|
1974 In Paleontology
Bryophytes Plants Angiosperms Archosauromorphs General research * ''Massospondylus'' gastroliths are documented.Raath (1974). Sanders, Manley, and Carpenter (2001), "Table 12.1" page 167. Newly named dinosaurs Data courtesy of George Olshevsky's dinosaur genera list. Newly named birds Newly named pterosaurs References {{Reflist * Raath, M.A. (1974). Fossil vertebrate studies in Rhodesia: further evidence of gastroliths in Prosauropod dinosaurs. Arnoldia Rhodesia. 7 (5): 1–7. * Sanders F, Manley K, Carpenter K. Gastroliths from the Lower Cretaceous sauropod Cedarosaurus weiskopfae. In: Tanke D.H, Carpenter K, editors. Mesozoic vertebrate life: new research inspired by the paleontology of Philip J. Currie. Indiana University Press; Bloomington, IN: 2001. pp. 166–180. Paleontology Paleontology (), also spelled palaeontology or palæontology, is the scientific study of life that existed prior to, and sometimes including, the start of the Holocene ep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerro Barcino Formation
The Cerro Barcino Formation (also known as the Gorro Frigio Formation) is a geological formation in South America whose strata span the Early Cretaceous to the earliest Late Cretaceous. The top age for the formation has been estimated to be Cenomanian. Earlier estimates placed the formation until the Campanian. The formation was deposited in the Cañadón Asfalto Basin, a rift basin that started forming in the earliest Jurassic. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation. The Cerro Barcino Formation is the second-youngest unit of the Chubut Group, which also includes the older Los Adobes Formation. Both formations cover a vast area in Chubut Province, Argentina. The two formations are distinguished by geological features suggesting a distinct change in climate, from a wetter, flood plain environment in the Los Adobes to a much more arid, desert-like environment in the Cerro Barcino.Rauhut et al., 2003 The Cerro Barcino Formation is subdiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prenocephale PrenesNV
''Prenocephale'' (meaning "sloping head") is a genus of small pachycephalosaurid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Nemegt Formation of Mongolia. It was similar in many ways to its close relative, ''Homalocephale''. Description Adult ''Prenocephale'' measured in length and in body mass. Unlike the flattened wedge-shaped skull of ''Homalocephale'' (a possible juvenile trait also potentially seen in early growth stages of '' Pachycephalosaurus''), the head of ''Prenocephale'' was rounded and sloping. The dome had a row of small bony spikes and bumps. Like some other pachycephalosaurs, ''Prenocephale'' is known only from skulls and a few other small bones. For this reason, reconstructions usually depict ''Prenocephale'' as sharing the basic body plan common to all of the other Pachycephalosauria: a stout body with a short, thick neck, short forelimbs and tall hind legs. The head of ''Prenocephale'' was comparable to that of ''Stegoceras'', albeit with closed supratemporal fenestr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prenocephale
''Prenocephale'' (meaning "sloping head") is a genus of small pachycephalosaurid dinosaur from the Late Cretaceous Nemegt Formation of Mongolia. It was similar in many ways to its close relative, ''Homalocephale''. Description Adult ''Prenocephale'' measured in length and in body mass. Unlike the flattened wedge-shaped skull of ''Homalocephale'' (a possible juvenile trait also potentially seen in early growth stages of '' Pachycephalosaurus''), the head of ''Prenocephale'' was rounded and sloping. The dome had a row of small bony spikes and bumps. Like some other pachycephalosaurs, ''Prenocephale'' is known only from skulls and a few other small bones. For this reason, reconstructions usually depict ''Prenocephale'' as sharing the basic body plan common to all of the other Pachycephalosauria: a stout body with a short, thick neck, short forelimbs and tall hind legs. The head of ''Prenocephale'' was comparable to that of ''Stegoceras'', albeit with closed supratemporal fenestr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labocania Anomala
''Labocania'' is a genus of carnivorous theropod dinosaur of uncertain affinities from Baja California, Mexico, which lived 73 million years ago, in the Campanian stage of the late Cretaceous Period. In the summer of 1970, the National Geographic Society and the Los Angeles County Museum of Natural History organized a joint paleontological expedition, led by geologist William J. Morris, to the Arroyo del Rosario in Baja California. While prospecting, volunteer Harley James Garbani discovered the skeleton of a theropod north of Punta Baja near Cerro Rayado. Garbani excavated the site in 1970 and 1971. The type species, ''Labocania anomala'', was described and named by Ralph Molnar in 1974. The generic name references the La Bocana Roja Formation, named after ''la Bocana Roja'', "the red estuary". The specific name means "anomalous" in Latin, in reference to the distinctive build. The holotype, LACM 20877, was found in a layer of the La Bocana Roja Formation, dating from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tyrannosauroidea
Tyrannosauroidea (meaning 'tyrant lizard forms') is a superfamily (or clade) of coelurosaurian theropod dinosaurs that includes the family Tyrannosauridae as well as more basal relatives. Tyrannosauroids lived on the Laurasian supercontinent beginning in the Jurassic Period. By the end of the Cretaceous Period, tyrannosauroids were the dominant large predators in the Northern Hemisphere, culminating in the gigantic ''Tyrannosaurus''. Fossils of tyrannosauroids have been recovered on what are now the continents of North America, Europe and Asia, with fragmentary remains possibly attributable to tyrannosaurs also known from South America and Australia. Tyrannosauroids were bipedal carnivores, as were most theropods, and were characterized by numerous synapomorphy, skeletal features, especially of the skull and pelvis. Early in their existence, tyrannosauroids were small predators with long, three-fingered forelimbs. Late Cretaceous genera became much larger, including some of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Bocana Roja Formation
La Bocana Roja Formation is a geological formation in Baja California, Mexico whose strata date back to the Late Cretaceous. Dinosaur remains are among the fossils that have been recovered from the formation.Weishampel, David B; et al. (2004). "Dinosaur distribution (Late Cretaceous, North America)." In: Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; and Osmólska, Halszka (eds.): The Dinosauria, 2nd, Berkeley: University of California Press. Pp. 574-588. . Vertebrate paleofauna See also * List of dinosaur-bearing rock formations This list of dinosaur-bearing rock formations is a list of geologic formations in which dinosaur fossils have been documented. Containing body fossils * List of stratigraphic units with dinosaur body fossils ** List of stratigraphic units with ... Footnotes References * Hilton, Richard P. 2003. Dinosaurs and Other Mesozoic Reptiles of California. Berkeley: University of California Press. 318 pp. * Weishampel, David B.; Dodson, Peter; and Osmólska, Hals ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campanian
The Campanian is the fifth of six ages of the Late Cretaceous Epoch on the geologic timescale of the International Commission on Stratigraphy (ICS). In chronostratigraphy, it is the fifth of six stages in the Upper Cretaceous Series. Campanian spans the time from 83.6 (± 0.2) to 72.1 (± 0.2) million years ago. It is preceded by the Santonian and it is followed by the Maastrichtian. The Campanian was an age when a worldwide sea level rise covered many coastal areas. The morphology of some of these areas has been preserved: it is an unconformity beneath a cover of marine sedimentary rocks. Etymology The Campanian was introduced in scientific literature by Henri Coquand in 1857. It is named after the French village of Champagne in the department of Charente-Maritime. The original type locality was a series of outcrop near the village of Aubeterre-sur-Dronne in the same region. Definition The base of the Campanian Stage is defined as a place in the stratigraphic column wher ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ralph Molnar
Ralph E. Molnar is a paleontologist who had been Curator of Mammals at the Queensland Museum and more recently associated with the Museum of Northern Arizona. He is also a research associate at the Texas natural Science Centre. He co-authored descriptions of the dinosaurs ''Muttaburrasaurus'', '' Kakuru'',Molnar, R.E. & Pledge, N.S. (1980) "A new theropod dinosaur from South Australia." ''Alcheringa'' 4:281-287 ''Minmi'' and ''Ozraptor'', as well as the mammal ''Steropodon ''Steropodon'' is a genus of prehistoric monotreme, or egg-laying mammal. It contains a single species, ''Steropodon galmani'', that lived about 105 to 93.3 million years ago (mya) in the Early to Late Cretaceous period. It is one of the oldest m ...''. References Living people Year of birth missing (living people) {{paleontologist-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labocania
''Labocania'' is a genus of carnivorous theropod dinosaur of uncertain affinities from Baja California, Mexico, which lived 73 million years ago, in the Campanian stage of the late Cretaceous Period. In the summer of 1970, the National Geographic Society and the Los Angeles County Museum of Natural History organized a joint paleontological expedition, led by geologist William J. Morris, to the Arroyo del Rosario in Baja California. While prospecting, volunteer Harley James Garbani discovered the skeleton of a theropod north of Punta Baja near Cerro Rayado. Garbani excavated the site in 1970 and 1971. The type species, ''Labocania anomala'', was described and named by Ralph Molnar Ralph E. Molnar is a paleontologist who had been Curator of Mammals at the Queensland Museum and more recently associated with the Museum of Northern Arizona. He is also a research associate at the Texas natural Science Centre. He co-authored descr ... in 1974. The generic name references the La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
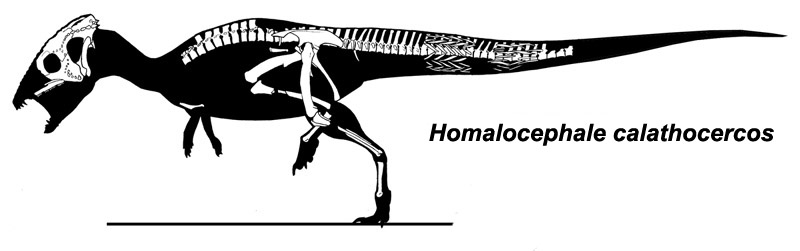
Homalocephale Body
''Homalocephale'' (from Greek ὁμαλός, ''homalos'', "even", and κεφαλή, ''kephalē'', "head") is a genus of pachycephalosaurid dinosaur that lived during the Late Cretaceous period of what is now the Nemegt Formation, Mongolia, about 70 million years ago. The genus was described in 1974 by Halszka Osmólska and Teresa Maryańska, and consists of a single species, ''H. calathocercos''. Though ''Homalocephale'' has been regarded as a synonym (and juvenile form) of ''Prenocephale'', juvenile specimens of the latter indicate that they were distinct. ''Homalocephale'' was long and possibly herbivorous. Discovery The type species, ''H. calathocercos'', was described from an incomplete skull and postcranial material (holotype MPC-D 100/1201) from the Nemegt locality of the Nemegt Formation. The specimen has large openings on the top of the skull, a distinct frontoparietal suture, low and long infratemporal fenestrae, and a large, round eye socket. The forehead is notably ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Late Cretaceous
The Late Cretaceous (100.5–66 Ma) is the younger of two epochs into which the Cretaceous Period is divided in the geologic time scale. Rock strata from this epoch form the Upper Cretaceous Series. The Cretaceous is named after ''creta'', the Latin word for the white limestone known as chalk. The chalk of northern France and the white cliffs of south-eastern England date from the Cretaceous Period. Climate During the Late Cretaceous, the climate was warmer than present, although throughout the period a cooling trend is evident. The tropics became restricted to equatorial regions and northern latitudes experienced markedly more seasonal climatic conditions. Geography Due to plate tectonics, the Americas were gradually moving westward, causing the Atlantic Ocean to expand. The Western Interior Seaway divided North America into eastern and western halves; Appalachia and Laramidia. India maintained a northward course towards Asia. In the Southern Hemisphere, Australia and Ant ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)