|
2-Methyl-5-hydroxytryptamine
2-Methyl-5-hydroxytryptamine (2-Methylserotonin, 2-Methyl-5-HT) is a tryptamine derivative closely related to the neurotransmitter serotonin which acts as a moderately selective full agonist at the 5-HT3 receptor. See also * 5-Carboxamidotryptamine * 5-Methoxytryptamine 5-Methoxytryptamine (5-MT), also known as mexamine, is a tryptamine derivative closely related to the neurotransmitters serotonin and melatonin. 5-MT has been shown to occur naturally in the body in low levels. It is biosynthesized via the deacet ... * α-Methyl-5-hydroxytryptamine References Serotonin receptor agonists Tryptamines Phenols 5-HT3 agonists {{nervous-system-drug-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tryptamines
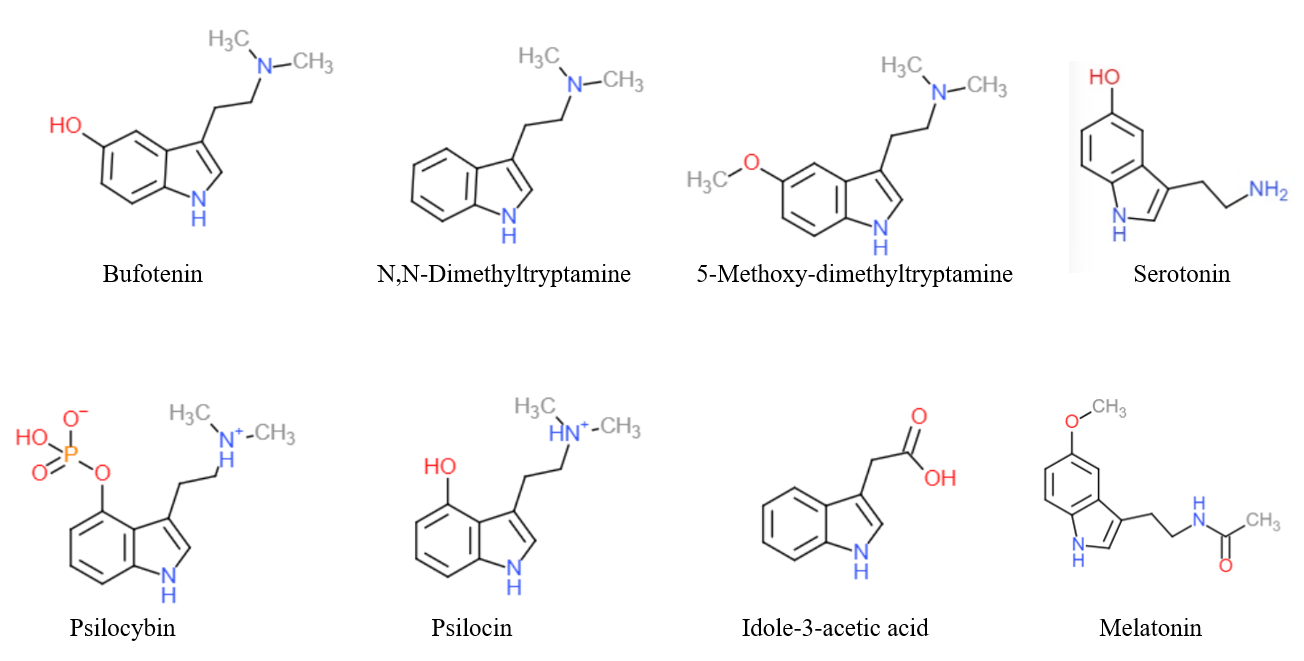
Substituted tryptamines, or serotonin analogues, are organic compounds which may be thought of as being derived from tryptamine itself. The molecular structures of all tryptamines contain an indole ring, joined to an amino (NH2) group via an ethyl (−CH2–CH2−) sidechain. In substituted tryptamines, the indole ring, sidechain, and/or amino group are modified by substituting another group for one of the hydrogen (H) atoms. Well-known tryptamines include serotonin, an important neurotransmitter, and melatonin, a hormone involved in regulating the sleep-wake cycle. Tryptamine alkaloids are found in fungi, plants and animals; and sometimes used by humans for the neurological or psychotropic effects of the substance. Prominent examples of tryptamine alkaloids include psilocybin (from "psilocybin mushrooms") and DMT. In South America, dimethyltryptamine is obtained from numerous plant sources, like chacruna, and it is often used in ayahuasca brews. Many synthetic tryptamines ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-Methoxytryptamine
5-Methoxytryptamine (5-MT), also known as mexamine, is a tryptamine derivative closely related to the neurotransmitters serotonin and melatonin. 5-MT has been shown to occur naturally in the body in low levels. It is biosynthesized via the deacetylation of melatonin in the pineal gland. 5-MT acts as a full agonist at the 5-HT1, 5-HT2, 5-HT4, 5-HT6, and 5-HT7 receptors. It has no affinity for the 5-HT3 receptor and its affinity for the 5-HT1E receptor is very weak in comparison to the other 5-HT1 receptors. Its affinity for the 5-HT5A receptor is unknown. Measured affinity for some receptors (not a complete list): * 5-HT1B receptors (Ki = 35 nM) S. Nigra / Domenech T, et al., 1997 * 5-HT1D receptors (Ki = 7.3 nM)Cortex / PEROUTKA ET AL., 1989 * 5-HT1E receptors (Ki = 3151 nM)Cloned / ZGOMBICK JM, ET AL., 1992 * 5-HT1F receptors (Ki = 1166 nM)Cloned / Adham N, et al., 1992 * 5-HT2A receptors (Ki = 295 nM)Cortex / HOYER ET AL., 1987 * 5-HT2B receptors (Ki = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
5-Carboxamidotryptamine
5-Carboxamidotryptamine (5-CT) is a tryptamine derivative closely related to the neurotransmitter serotonin. 5-CT acts as a non-selective, high-affinity full agonist at the 5-HT1A, 5-HT1B, 5-HT1D, 5-HT5A, and 5-HT7 receptors, as well as at the 5-HT2, 5-HT3, 5-HT6 receptors with lower affinity. It has negligible affinity for the 5-HT1E and 5-HT1F receptors. 5-CT binds most strongly to the 5-HT1A receptor and it was once thought to be selective for this site. Recently, a close derivative of 5-CT, AH-494 has been shown to function as an agonist of 5-HT7, although being more selective over 5-HT1A. Structural study indicated residue Ser5x43 might play critical roles in the selectivity of 5-CT across the serotonin receptor family. See also * 2-Methyl-5-hydroxytryptamine * 5-Benzyloxytryptamine * 5-Methoxytryptamine * α-Methyl-5-hydroxytryptamine * Frovatriptan * AH-494 * Acetryptine Acetryptine (INN) (developmental code name W-2965-A), also known as 5-acetyltryp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Α-Methyl-5-HT
α-Methylserotonin (αMS), also known as α-methyl-5-hydroxytryptamine (α-methyl-5-HT) or 5-hydroxy-α-methyltryptamine (5-HO-αMT), is a tryptamine derivative closely related to the neurotransmitter serotonin (5-HT). It acts as a non- selective serotonin receptor agonist and has been used extensively in scientific research to study the function of the serotonin system. Unlike serotonin, αMS is not metabolized by monoamine oxidase on account of the α- methyl substituent blocking the enzyme's access to the amine. As a result, it has a much longer half-life in comparison. Similarly to serotonin however, αMS poorly crosses the blood-brain-barrier due to its free hydroxyl group, and thus has only weak or no central effects when administered peripherally. α-Methyltryptophan (αMTP) is a prodrug to αMS which does cross the blood-brain-barrier and thus efficiently delivers αMS into the central nervous system. As a result, αMTP acts as an orally bioavailable false or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tryptamine
Tryptamine is an indolamine metabolite of the essential amino acid, tryptophan. The chemical structure is defined by an indole ─ a fused benzene and pyrrole ring, and a 2-aminoethyl group at the second carbon (third aromatic atom, with the first one being the heterocyclic nitrogen). The structure of tryptamine is a shared feature of certain aminergic neuromodulators including melatonin, serotonin, bufotenin and psychedelic derivatives such as dimethyltryptamine (DMT), psilocybin, psilocin and others. Tryptamine has been shown to activate trace amine-associated receptors expressed in the mammalian brain, and regulates the activity of dopaminergic, serotonergic and glutamatergic systems. In the human gut, symbiotic bacteria convert dietary tryptophan to tryptamine, which activates 5-HT4 receptors and regulates gastrointestinal motility. Multiple tryptamine-derived drugs have been developed to treat migraines, while trace amine-associated receptors are being explored as a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chemical Derivative
In chemistry, a derivative is a compound that is derived from a similar compound by a chemical reaction. In the past, derivative also meant a compound that ''can be imagined to'' arise from another compound, if one atom or group of atoms is replaced with another atom or group of atoms, but modern chemical language now uses the term structural analog for this meaning, thus eliminating ambiguity. The term "structural analogue" is common in organic chemistry. In biochemistry, the word is used for compounds that at least theoretically can be formed from the precursor compound. Chemical derivatives may be used to facilitate analysis. For example, melting point (MP) analysis can assist in identification of many organic compounds. A crystalline derivative may be prepared, such as a semicarbazone or 2,4-dinitrophenylhydrazone (derived from aldehydes or ketones), as a simple way of verifying the identity of the original compound, assuming that a table of derivative MP values is available ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neurotransmitter
A neurotransmitter is a signaling molecule secreted by a neuron to affect another cell across a synapse. The cell receiving the signal, any main body part or target cell, may be another neuron, but could also be a gland or muscle cell. Neurotransmitters are released from synaptic vesicles into the synaptic cleft where they are able to interact with neurotransmitter receptors on the target cell. The neurotransmitter's effect on the target cell is determined by the receptor it binds. Many neurotransmitters are synthesized from simple and plentiful precursors such as amino acids, which are readily available and often require a small number of biosynthetic steps for conversion. Neurotransmitters are essential to the function of complex neural systems. The exact number of unique neurotransmitters in humans is unknown, but more than 100 have been identified. Common neurotransmitters include glutamate, GABA, acetylcholine, glycine and norepinephrine. Mechanism and cycle Synthes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serotonin
Serotonin () or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Its biological function is complex and multifaceted, modulating mood, cognition, reward, learning, memory, and numerous physiological processes such as vomiting and vasoconstriction. Approximately 90% of the serotonin that the body produces is in the intestinal tract. Biochemically, the indoleamine molecule derives from the amino acid tryptophan, via the (rate-limiting) hydroxylation of the 5 position on the ring (forming the intermediate 5-hydroxytryptophan), and then decarboxylation to produce serotonin. Serotonin is primarily found in the enteric nervous system located in the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract). However, it is also produced in the central nervous system (CNS), specifically in the raphe nuclei located in the brainstem, Merkel cells located in the skin, pulmonary neuroendocrine cells and taste receptor cells in the tongue. Additionally, serotonin is stored in blood platelets and is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Functional Selectivity
Functional selectivity (or “agonist trafficking”, “biased agonism”, “biased signaling”, "ligand bias" and “differential engagement”) is the ligand-dependent selectivity for certain signal transduction pathways relative to a reference ligand (often the endogenous hormone or peptide) at the same receptor. Functional selectivity can be present when a receptor has several possible signal transduction pathways. To which degree each pathway is activated thus depends on which ligand binds to the receptor. Functional selectivity, or biased signaling, is most extensively characterized at G protein coupled receptors (GPCRs). A number of biased agonists, such as those at muscarinic M2 receptors tested as analgesics or antiproliferative drugs, or those at opioid receptors that mediate pain, show potential at various receptor families to increase beneficial properties while reducing side effects. For example, pre-clinical studies with G protein biased agonists at the μ-opioid re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Full Agonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the agonist, while an inverse agonist causes an action opposite to that of the agonist. Etymology From the Greek αγωνιστής (agōnistēs), contestant; champion; rival < αγων (agōn), contest, combat; exertion, struggle < αγω (agō), I lead, lead towards, conduct; drive Types of agonists can be activated by either endogenous agonists (such as |
5-HT3
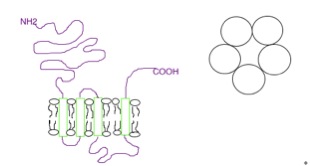
The 5-HT3 receptor belongs to the Cys-loop superfamily of ligand-gated ion channels (LGICs) and therefore differs structurally and functionally from all other 5-HT receptors (5-hydroxytryptamine, or serotonin receptors) which are G protein-coupled receptors. This ion channel is cation-selective and mediates neuronal depolarization and excitation within the central and peripheral nervous systems. As with other ligand gated ion channels, the 5-HT3 receptor consists of five subunits arranged around a central ion conducting pore, which is permeable to sodium (Na), potassium (K), and calcium (Ca) ions. Binding of the neurotransmitter 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin) to the 5-HT3 receptor opens the channel, which, in turn, leads to an excitatory response in neurons. The rapidly activating, desensitizing, inward current is predominantly carried by sodium and potassium ions. 5-HT3 receptors have a negligible permeability to anions. They are most closely related by homology to the nicotinic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serotonin Receptor Agonists
Serotonin () or 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) is a monoamine neurotransmitter. Its biological function is complex and multifaceted, modulating mood, cognition, reward, learning, memory, and numerous physiological processes such as vomiting and vasoconstriction. Approximately 90% of the serotonin that the body produces is in the intestinal tract. Biochemically, the indoleamine molecule derives from the amino acid tryptophan, via the (rate-limiting) hydroxylation of the 5 position on the ring (forming the intermediate 5-hydroxytryptophan), and then decarboxylation to produce serotonin. Serotonin is primarily found in the enteric nervous system located in the gastrointestinal tract (GI tract). However, it is also produced in the central nervous system (CNS), specifically in the raphe nuclei located in the brainstem, Merkel cells located in the skin, pulmonary neuroendocrine cells and taste receptor cells in the tongue. Additionally, serotonin is stored in blood platelets and is rel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |