsunami occurred on the coast between Río Verde, Ecuador and Micay, Colombia. Estimates of the number of deaths caused by the tsunami vary between 500 and 1,500. Char ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Megathrust Earthquake
Megathrust earthquakes occur at convergent plate boundaries, where one tectonic plate is forced underneath another. The earthquakes are caused by slip along the thrust fault that forms the contact between the two plates. These interplate earthquakes are the planet's most powerful, with moment magnitudes (''Mw'') that can exceed 9.0. Since 1900, all earthquakes of magnitude 9.0 or greater have been megathrust earthquakes. The thrust faults responsible for megathrust earthquakes often lie at the bottom of oceanic trenches; in such cases, the earthquakes can abruptly displace the sea floor over a large area. As a result, megathrust earthquakes often generate tsunamis that are considerably more destructive than the earthquakes themselves. Teletsunamis can cross ocean basins to devastate areas far from the original earthquake. Terminology and mechanism The term ''megathrust'' refers to an extremely large thrust fault, typically formed at the plate interface along a subduction zone ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Focal Mechanism
The focal mechanism of an earthquake describes the deformation in the source region that generates the seismic waves. In the case of a fault-related event it refers to the orientation of the fault plane that slipped and the slip vector and is also known as a fault-plane solution. Focal mechanisms are derived from a solution of the moment tensor for the earthquake, which itself is estimated by an analysis of observed seismic waveforms. The focal mechanism can be derived from observing the pattern of "first motions", that is, whether the first arriving P waves break up or down. This method was used before waveforms were recorded and analysed digitally and this method is still used for earthquakes too small for easy moment tensor solution. Focal mechanisms are now mainly derived using semi-automatic analysis of the recorded waveforms. Moment tensor solutions The moment tensor solution is typically displayed graphically using a so-called ''beachball'' diagram. The pattern of en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
South American Plate
The South American Plate is a major tectonic plate which includes the continent of South America as well as a sizable region of the Atlantic Ocean seabed extending eastward to the African Plate, with which it forms the southern part of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. The easterly edge is a divergent boundary with the African Plate; the southerly edge is a complex boundary with the Antarctic Plate, the Scotia Plate, and the Sandwich Plate; the westerly edge is a convergent boundary with the subducting Nazca Plate; and the northerly edge is a boundary with the Caribbean Plate and the oceanic crust of the North American Plate. At the Chile Triple Junction, near the west coast of the Taitao–Tres Montes Peninsula, an oceanic ridge known as the Chile Rise is actively subducting under the South American Plate. Geological research suggests that the South American Plate is moving westward away from the Mid-Atlantic Ridge: "Parts of the plate boundaries consisting of alternations of relati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subduction
Subduction is a geological process in which the oceanic lithosphere is recycled into the Earth's mantle at convergent boundaries. Where the oceanic lithosphere of a tectonic plate converges with the less dense lithosphere of a second plate, the heavier plate dives beneath the second plate and sinks into the mantle. A region where this process occurs is known as a subduction zone, and its surface expression is known as an arc-trench complex. The process of subduction has created most of the Earth's continental crust. Rates of subduction are typically measured in centimeters per year, with the average rate of convergence being approximately two to eight centimeters per year along most plate boundaries. Subduction is possible because the cold oceanic lithosphere is slightly denser than the underlying asthenosphere, the hot, ductile layer in the upper mantle underlying the cold, rigid lithosphere. Once initiated, stable subduction is driven mostly by the negative buoyancy of the de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |