|
2007–2008 Nazko Earthquakes
The 2007–2008 Nazko earthquakes were a series of small volcanic earthquakes measuring less than 4.0 on the Richter magnitude scale. They took place in the sparsely populated Nazko area of the Central Interior of British Columbia, Canada starting on October 9, 2007 and ending on June 12, 2008. They occurred just west of Nazko Cone, a small tree-covered cinder cone that last erupted about 7,200 years ago. No damage or casualties resulted from the Nazko earthquakes, which were too small to be felt by people, but local seismographs recorded them. The earthquake swarm occurred at the eastern end of a known volcanic zone called the Anahim Volcanic Belt. This is an east-west trending line of volcanic formations extending from the Central Coast to the Central Interior of British Columbia. Geology The 2007–2008 Nazko earthquake swarm is interpreted to have originated below the surface. The character of the seismic waves indicated that the swarm originated from a magmat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by total area. Its southern and western border with the United States, stretching , is the world's longest binational land border. Canada's capital is Ottawa, and its three largest metropolitan areas are Toronto, Montreal, and Vancouver. Indigenous peoples have continuously inhabited what is now Canada for thousands of years. Beginning in the 16th century, British and French expeditions explored and later settled along the Atlantic coast. As a consequence of various armed conflicts, France ceded nearly all of its colonies in North America in 1763. In 1867, with the union of three British North American colonies through Confederation, Canada was formed as a federal dominion of four provinces. This began an accretion of provinces an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
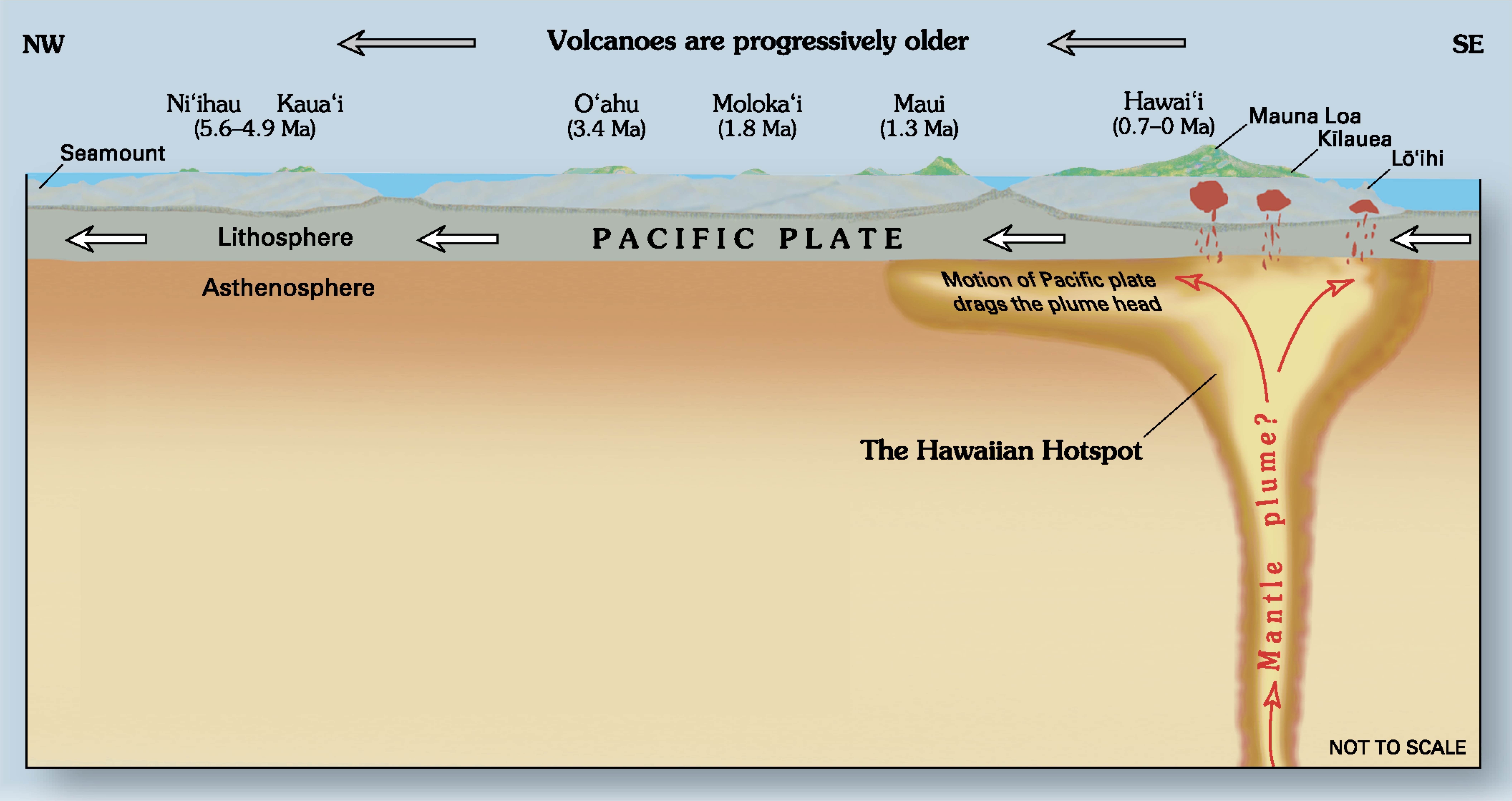
Anahim Hotspot
The Anahim hotspot is a hypothesized hotspot in the Central Interior of British Columbia, Canada. It has been proposed as the candidate source for volcanism in the Anahim Volcanic Belt, a long chain of volcanoes and other magmatic features that have undergone erosion. This chain extends from the community of Bella Bella in the west to near the small city of Quesnel in the east. While most volcanoes are created by geological activity at tectonic plate boundaries, the Anahim hotspot is located hundreds of kilometres away from the nearest plate boundary. The hotspot was first proposed in the 1970s by three scientists who used John Tuzo Wilson's classic hotspot theory. This theory proposes that a single, fixed mantle plume builds volcanoes that then, cut off from their source by the movement of the North American Plate, become increasingly inactive and eventually erode over millions of years. A more recent theory, published in 2001 by the Geological Society of America, suggests th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Geological Survey
The United States Geological Survey (USGS), formerly simply known as the Geological Survey, is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The organization's work spans the disciplines of biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility. The agency was founded on March 3, 1879. The USGS is a bureau of the United States Department of the Interior; it is that department's sole scientific agency. The USGS employs approximately 8,670 people and is headquartered in Reston, Virginia. The USGS also has major offices near Lakewood, Colorado, at the Denver Federal Center, and Menlo Park, California. The current motto of the USGS, in use since August 1997, is "science for a changing world". The agency's previous slogan, adopted on the occasion of its hundredt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnitude (mathematics)
In mathematics, the magnitude or size of a mathematical object is a property which determines whether the object is larger or smaller than other objects of the same kind. More formally, an object's magnitude is the displayed result of an order theory, ordering (or ranking)—of the class (mathematics), class of objects to which it belongs. In physics, magnitude can be defined as quantity or distance. History The Greeks distinguished between several types of magnitude, including: *Positive fractions *Line segments (ordered by length) *Geometric shape, Plane figures (ordered by area) *Solid geometry, Solids (ordered by volume) *Angle, Angles (ordered by angular magnitude) They proved that the first two could not be the same, or even isomorphic systems of magnitude. They did not consider negative number, negative magnitudes to be meaningful, and ''magnitude'' is still primarily used in contexts in which zero is either the smallest size or less than all possible sizes. Numbers Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anahim Volcanic Belt-en
Anahim is a name used for several features in British Columbia, Canada, derived from the name of Chief Anahim, a leader of the Tsilhqot'in people in the mid-19th Century: *Anahim Lake, British Columbia, a community in the west-central part of the province * Anahim Lake Airport, the airport of the community of Anahim Lake *Anahim Peak, a volcano in the Anahim Volcanic Belt *Anahim hotspot, an inferred mantle plume feeding the Anahim Volcanic Belt *Anahim Volcanic Belt The Anahim Volcanic Belt (AVB) is a west–east trending chain of volcanoes and related magmatic features in British Columbia, Canada. It extends from Athlone Island on the Central Coast, running eastward through the strongly uplifted and deeply ..., a linear belt of volcanoes Various Indian Reserves of the Tl'etinqox-t'in Government are named Anahim No. 10, Anahim No. 11 etc. Their main reserve community is known by a variant name, Anaham. {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Resources Canada
Natural Resources Canada (NRCan; french: Ressources naturelles Canada; french: RNCan, label=none)Natural Resources Canada is the applied title under the Federal Identity Program; the legal title is Department of Natural Resources (). is the department of the Government of Canada responsible for natural resources, energy, minerals and metals, forests, earth sciences, mapping, and remote sensing. It was formed in 1994 by amalgamating the Department of Energy, Mines and Resources with the Department of Forestry. Under the ''Constitution Act, 1867'', primary responsibility for natural resources falls to provincial governments, however, the federal government has jurisdiction over off-shore resources, trade and commerce in natural resources, statistics, international relations, and boundaries. The department administers federal legislation relating to natural resources, including energy, forests, minerals and metals. The department also collaborates with American and Mexican governme ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hotspot (geology)
In geology, hotspots (or hot spots) are volcanic locales thought to be fed by underlying mantle that is anomalously hot compared with the surrounding mantle. Examples include the Hawaii, Iceland, and Yellowstone hotspots. A hotspot's position on the Earth's surface is independent of tectonic plate boundaries, and so hotspots may create a chain of volcanoes as the plates move above them. There are two hypotheses that attempt to explain their origins. One suggests that hotspots are due to mantle plumes that rise as thermal diapirs from the core–mantle boundary. The alternative plate theory is that the mantle source beneath a hotspot is not anomalously hot, rather the crust above is unusually weak or thin, so that lithospheric extension permits the passive rising of melt from shallow depths. Origin The origins of the concept of hotspots lie in the work of J. Tuzo Wilson, who postulated in 1963 that the formation of the Hawaiian Islands resulted from the slow movement of a tecton ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
North American Plate
The North American Plate is a tectonic plate covering most of North America, Cuba, the Bahamas, extreme northeastern Asia, and parts of Iceland and the Azores. With an area of , it is the Earth's second largest tectonic plate, behind the Pacific Plate (which borders the plate to the west). It extends eastward to the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and westward to the Chersky Range in eastern Siberia. The plate includes both continental and oceanic crust. The interior of the main continental landmass includes an extensive granitic core called a craton. Along most of the edges of this craton are fragments of crustal material called terranes, which are accreted to the craton by tectonic actions over a long span of time. It is thought that much of North America west of the Rocky Mountains is composed of such terranes. Boundaries The southern boundary with the Cocos Plate to the west and the Caribbean Plate to the east is a transform fault, represented by the Swan Islands Transform Fault unde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shield Volcano
A shield volcano is a type of volcano named for its low profile, resembling a warrior's shield lying on the ground. It is formed by the eruption of highly fluid (low viscosity) lava, which travels farther and forms thinner flows than the more viscous lava erupted from a stratovolcano. Repeated eruptions result in the steady accumulation of broad sheets of lava, building up the shield volcano's distinctive form. Shield volcanoes are found wherever fluid low-silica lava reaches the surface of a rocky planet. However, they are most characteristic of ocean island volcanism associated with hot spots or with continental rift volcanism. They include the largest volcanoes on earth, such as Tamu Massif and Mauna Loa. Giant shield volcanoes are found on other planets of the Solar System, including Olympus Mons on Mars and Sapas Mons on Venus. Etymology The term 'shield volcano' is taken from the German term ''Schildvulkan'', coined by the Austrian geologist Eduard Suess in 1888 an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Itcha Range
The Itcha Range, also known as the Itchas, is a small isolated mountain range in the West-Central Interior of British Columbia, Canada. It is located northeast of the community of Anahim Lake. With a maximum elevation of , it is the lowest of three mountain ranges on the Chilcotin Plateau extending east from the Coast Mountains. Two mountains are named in the Itcha Range; Mount Downton and Itcha Mountain. A large provincial park surrounds the Itcha Range and other features in its vicinity. More than 15 animal species are known to exist in the Itcha Range area, as well as a grassland community that is limited only to this location of British Columbia. The Itcha Range is within territory which has been occupied by aboriginal peoples for millennia. This area has a relatively dry environment compared to the Coast Mountains in the west. In contrast to most mountain ranges in British Columbia, the Itcha Range represents an inactive shield volcano. This highly dissected volcanic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ilgachuz Range
The Ilgachuz Range is a name given to an extinct shield volcano in British Columbia, Canada. It is not a mountain range in the normal sense, because it was formed as a single volcano that has been eroded for the past 5 million years. It lies on the Chilcotin Plateau, located some north-northwest of Vancouver and 30 km north of Anahim Lake. The highest peak of the range is Far Mountain. The range supports a unique grassland ecosystem. This type of grassland has not been seen anywhere else in central and southern British Columbia. The climate is cool and dry; typical of higher elevations of the Interior Plateau. The long West Road River rises in the Ilgachuz Range and flows east to its confluence with the Fraser River between Prince George and Quesnel. It drains an area of approximately 12,000 km2 and loses over 900 m elevation before joining the Fraser. Geology and history Origins The Ilgachuz Range began erupting 6.1 million years ago and has grown steadily ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rainbow Range (Chilcotin Plateau)
The Rainbow Range, formerly gazetted as the Rainbow Mountains, is a mountain range in British Columbia, Canada, located northwest of Anahim Lake. Located on the western edge of the Chilcotin Plateau, the range adjoins the Coast Mountains Pacific Ranges to the south, and the Kitimat Ranges to the north. In some classification systems it is considered part of the Coast Mountains. It lies north of the Bella Coola and Atnarko Rivers and south and west of the Dean River, which curves around its north flank, and is relatively drier in climate and easier of terrain than more mountainous areas immediately west. Once called Tsitsutl, meaning "rainbow mountains" in the Ulkatcho dialect of the Carrier language, that name is now the name of the range's highest peak. Geology The Rainbow Range is an eight-million-year-old (Miocene) massive peralkaline shield volcano in the Anahim Volcanic Belt which includes the lower but similar Itcha and Ilgachuz Ranges. The shield has a diameter of is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |