|
15th Hussars
The 15th The King's Hussars was a cavalry regiment in the British Army. First raised in 1759, it saw service over two centuries, including the First World War, before being amalgamated with the 19th Royal Hussars into the 15th/19th The King's Royal Hussars in 1922. History Early wars The regiment was raised in the London area by George Augustus Eliott, 1st Baron Heathfield as Elliots Light Horse as the first of the new regiments of light dragoons in 1759. It was renamed the 15th Regiment of (Light) Dragoons in 1760. The regiment landed in Bremen in June 1760 for service in the Seven Years' War. The regiment were largely responsible for the victory, suffering 125 of the 186 allied casualties at the Battle of Emsdorf in July 1760. Lieutenant Colonel William Erskine, commanding the regiment, presented King George III with 16 colours captured by his regiment after the battle. During the battle the French commander, Major-General Christian-Sigismund von Glaubitz, was taken pris ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flag Of The British Army
A flag is a piece of fabric (most often rectangular or quadrilateral) with a distinctive design and colours. It is used as a symbol, a signalling device, or for decoration. The term ''flag'' is also used to refer to the graphic design employed, and flags have evolved into a general tool for rudimentary signalling and identification, especially in environments where communication is challenging (such as the maritime environment, where semaphore is used). Many flags fall into groups of similar designs called flag families. The study of flags is known as " vexillology" from the Latin , meaning "flag" or " banner". National flags are patriotic symbols with widely varied interpretations that often include strong military associations because of their original and ongoing use for that purpose. Flags are also used in messaging, advertising, or for decorative purposes. Some military units are called "flags" after their use of flags. A ''flag'' (Arabic: ) is equivalent to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
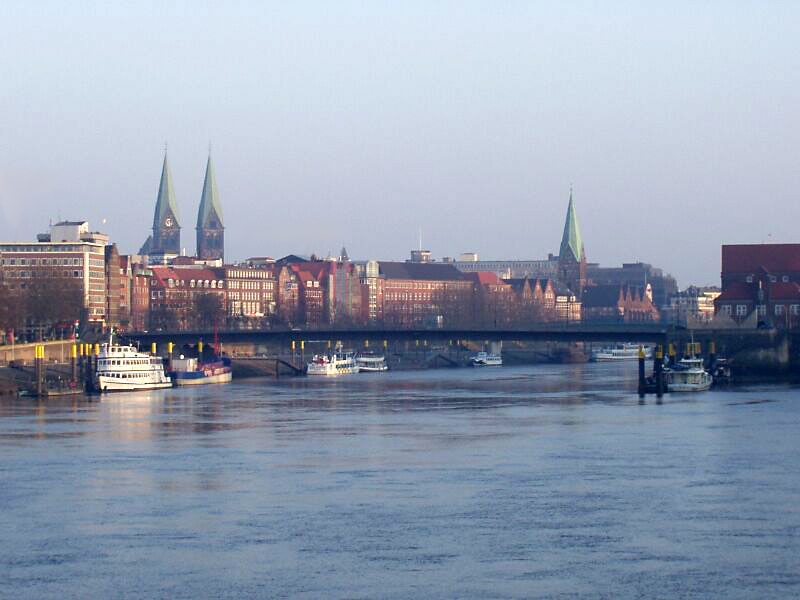
Bremen
Bremen (Low German also: ''Breem'' or ''Bräm''), officially the City Municipality of Bremen (german: Stadtgemeinde Bremen, ), is the capital of the Germany, German States of Germany, state Bremen (state), Free Hanseatic City of Bremen (''Freie Hansestadt Bremen''), a two-city-state consisting of the cities of Bremen and Bremerhaven. With about 570,000 inhabitants, the Hanseatic League, Hanseatic city is the List of cities in Germany by population, 11th largest city of Germany and the second largest city in Northern Germany after Hamburg. Bremen is the largest city on the River Weser, the longest river flowing entirely in Germany, lying some upstream from its River mouth, mouth into the North Sea, and is surrounded by the state of Lower Saxony. A commercial and industrial city, Bremen is, together with Oldenburg (city), Oldenburg and Bremerhaven, part of the Bremen/Oldenburg Metropolitan Region, with 2.5 million people. Bremen is contiguous with the Lower Saxon towns of Delmenhor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Willems
The Battle of Willems (10 May 1794) saw a Republican French army under Jean-Charles Pichegru oppose Coalition forces commanded by Prince Frederick, Duke of York and Albany, as part of a French attempt to defeat an Allied counteroffensive and continue its own 1794 offensive in the Low Countries, which had already seen success with the battle of Mouscron and the capture of the important cities of Menin and Courtrai. The battle was a French tactical defeat, but victory in the battle of Courtrai the next day, coupled with the Duke of York's realisation that he was badly outnumbered, led to Allied withdrawal and a strategic victory for the French, who retained their hold on Menin and Courtrai. During this action, French infantry formed in squares and repulsed Coalition cavalry for the first time during the war. The fighting occurred during the War of the First Coalition near Kortrijk, Belgium, located about west of Brussels. Background Plans For the spring 1794 campaign, Lazare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
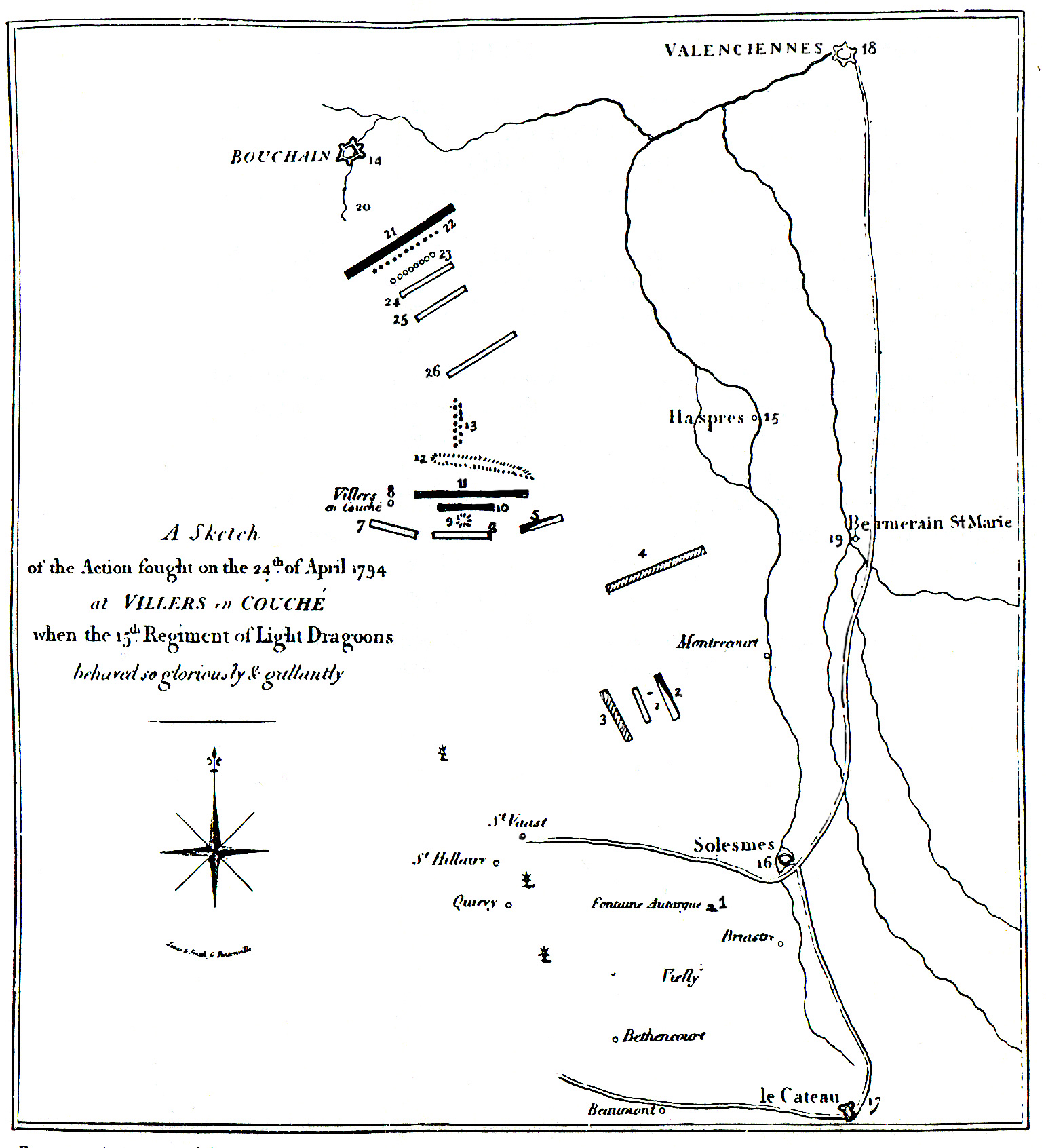
Battle Of Villers-en-Cauchies
In the Battle of Villers-en-Cauchies, fought on 24 April 1794, a small Anglo-Austrian cavalry force routed a vastly more numerous French division during the Flanders Campaign of the French Revolutionary Wars. Villers-en-Cauchies is 15 km south of Valenciennes. Background At the beginning of the Flanders Campaign in 1794, the main Coalition army led by the Prince Josias of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld advanced against the French Army of the North under Charles Pichegru. By mid-April the Coalition began the Siege of Landrecies while the observation army took position in a broad semi-circle to cover the operation. On 23 April a French force was mustered in an attempt to cut off the Allied column of Ludwig von Wurmb from the rest of the observation army which consisted of the corps of François Sébastien de Croix de Clerfayt and Prince Frederick, Duke of York and Albany. Wurmb's command lay in a cordon of detachments between Denain and Hellesmes. All the available French troo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Landrecies (1794)
The siege of Landrecies (17 – 30 April 1794) was a military operation conducted by the (mobile army) of the Dutch States Army, commanded by the William I of the Netherlands, Hereditary Prince (assisted by auxiliary forces from the army of the Austrian empire), against the fortress of Landrecies, garrisoned by troops of the First French Republic under general Henri Victor Roulland during the Spring 1794 campaign of the Flanders Campaign, part of the War of the First Coalition. The fortress capitulated on 30 April 1794. Background In the amended that the military leaders of the Coalition agreed upon in The Hague in early April the capture of the fortress of Landrecies was a key objective. The mobile army of the States Army (which had not been active since the Battle of Menin (1793)) was charged with obtaining this objective. Landrecies had long been a contested city between France and the Habsburg Netherlands of which it originally a part. In 1543 the French conquered it and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
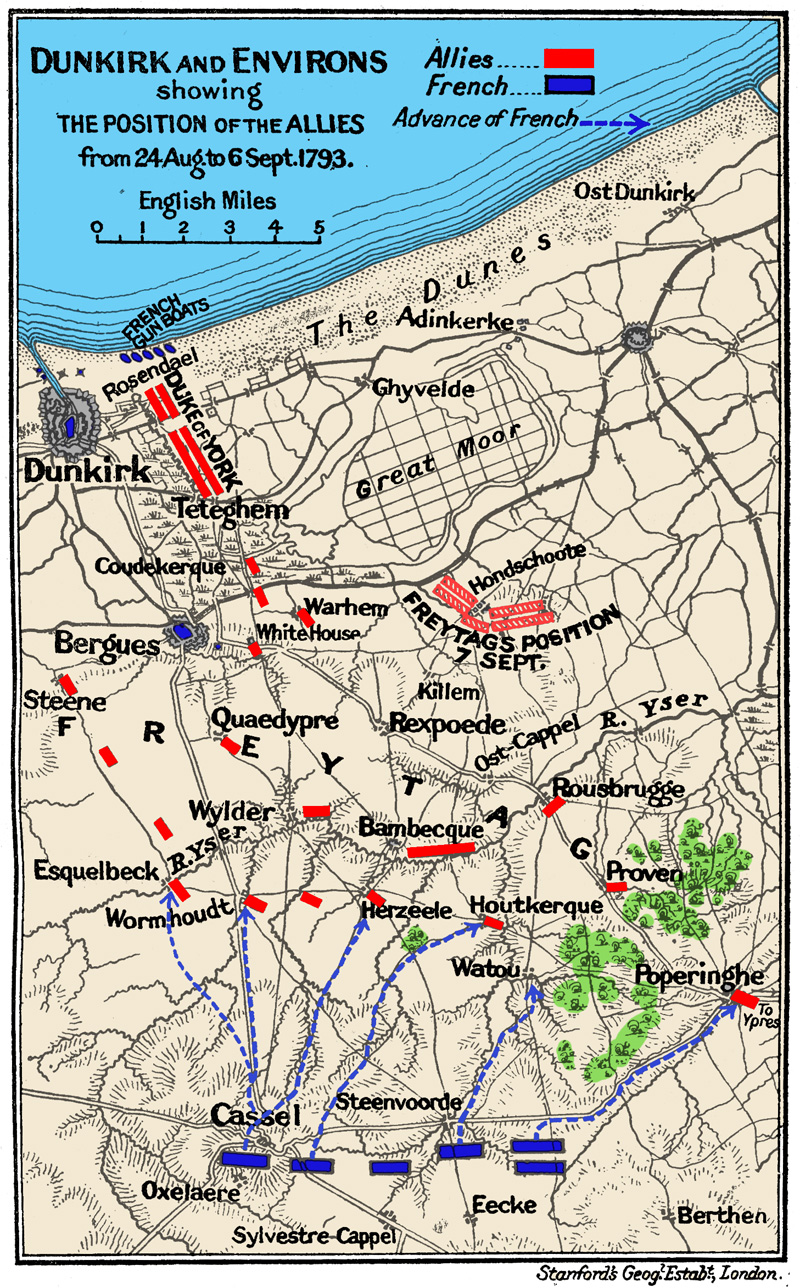
Siege Of Dunkirk (1793)
The siege of Dunkirk took place in the Autumn of 1793 when British, Hanoverian, Austrian, and Hesse-Kassel troops under the command of Prince Frederick, Duke of York besieged the fortified French border port of Dunkirk, as part as the Flanders campaign of the French Revolutionary Wars. Following a Coalition defeat at the Battle of Hondshoote they were forced to raise the siege and withdraw northeast. Siege The decision to besiege Dunkirk was taken not by military commanders, but by the British government, chiefly by William Pitt's closest advisor, War Minister Henry Dundas. Right from the beginning of the campaign Dundas had considered the possession of Dunkirk as desirable, both as a bargaining counter in peace negotiations and as a potential British base in Europe. As a military objective towards winning the war, however, its value was far less significant, as it arguably prevented Prince Frederick, Duke of York from supporting the main Allied thrust further inland. N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siege Of Valenciennes (1793)
The siege of Valenciennes took place between 13 June and 28 July 1793, during the Flanders Campaign of the War of the First Coalition. The French garrison under Jean Henri Becays Ferrand was blockaded by part of the army of Prince Josias of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld, commanded by the Prince Frederick, Duke of York and Albany. Valenciennes fell on 28 July, resulting in an Allied victory. Background Following the defeat of the French Republican armies at Neerwinden, the Allied army under the Prince of Coburg recovered much of the Austrian Netherlands and began besieging Condé-sur-l'Escaut, while the demoralised French army's attempts to relieve the fortress in actions at Saint-Amand and Raismes were driven back. By mid-May Coburg was reinforced to a strength approaching 90,000, which allowed the Allies to drive the French from an entrenched camp in the Battle of Famars on 23 May, and lay siege to Valenciennes. Many of the French who had been driven from Famars took refuge in the fort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Famars
The Battle of Famars was fought on 23 May 1793 during the Flanders Campaign of the War of the First Coalition. An Allied Austrian, Hanoverian, and British army under Prince Josias of Saxe-Coburg-Saalfeld defeated the French Army of the North led by François Joseph Drouot de Lamarche. The battle occurred near the village of Famars in northern France, five km south of Valenciennes. Background In May 1793, following a series of reverses the French Republican army in the Low Countries was in a desperate situation. Dispirited after the death of its former commander Augustin-Marie Picot de Dampierre, it was tired and disorganised. In addition it was further weakened by detachments taken from each battalion to serve in the war in the Vendée. Although new recruits were being allocated from the levy of 300,000, many of these deserted or were otherwise unfit for service. The new temporary commander Lamarche realised that all that could be done for the moment was to draw back to an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flanders Campaign
The Flanders Campaign (or Campaign in the Low Countries) was conducted from 20 April 1792 to 7 June 1795 during the first years of the War of the First Coalition. A coalition of states representing the Ancien Régime in Western Europe – Austria (including the Southern Netherlands), Prussia, Great Britain, the Dutch Republic (the Northern Netherlands), Hanover and Hesse-Kassel – mobilised military forces along all the French frontiers, with the intention to invade Revolutionary France and end the French First Republic. The radicalised French revolutionaries, who broke the Catholic Church's power (1790), abolished the monarchy (1792) and even executed the deposed king Louis XVI of France (1793), vied to spread the Revolution beyond France's borders, by violent means if necessary. A quick French success in the Battle of Jemappes in November 1792 was followed by a major Coalition victory at Neerwinden in March 1793. After this initial stage, the largest of these for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ostend
Ostend ( nl, Oostende, ; french: link=no, Ostende ; german: link=no, Ostende ; vls, Ostende) is a coastal city and municipality, located in the province of West Flanders in the Flemish Region of Belgium. It comprises the boroughs of Mariakerke, Raversijde, Stene and Zandvoorde, and the city of Ostend proper – the largest on the Belgian coast. History Origin to Middle Ages In the Early Middle Ages, Ostend was a small village built on the east-end () of an island (originally called Testerep) between the North Sea and a beach lake. Although small, the village rose to the status of "town" around 1265, when the inhabitants were allowed to hold a market and to build a market hall. The major source of income for the inhabitants was fishing. The North Sea coastline has always been rather unstable due to the power of the water. In 1395 the inhabitants decided to build a new Ostend behind large dikes and further away from the always-threatening sea. 15th to 18th century T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Wilhelmsthal
The Battle of Wilhelmsthal (sometimes written as the Battle of Wilhelmstadt) was fought on 24 June 1762 during the Seven Years' War between the allied forces of Britain, Prussia, Hanover, Brunswick and Hesse under the command of the Duke of Brunswick against France. Once again, the French threatened Hanover, so the Allies manoeuvered around the French, surrounded the invasion force, and forced them to retreat. It was the last major action fought by Brunswick's force before the Peace of Paris brought an end to the war. Background France had made a number of attempts to invade and overrun Hanover since 1757 in the hope of occupying the Electorate and using it as a bargaining counter to exchange for the return of French colonies captured by the British. The Allied army under the Duke of Brunswick had prevented them from taking Hanover, and by 1762, aware that the war was likely to draw to a close, the French had decided on a final thrust to try to defeat Brunswick and occupy Hanov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George III Of The United Kingdom
George III (George William Frederick; 4 June 173829 January 1820) was King of Great Britain and of Monarchy of Ireland, Ireland from 25 October 1760 until Acts of Union 1800, the union of the two kingdoms on 1 January 1801, after which he was King of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland until his death in 1820. He was the longest-lived and longest-reigning king in British history. He was concurrently Duke and Prince-elector of Electorate of Brunswick-Lüneburg, Brunswick-Lüneburg ("Hanover") in the Holy Roman Empire before becoming King of Hanover on 12 October 1814. He was a monarch of the House of Hanover but, unlike his two predecessors, he was born in Great Britain, spoke English as his first language and never visited Hanover. George's life and reign were marked by a series of military conflicts involving his kingdoms, much of the rest of Europe, and places farther afield in Africa, the Americas and Asia. Early in his reign, Great Britain defeated France in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)