|
2008–09 Australian Region Cyclone Season
The 2008–09 Australian region cyclone season was a near average tropical cyclone season. It officially started on 1 November 2008, and officially ended on 30 April 2009. This season was also the first time that the BoM implemented a "tropical cyclone year." The regional tropical cyclone operational plan defines a "tropical cyclone year" separately from a "tropical cyclone season"; the "tropical cyclone year" began on 1 July 2008 and ended on 30 June 2009. The scope of the Australian region is limited to all areas south of the equator, east of 90°E and west of 160°E. This area includes Australia, Papua New Guinea, western parts of the Solomon Islands, East Timor and southern parts of Indonesia. Tropical cyclones in this area are monitored by five Tropical Cyclone Warning Centres (TCWCs): the Australian Bureau of Meteorology in Perth, Darwin, and Brisbane; TCWC Jakarta in Indonesia; and TCWC Port Moresby in Papua New Guinea. The Joint Typhoon Warning Center issues unoffici ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyclone Hamish (2009)
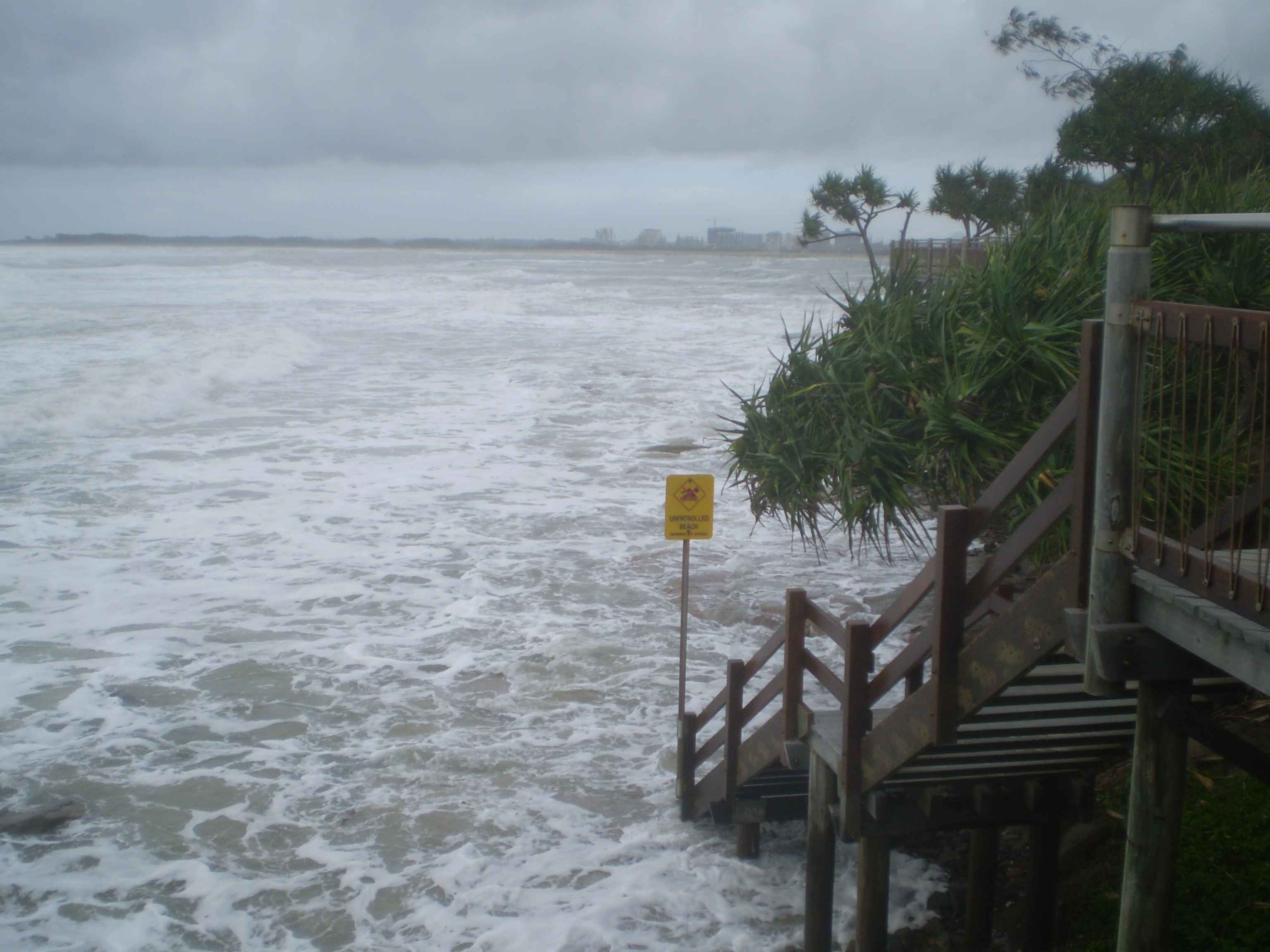
Severe Tropical Cyclone Hamish was a powerful tropical cyclone that caused extensive damage to the Great Barrier Reef and coastal Queensland, Australia, in March 2009. The eighth Tropical cyclone naming, named storm of the 2008–09 Australian region cyclone season, Hamish developed out of an low-pressure area, area of low pressure on 4 March near the Cape York Peninsula. The storm rapidly developed into a Category 1 cyclone on the Tropical cyclone scales#Australia, Australian intensity scale the next day. On 6 March, an eye (cyclone), eye developed, and Hamish strengthened into a Category 3 cyclone. Deep Atmospheric convection, convection developed around the eye, fueling further intensification, which allowed the storm to become a Category 5 tropical cyclone late on 7 March. Hamish made its closest approach to land on 8 March, but continued moving southeastward. Eventually, the cyclone weakened and turned back towards the northwest, weakening into a remnant low on 11 March, befo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Darwin, Northern Territory
Darwin ( Larrakia: ') is the capital city of the Northern Territory, Australia. The city has nearly 53% of the Northern Territory's population, with 139,902 at the 2021 census. It is the smallest, wettest, and most northerly of the Australian capital cities and serves as the Top End's regional centre. Darwin's proximity to Southeast Asia makes it a key link between Australia and countries such as Indonesia and Timor-Leste. The Stuart Highway begins in Darwin and extends southerly across central Australia through Tennant Creek and Alice Springs, concluding in Port Augusta, South Australia. The city is built upon a low bluff overlooking Darwin Harbour. Darwin's suburbs extend to Lee Point in the north and to Berrimah in the east. The Stuart Highway extends to Darwin's eastern satellite city of Palmerston and its suburbs. The Darwin region, like much of the Top End, has a tropical climate, with a wet and dry season. A period known locally as "the build up" leading up ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Knot (unit)
The knot () is a unit of speed equal to one nautical mile per hour, exactly (approximately or ). The ISO standard symbol for the knot is kn. The same symbol is preferred by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers ( IEEE), while kt is also common, especially in aviation, where it is the form recommended by the International Civil Aviation Organization ( ICAO). The knot is a non- SI unit. The knot is used in meteorology, and in maritime and air navigation. A vessel travelling at 1 knot along a meridian travels approximately one minute of geographic latitude in one hour. Definitions ;1 international knot = :1 nautical mile per hour (by definition), : (exactly), : (approximately), : (approximately), : (approximately) : (approximately). The length of the internationally agreed nautical mile is . The US adopted the international definition in 1954, having previously used the US nautical mile (). The UK adopted the international nautical mile defi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
2008–09 South Pacific Cyclone Season
The 2008–09 South Pacific cyclone season was a below average tropical cyclone season, which featured six named tropical cyclones compared to an average of about nine. Ahead of the season officially starting on November 1, 2008, the Island Climate Update tropical cyclone outlook predicted that the season, would feature an average risk of tropical cyclones impacting the South Pacific between 160°E and 120°W. The first tropical disturbance of the season developed to the northeast of the Samoan Islands on December 1, however, it remained weak and was last noted during the next day. Seasonal forecasts Ahead of the cyclone season formally starting on November 1, 2008, New Zealand's MetService and National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research (NIWA), the Fiji Meteorological Service (FMS), as well as various other Pacific Meteorological services, all contributed towards the Island Climate Update tropical cyclone outlook that was released during September 2008. The outlook t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
150th Meridian East
Fifteen or 15 may refer to: *15 (number) *one of the years 15 BC, AD 15, 1915, 2015 Music *Fifteen (band), a punk rock band Albums * ''15'' (Buckcherry album), 2005 * ''15'' (Ani Lorak album), 2007 * ''15'' (Phatfish album), 2008 * ''15'' (Tuki album), 2025 * ''15'' (mixtape), a 2018 mixtape by Bhad Bhabie * ''Fifteen'' (Green River Ordinance album), 2016 * ''Fifteen'' (The Wailin' Jennys album), 2017 * ''Fifteen'', a 2012 album by Colin James Songs * "Fifteen" (song), a 2008 song by Taylor Swift *"Fifteen", a song by Harry Belafonte from the album '' Love Is a Gentle Thing'' *"15", a song by Rilo Kiley from the album ''Under the Blacklight'' *"15", a song by Marilyn Manson from the album ''The High End of Low'' Other media * ''15'' (film), a 2003 Singaporean film * ''Fifteen'' (TV series), international release name of ''Hillside'', a Canadian-American teen drama * "Fifteen" (''Runaways''), an episode of ''Runaways'' *Fifteen (novel), a 1956 juvenile fict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New Zealand
New Zealand () is an island country in the southwestern Pacific Ocean. It consists of two main landmasses—the North Island () and the South Island ()—and List of islands of New Zealand, over 600 smaller islands. It is the List of island countries, sixth-largest island country by area and lies east of Australia across the Tasman Sea and south of the islands of New Caledonia, Fiji, and Tonga. The Geography of New Zealand, country's varied topography and sharp mountain peaks, including the Southern Alps (), owe much to tectonic uplift and volcanic eruptions. Capital of New Zealand, New Zealand's capital city is Wellington, and its most populous city is Auckland. The islands of New Zealand were the last large habitable land to be settled by humans. Between about 1280 and 1350, Polynesians began to settle in the islands and subsequently developed a distinctive Māori culture. In 1642, the Dutch explorer Abel Tasman became the first European to sight and record New Zealand. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Institute Of Water And Atmospheric Research
The National Institute of Water and Atmospheric Research or NIWA (), is a Crown Research Institute of New Zealand. Established in 1992, NIWA conducts research across a broad range of disciplines in the environmental sciences. It also maintains nationally and, in some cases, internationally important environmental monitoring networks, databases, and collections. , NIWA had 697 staff spread across 14 sites in New Zealand and one in Perth, Australia. Its head office is in Auckland, with regional offices in Hamilton, Wellington, Christchurch, Nelson, and Lauder (Central Otago). It also has small field teams, focused mostly on hydrology, stationed in Bream Bay, Lake Tekapo, Rotorua, Napier, Whanganui, Greymouth, Alexandra, and Dunedin. NIWA maintains a fleet of about 30 vessels for freshwater, marine, and atmospheric research. On 1 July 2025 NIWA will become part of the new Public Research Organisation New Zealand Institute for Earth Science. History NIWA was formed as a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
El Niño–Southern Oscillation
El Niño–Southern Oscillation (ENSO) is a global climate phenomenon that emerges from variation in winds and sea surface temperatures over the tropical Pacific Ocean. Those variations have an irregular pattern but do have some semblance of cycles. The occurrence of ENSO is not predictable. It affects the climate of much of the tropics and subtropics, and has links (Teleconnection, teleconnections) to higher-latitude regions of the world. The warming phase of the sea surface temperature is known as "El Niño" and the cooling phase as "La Niña". The Southern Oscillation is the accompanying atmospheric oscillation, which is coupled with the sea temperature change. El Niño is associated with higher than normal air sea level pressure over Indonesia, Australia and across the Indian Ocean to the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic. La Niña has roughly the reverse pattern: high pressure over the central and eastern Pacific and lower pressure through much of the rest of the tropics and subtrop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
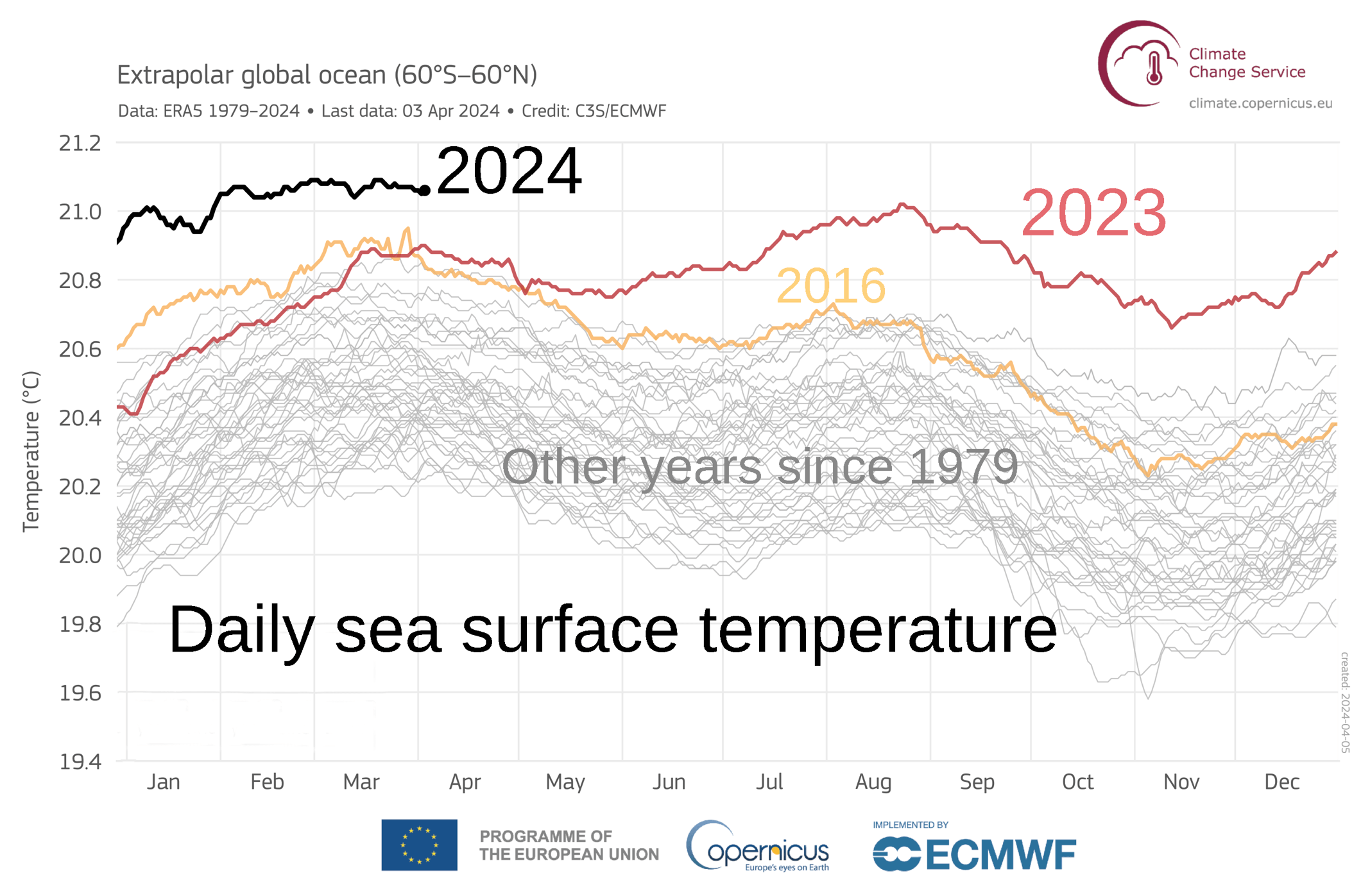
Sea Surface Temperatures
Sea surface temperature (or ocean surface temperature) is the ocean temperature, temperature of ocean water close to the surface. The exact meaning of ''surface'' varies in the literature and in practice. It is usually between and below the sea surface. Sea surface temperatures greatly modify air masses in the Atmosphere of Earth, Earth's atmosphere within a short distance of the shore. The thermohaline circulation has a major impact on average sea surface temperature throughout most of the world's oceans. Warm sea surface temperatures can develop and Tropical cyclogenesis, strengthen cyclones over the ocean. Tropical cyclones can also cause a cool wake. This is due to turbulent mixing of the upper of the ocean. Sea surface temperature changes during the day. This is like the air above it, but to a lesser degree. There is less variation in sea surface temperature on breezy days than on calm days. Coastal sea surface temperatures can cause offshore winds to generate upwelling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southern Oscillation Index
Southern may refer to: Businesses * China Southern Airlines, airline based in Guangzhou, China * Southern Airways, defunct US airline * Southern Air, air cargo transportation company based in Norwalk, Connecticut, US * Southern Airways Express, Memphis-based passenger air transportation company, serving eight cities in the US * Southern Company, US electricity corporation * Southern Music (now Peermusic), US record label * Southern Railway (other), various railways * Southern Records, independent British record label * Southern Studios, recording studio in London, England * Southern Television, defunct UK television company * Southern (Govia Thameslink Railway), brand used for some train services in Southern England Media * 88.3 Southern FM, a non-commercial community radio station based in Melbourne, Australia * Heart Sussex, a radio station in Sussex, England, previously known as "Southern FM" * '' Nanfang Daily'' or ''Southern Daily'', the official Communis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
135th Meridian East
The meridian 135° east of Greenwich is a line of longitude that extends from the North Pole across the Arctic Ocean, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, Australasia, the Indian Ocean, the Southern Ocean, and Antarctica to the South Pole. The 135th meridian east forms a great ellipse with the 45th meridian west, meaning it is a quarter away from the 180th meridian and 3 quarters from the 0th meridian. From Pole to Pole Starting at the North Pole and heading south to the South Pole, the 135th meridian east passes through: : See also * 134th meridian east *136th meridian east The meridian 136° east of Greenwich is a line of longitude that extends from the North Pole across the Arctic Ocean, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, Australasia, the Indian Ocean, the Southern Ocean, and Antarctica to the South Pole. The 136th meridia ... References {{Use dmy dates, date=March 2017 e135 meridian east ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joint Typhoon Warning Center
The Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) is a joint United States Navy – United States Air Force command in Pearl Harbor, Hawaii. The JTWC is responsible for the issuing of tropical cyclone warnings in the North-West Pacific Ocean, South Pacific Ocean, and Indian Ocean for all branches of the U.S. Department of Defense and other U.S. government agencies. Their warnings are intended primarily for the protection of U.S. military ships and aircraft, as well as military installations jointly operated with other countries around the world. Its U.S. Navy components are aligned with the Naval Meteorology and Oceanography Command. History The origins of the Joint Typhoon Warning Center (JTWC) can be traced back to June 1945, when the Fleet Weather Center/Typhoon Tracking Center was established on the island of Guam, after multiple typhoons, including Typhoon Cobra of December 1944 and Typhoon Connie in June 1945, had caused a significant loss of men and ships. At this time th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |