|
2011 Vancouver Earthquake
This is a list of earthquakes in Canada. List Abbreviations used: See also *Hydraulic fracturing in Canada References External links *Natural Resources CanadEarthquakes Canada*Earthquakes CanadRecent earthquakes {{DEFAULTSORT:Earthquakes In Canada Earthquakes An earthquake (also known as a quake, tremor or temblor) is the shaking of the surface of the Earth resulting from a sudden release of energy in the Earth's lithosphere that creates seismic waves. Earthquakes can range in intensity, from ... Canada Lists of disasters in Canada ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pole, with 0° at the Equator. Lines of constant latitude, or ''parallels'', run east–west as circles parallel to the equator. Latitude and ''longitude'' are used together as a coordinate pair to specify a location on the surface of the Earth. On its own, the term "latitude" normally refers to the ''geodetic latitude'' as defined below. Briefly, the geodetic latitude of a point is the angle formed between the vector perpendicular (or ''normal'') to the ellipsoidal surface from the point, and the plane of the equator. Background Two levels of abstraction are employed in the definitions of latitude and longitude. In the first step the physical surface is modeled by the geoid, a surface which approximates the mean sea level over the ocean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baffin Bay
Baffin Bay ( Inuktitut: ''Saknirutiak Imanga''; kl, Avannaata Imaa; french: Baie de Baffin), located between Baffin Island and the west coast of Greenland, is defined by the International Hydrographic Organization as a marginal sea of the Arctic Ocean. It is sometimes considered a sea of the North Atlantic Ocean. It is connected to the Atlantic via Davis Strait and the Labrador Sea. The narrower Nares Strait connects Baffin Bay with the Arctic Ocean. The bay is not navigable most of the year because of the ice cover and high density of floating ice and icebergs in the open areas. However, a polynya of about , known as the North Water, opens in summer on the north near Smith Sound. Most of the aquatic life of the bay is concentrated near that region. Extent The International Hydrographic Organization defines the limits of Baffin Bay as follows: History The area of the bay has been inhabited since BC. Around AD 1200, the initial Dorset settlers were replaced by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
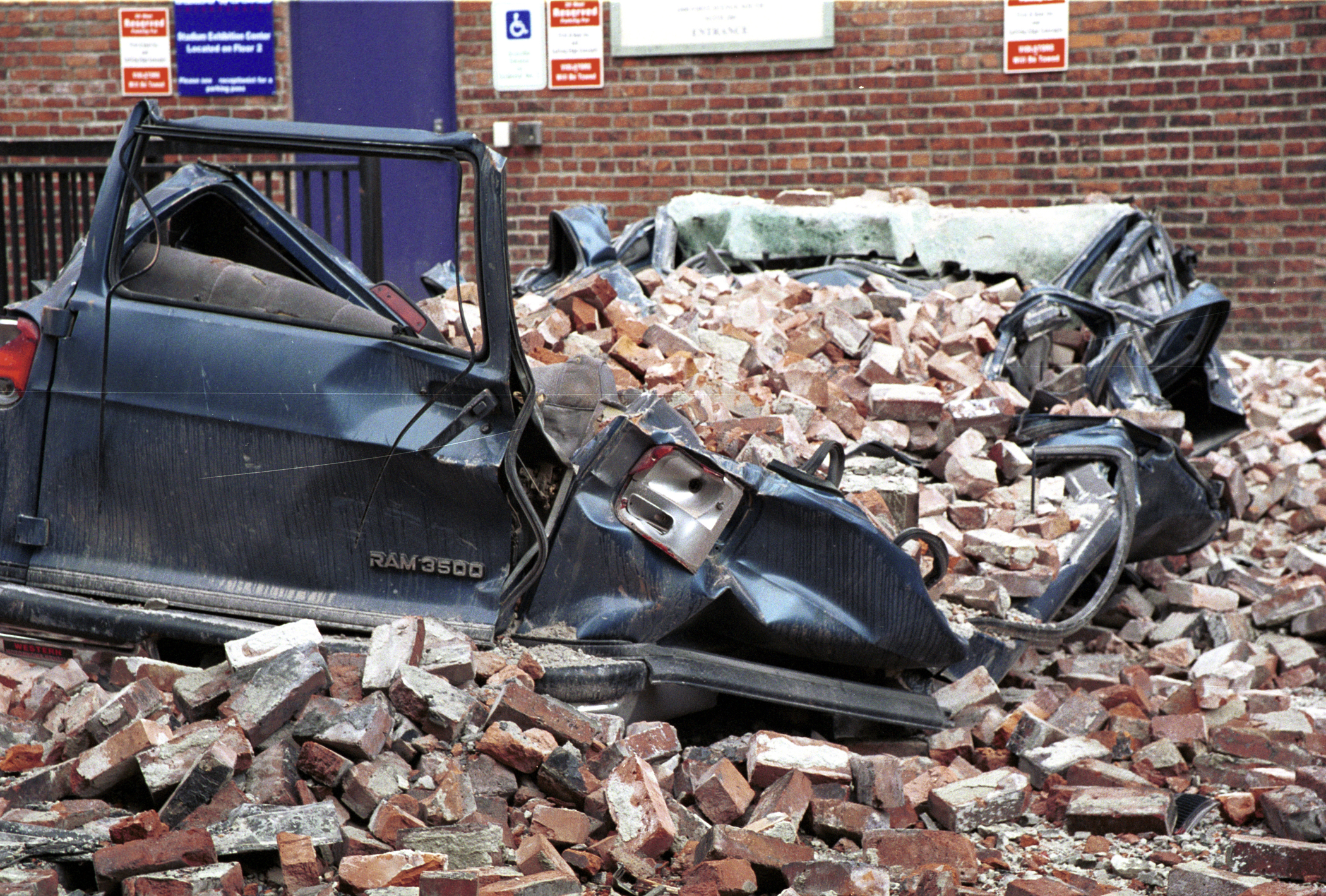
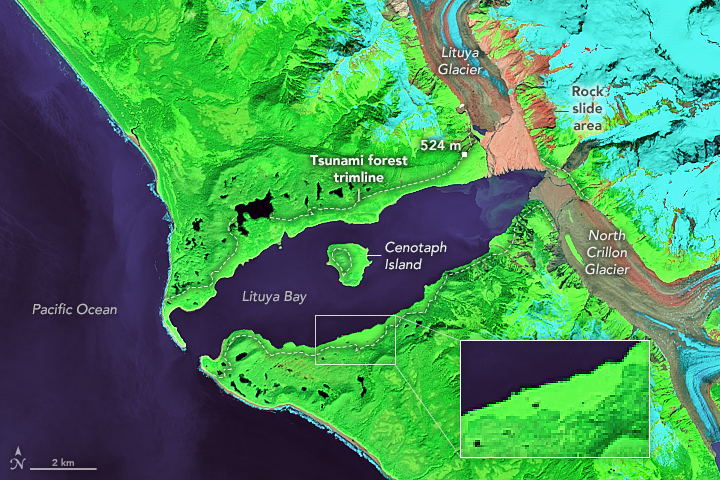
1958 Lituya Bay Megatsunami
The 1958 Lituya Bay earthquake occurred on PST with a moment magnitude of 7.8 to 8.3 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of XI (''Extreme''). The strike-slip earthquake took place on the Fairweather Fault and triggered a rockslide of 30 million cubic meters (40 million cubic yards) and about 90 million tons into the narrow inlet of Lituya Bay, Alaska. The impact was heard away, and the sudden displacement of water resulted in a megatsunami that washed out trees to a maximum elevation of at the entrance of Gilbert Inlet. This is the largest and most significant megatsunami in modern times; it forced a re-evaluation of large-wave events and the recognition of impact events, rockfalls, and landslides as causes of very large waves. Event outline Lituya Bay is a fjord located on the Fairweather Fault in the northeastern part of the Gulf of Alaska. It is a T-shaped bay with a width of and a length of . Lituya Bay is an ice-scoured tidal inlet with a maximum depth of . The narro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Miramichi, New Brunswick
Miramichi () is the largest city in northern New Brunswick, Canada. It is situated at the mouth of the Miramichi River where it enters Miramichi Bay. The Miramichi Valley is the second longest valley in New Brunswick, after the Saint John River (Bay of Fundy), Saint John River Valley. Neighbourhoods The city of Miramichi was formed in 1995 through the forced Municipal amalgamations in New Brunswick, amalgamation of two towns, Newcastle, New Brunswick, Newcastle and Chatham, New Brunswick, Chatham, and several smaller communities, including Douglastown, New Brunswick, Douglastown, Loggieville, New Brunswick, Loggieville, and Nelson-Miramichi, New Brunswick, Nelson. Also the local service districts of Nordin, New Brunswick, Nordin, Moorefield, New Brunswick, Moorefield, Chatham Head, New Brunswick, Chatham Head, and Douglasfield, New Brunswick, Douglasfield. The amalgamation also included portions of the former local service district of Ferry Road-Russellville (Now separated and m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Northwest Territories
The Northwest Territories (abbreviated ''NT'' or ''NWT''; french: Territoires du Nord-Ouest, formerly ''North-Western Territory'' and ''North-West Territories'' and namely shortened as ''Northwest Territory'') is a federal territory of Canada. At a land area of approximately and a 2016 census population of 41,790, it is the second-largest and the most populous of the three territories in Northern Canada. Its estimated population as of 2022 is 45,605. Yellowknife is the capital, most populous community, and only city in the territory; its population was 19,569 as of the 2016 census. It became the territorial capital in 1967, following recommendations by the Carrothers Commission. The Northwest Territories, a portion of the old North-Western Territory, entered the Canadian Confederation on July 15, 1870. Since then, the territory has been divided four times to create new provinces and territories or enlarge existing ones. Its current borders date from April 1, 1999, when the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1985 Nahanni Earthquakes
The 1985 Nahanni earthquakes is the name for a continuous sequence of earthquakes that began in 1985 in the Nahanni region of the Northwest Territories, Canada.Natural Resources Canada: Rock and Roll in the N.W.T.: The 1985 Nahanni Earthquakes The largest of these earthquakes occurred on December 23, reaching 6.9 on the . This is one of the most significant earthquakes in Canada during the 20th century. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1988 Saguenay Earthquake
The 1988 Saguenay earthquake struck Quebec, Canada with a moment magnitude of 5.9 on November 25. It is one of the largest recorded earthquakes in eastern Canada and eastern North America during the 20th century. The earthquake was felt by millions, and damaged some buildings. It could be felt as far as Toronto, Halifax, and Boston. The earthquake was triggered by faults associated with the Saguenay Graben. See also *List of earthquakes in Canada References External links * 1988 in Canada 1988 File:1988 Events Collage.png, From left, clockwise: The oil platform Piper Alpha explodes and collapses in the North Sea, killing 165 workers; The USS Vincennes (CG-49) mistakenly shoots down Iran Air Flight 655; Australia celebrates its Australian ... 1988 earthquakes History of Saguenay, Quebec 1988 in Quebec Laurentides Wildlife Reserve {{Canada-earthquake-stub 1988 disasters in Canada ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1989 Ungava Earthquake
The 1989 Ungava earthquake occurred at 09:24 local time (14:24 UTC) on 25 December to the north of Lac Bécard in a remote part of the Ungava Peninsula in northern Quebec. It had a magnitude of 6.3 on the surface wave magnitude scale and 6.2–6.5 on the moment magnitude scale and a maximum felt intensity of only IV (''Light'') on the Mercalli intensity scale, due to its remoteness from any inhabited areas. The mainshock was preceded by a magnitude 5.1 foreshock ten hours earlier. It was the first earthquake in eastern North America known to be associated with ground rupture. Tectonic setting The northern part of Quebec lies mainly on the Minto block of the Superior craton. The earthquake occurred within the Utsalik domain, which consists mainly of Archean granitic and granodioritic rocks. A number of northerly trending brittle faults zones have been recognized in the domain. The area has been tectonically quiescent since the Archean. However, like most of the Canadian shield, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2000 Kipawa Earthquake
The 2000 Kipawa earthquake (or 2000 Kipawa "Millennium" earthquake ) struck Quebec and Ontario, Canada with a moment magnitude of 5.2 at 6:22 a.m. on January 1. It occurred in the Western Quebec Seismic Zone. The main shock epicenter was located in Lake Kipawa about north of Témiscaming in southwestern Quebec and northeast of North Bay, Ontario. The shaking was strongest within of the epicenter. It was felt in Témiscaming, North Bay and as far away as Toronto, making it one of the most significant earthquakes in Canada in 2000. The earthquake was triggered by major thrust faults associated with the Ottawa-Bonnechere Graben. Minor damage was reported during this earthquake, including fallen light objects, a damaged ventilation pipe and fractures in plaster. Its epicenter was very close to that of the 1935 Timiskaming earthquake and lies in a group of 76 located earthquakes since 1935. Seventeen aftershocks were recorded. See also * List of earthquakes in 2000 *List of e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Puget Sound
Puget Sound ( ) is a sound of the Pacific Northwest, an inlet of the Pacific Ocean, and part of the Salish Sea. It is located along the northwestern coast of the U.S. state of Washington. It is a complex estuarine system of interconnected marine waterways and basins, with one major and two minor connections to the open Pacific Ocean via the Strait of Juan de Fuca—Admiralty Inlet being the major connection and Deception Pass and Swinomish Channel being the minor. Water flow through Deception Pass is approximately equal to 2% of the total tidal exchange between Puget Sound and the Strait of Juan de Fuca. Puget Sound extends approximately from Deception Pass in the north to Olympia in the south. Its average depth is and its maximum depth, off Jefferson Point between Indianola and Kingston, is . The depth of the main basin, between the southern tip of Whidbey Island and Tacoma, is approximately . In 2009, the term Salish Sea was established by the United States Board o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2001 Nisqually Earthquake
The 2001 Nisqually earthquake occurred at on February 28, 2001 and lasted nearly a minute. The intraslab earthquake had a moment magnitude of 6.8 and a maximum Mercalli intensity of VIII (''Severe''). The epicenter was in the southern Puget Sound, northeast of Olympia, but the shock was felt in Oregon, British Columbia, eastern Washington, and Idaho. This was the most recent of several large earthquakes that occurred in the Puget Sound region over a 52-year period and caused property damage valued at $1–4 billion. One person died of a heart attack and several hundred were injured. Tectonic setting The Puget Sound area is prone to deep earthquakes due to the Juan de Fuca tectonic plate's subduction under the North American Plate at 3.5 to 4.5 cm a year as part of the Cascadia subduction zone. Three types of earthquake are observed in the area: rare megathrust events, such as the 1700 Cascadia earthquake, shallow events within the North American Plate and deeper intra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Territories (NWT) to the north, and the U.S. state of Montana to the south. It is one of the only two landlocked provinces in Canada (Saskatchewan being the other). The eastern part of the province is occupied by the Great Plains, while the western part borders the Rocky Mountains. The province has a predominantly continental climate but experiences quick temperature changes due to air aridity. Seasonal temperature swings are less pronounced in western Alberta due to occasional Chinook winds. Alberta is the fourth largest province by area at , and the fourth most populous, being home to 4,262,635 people. Alberta's capital is Edmonton, while Calgary is its largest city. The two are Alberta's largest census metropolitan areas. More tha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |