|
168th (2nd London) Brigade
The 168th (2nd London) Brigade was an infantry brigade formation of the British Army that saw service during both the First and the Second World Wars. Throughout its existence, serving under many different titles and designations, the brigade was an integral part of the 56th (London) Infantry Division. It served on the Western Front during First World War and in the Italian Campaign during the Second World War. It was finally disbanded in the 1960s. Origin The Volunteer Force of part-time soldiers was created following an invasion scare in 1859, and its constituent units were progressively aligned with the Regular British Army during the later 19th Century. The Stanhope Memorandum of December 1888 introduced a Mobilisation Scheme for Volunteer units, which would assemble in their own brigades at key points in case of war. In peacetime these brigades provided a structure for collective training. The East London Brigade was one of the formations organised at this time. The Command ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Infantry
Infantry is a military specialization which engages in ground combat on foot. Infantry generally consists of light infantry, mountain infantry, motorized infantry & mechanized infantry, airborne infantry, air assault infantry, and marine infantry. Although disused in modern times, heavy infantry also commonly made up the bulk of many historic armies. Infantry, cavalry, and artillery have traditionally made up the core of the combat arms professions of various armies, with the infantry almost always comprising the largest portion of these forces. Etymology and terminology In English, use of the term ''infantry'' began about the 1570s, describing soldiers who march and fight on foot. The word derives from Middle French ''infanterie'', from older Italian (also Spanish) ''infanteria'' (foot soldiers too inexperienced for cavalry), from Latin '' īnfāns'' (without speech, newborn, foolish), from which English also gets ''infant''. The individual-soldier te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grenadier Guards
"Shamed be whoever thinks ill of it." , colors = , colors_label = , march = Slow: " Scipio" , mascot = , equipment = , equipment_label = , battles = OudenardeWaterlooAlma Inkerman SevastopolOmdurman Ypres Battle of the Bulge Cyprus Emergency , anniversaries = , decorations = , battle_honours = , battle_honours_label = , disbanded = , flying_hours = , website = , commander1 = The King , commander1_label = Colonel-in-Chief , commander2 = The Queen Consort , commander2_label = Colonel of the Regiment , commander3 = , commander3_label = , commander4 = , commander4_label ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Army Medical Corps
The Royal Army Medical Corps (RAMC) is a specialist corps in the British Army which provides medical services to all Army personnel and their families, in war and in peace. The RAMC, the Royal Army Veterinary Corps, the Royal Army Dental Corps and Queen Alexandra's Royal Army Nursing Corps form the Army Medical Services. History Origins Medical services in the British armed services date from the formation of the Standing Regular Army after the Restoration of Charles II in 1660. Prior to this, from as early as the 13th century there are records of surgeons and physicians being appointed by the English army to attend in times of war; but this was the first time a career was provided for a Medical Officer (MO), both in peacetime and in war. For much of the next two hundred years, army medical provision was mostly arranged on a regimental basis, with each battalion arranging its own hospital facilities and medical supplies. An element of oversight was provided by the appoin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Army Service Corps
The Royal Army Service Corps (RASC) was a corps of the British Army responsible for land, coastal and lake transport, air despatch, barracks administration, the Army Fire Service, staffing headquarters' units, supply of food, water, fuel and domestic materials such as clothing, furniture and stationery and the supply of technical and military equipment. In 1965 its functions were divided between other Corps ( RCT and RAOC) and the RASC ceased to exist; subsequently, in 1993, they in their turn (with some functions of the Royal Engineers) became the "Forming Corps" of the Royal Logistic Corps. History For centuries, army transport was operated by contracted civilians. The first uniformed transport corps in the British Army was the Royal Waggoners formed in 1794. It was not a success and was disbanded the following year. In 1799, the Royal Waggon Corps was formed; by August 1802, it had been renamed the Royal Waggon Train. This was reduced to only two troops in 1818 and fin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Post Office Rifles
The Post Office Rifles was a unit of the British Army, first formed in 1868 from volunteers as part of the Volunteer Force, which later became the Territorial Force (and later the Territorial Army). The unit evolved several times until 1921, after which the name was lost during one of many reorganisations. History Beginnings – 49th Middlesex Rifle Volunteers Corps (Post Office Rifles) When the Volunteer Force was formed in 1859/60 Viscount Bury raised the 21st Middlesex Rifles Volunteer Corps (Civil Service Rifles) drawing its recruits from civil servants based in London. There were sufficient recruits from the GPO staff to form a Post Office company, which was placed under Captain John Lowther du Plat Taylor's command. On 13 December 1867 a bomb exploded outside Middlesex House of Detention, Clerkenwell. It was an attempt to rescue two members of Irish Republican Brotherhood (IRB) detained there awaiting trial. The Government's response was to raise special constables t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
4th (City Of London) Battalion, London Regiment
The 4th (City of London) Battalion, London Regiment (Royal Fusiliers) was a Volunteer unit of Britain's Territorial Army (United Kingdom), Territorial Army (TA) recruited from East London. During World War I it raised four battalions, which carried out garrison duty in Malta and Egypt, served at Gallipoli Campaign, Gallipoli and against the Senussi Campaign, Senussi, and saw a great deal of action on the Western Front (World War I), Western Front, notably in the Attack on the Gommecourt Salient in 1916, at Battle of Bullecourt#Second Battle of Bullecourt .283.E2.80.9317 May 1917.29, Bullecourt in 1917 and at Operation Michael#First Battle of Arras.2C 28 March, Oppy Wood and Battle of Amiens (1918), Chipilly Ridge in 1918. During World War II it served as an anti-aircraft regiment in the Battle of France and during the Blitz in 1940 and in Western Front (World War II), North West Europe in 1944–45. It continued in the TA until 1961. Volunteer Force An invasion scare in 1859 led t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
7th (City Of London) Battalion, London Regiment
The 7th (City of London) Battalion of the London Regiment was a volunteer unit of the British Army from 1860 until 1961. Recruited from London working men, it sent volunteers to the Second Boer War, saw extensive service on the Western Front during World War I, and defended the United Kingdom as a searchlight regiment during World War II. Origins An invasion scare in 1859 led to the creation of the Volunteer Movement in Britain. One of the movement's leaders was the journalist, playwright and poet Alfred Bate Richards, who convened a meeting at St Martin's Hall, Long Acre, London, on 16 April 1859 that led the War Office to authorise the recruitment of Rifle Volunteer Corps (RVCs). Richards himself enlisted 1000 men to form the 'Workmen's Volunteer Brigade'. Although the unit began holding parades at the City of London's Guildhall in the autumn of 1860,''Morning Advertiser'', ''Times'', 24 Sep; ''Volunteer Services Gazette'', 29 Sep; ''Bengal Hurkaru'' 31 Oct 1860. the first of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
City Of London Rifles
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be defined as a permanent and densely settled place with administratively defined boundaries whose members work primarily on non-agricultural tasks. Cities generally have extensive systems for housing, transportation, sanitation, utilities, land use, production of goods, and communication. Their density facilitates interaction between people, government organisations and businesses, sometimes benefiting different parties in the process, such as improving efficiency of goods and service distribution. Historically, city-dwellers have been a small proportion of humanity overall, but following two centuries of unprecedented and rapid urbanization, more than half of the world population now lives in cities, which has had profound consequences for g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London Rifle Brigade
The London Rifle Brigade was a volunteer regiment of the British Army. History The regiment was first raised in the City of London on 14 December 1859 as 1st London (City of London Volunteer Rifle Brigade) Rifle Volunteer Corps, a rifle volunteer unit made up of five companies. On 1 July 1881 it was made part of the King's Royal Rifle Corps as its 9th Volunteer Battalion. Ten years later, in December 1891, it was renamed the 1st London Volunteer Rifle Corps (City of London Volunteer Rifle Brigade). One of its early officers was Sir Charles Hunter. In 1893 its headquarters was moved to 130 Bunhill Row Bunhill Row is a street located in St Luke's, London Borough of Islington, London. The street runs north–south from Old Street to Chiswell Street. On the east side are the cemetery of Bunhill Fields and the open space of the Honourable Art ... in London. When the volunteer and militia units were re-organised as the Territorial Force (TF) in 1908 the unit was again rename ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
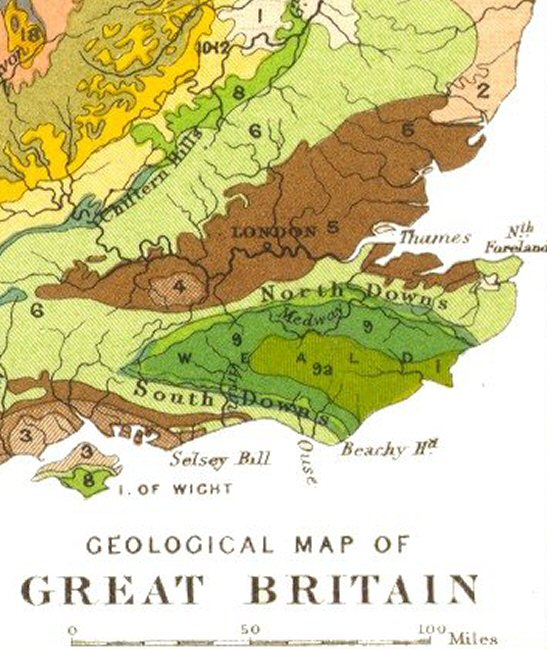
North Downs
The North Downs are a ridge of chalk hills in south east England that stretch from Farnham in Surrey to the White Cliffs of Dover in Kent. Much of the North Downs comprises two Areas of Outstanding Natural Beauty (AONBs): the Surrey Hills and the Kent Downs. The North Downs Way National Trail runs along the North Downs from Farnham to Dover. The highest point in the North Downs is Botley Hill, Surrey ( above sea level). The ''County Top'' of Kent is Betsom's Hill ( above sea level), which is less than 1 km from Westerham Heights, Bromley, the highest point in Greater London at an elevation of . Etymology 'Downs' is from Old English ''dun'', meaning, amongst other things, "hill". The word acquired the sense of "elevated rolling grassland" around the 14th century. The name contains "North" to distinguish them from a similar range of hills – the South Downs – which runs roughly parallel to them but some to the south. Geography The narrow spine of the Hog's Bac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
London Defence Positions
The London Defence Positions were a late 19th century scheme of earthwork fortifications in the south-east of England, designed to protect London from foreign invasion landing on the south coast. The positions were a carefully surveyed contingency plan for a line of entrenchments, which could be quickly excavated in a time of emergency. The line to be followed by these entrenchments was supported by thirteen permanent small polygonal forts or redoubts called London Mobilisation Centres, which were equipped with all the stores and ammunition that would be needed by the troops tasked with digging and manning the positions. Origins The 1859 Royal Commission on the Defence of the United Kingdom report on Britain's defences believed that London was practically undefendable; they proposed a fort at Shooters Hill to defend the Royal Arsenal at Woolwich, but it was never acted upon. Following a number of proposals by senior military figures, an 1888 memorandum written by Colonel John ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caterham Barracks
Caterham Barracks was a military installation in Caterham, Surrey. History The barracks were built as a depot for the Foot Guards regiments in 1877. The construction reflected a more humane style of barrack design in the aftermath of the Crimean War; the barrack blocks included better sanitation as well as cross-ventilation and cross-lighting of sleeping facilities for the first time. A local public house (the Caterham Arms) which was frequented by soldiers was targeted by the IRA Ira or IRA may refer to: *Ira (name), a Hebrew, Sanskrit, Russian or Finnish language personal name *Ira (surname), a rare Estonian and some other language family name *Iran, UNDP code IRA Law *Indian Reorganization Act of 1934, US, on status of ... with a bomb injuring 23 civilians and 10 off-duty soldiers in August 1975. The barracks were closed in 1995 and the site was redeveloped for housing using urban village principles after planning consent was given in June 1990. References Installations ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |