|
1997 Qayen Earthquake
The Qayen earthquake, also known as the Ardekul or Qaen earthquake, struck northern Iran's Khorasan Province in the vicinity of Qaen on May 10, 1997 at 07:57 UTC (12:57 local time). The largest in the area since 1990, the earthquake registered 7.3 on the moment magnitude scale and was centered approximately south of Mashhad on the village of Ardekul. The third earthquake that year to cause severe damage, it devastated the Birjand– Qayen region, killing 1,567 and injuring more than 2,300. The earthquake—which left 50,000 homeless and damaged or destroyed over 15,000 homes—was described as the deadliest of 1997 by the United States Geological Survey. Some 155 aftershocks caused further destruction and drove away survivors. The earthquake was later discovered to have been caused by a rupture along a fault that runs underneath the Iran–Afghanistan border. Damage was eventually estimated at $100 million, and many countries responded to the emergency ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fault (geology)
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic forces, with the largest forming the boundaries between the plates, such as the megathrust faults of subduction zones or transform faults. Energy release associated with rapid movement on active faults is the cause of most earthquakes. Faults may also displace slowly, by aseismic creep. A ''fault plane'' is the plane that represents the fracture surface of a fault. A ''fault trace'' or ''fault line'' is a place where the fault can be seen or mapped on the surface. A fault trace is also the line commonly plotted on geologic maps to represent a fault. A ''fault zone'' is a cluster of parallel faults. However, the term is also used for the zone of crushed rock along a single fault. Prolonged motion along closely spaced faults can blur the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Geophysicist
Geophysics () is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term ''geophysics'' sometimes refers only to solid earth applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations and pure scientists use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial physics; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets. Gutenberg, B., 1929, Lehrbuch der Geophysik. Leipzig. Berlin (Gebruder Borntraeger). Runcorn, S.K, (editor-in-chief), 1967, International ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iranian Plate
The Iranian Plate is a small tectonic plate thought to underlie the Persian plateau, covering the modern-day countries of Iran and Afghanistan, and parts of Iraq and Pakistan. It is compressed between the Arabian Plate to the southwest, the Eurasian Plate to the north, and the Indian Plate to the southeast. This compression is likely a cause for the very mountainous terrain of the area including the Alborz and Zagros Mountains The Zagros Mountains ( ar, جبال زاغروس, translit=Jibal Zaghrus; fa, کوههای زاگرس, Kuh hā-ye Zāgros; ku, چیاکانی زاگرۆس, translit=Çiyakani Zagros; Turkish: ''Zagros Dağları''; Luri: ''Kuh hā-ye Zāgro .... References * William Bayne Fisher''The Middle East: a Physical, Social, and Regional Geography'' Routledge 1978, , p. 15–16 Tectonic plates Geology of Afghanistan Geology of Iran Geology of Iraq Geology of Pakistan {{tectonics-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
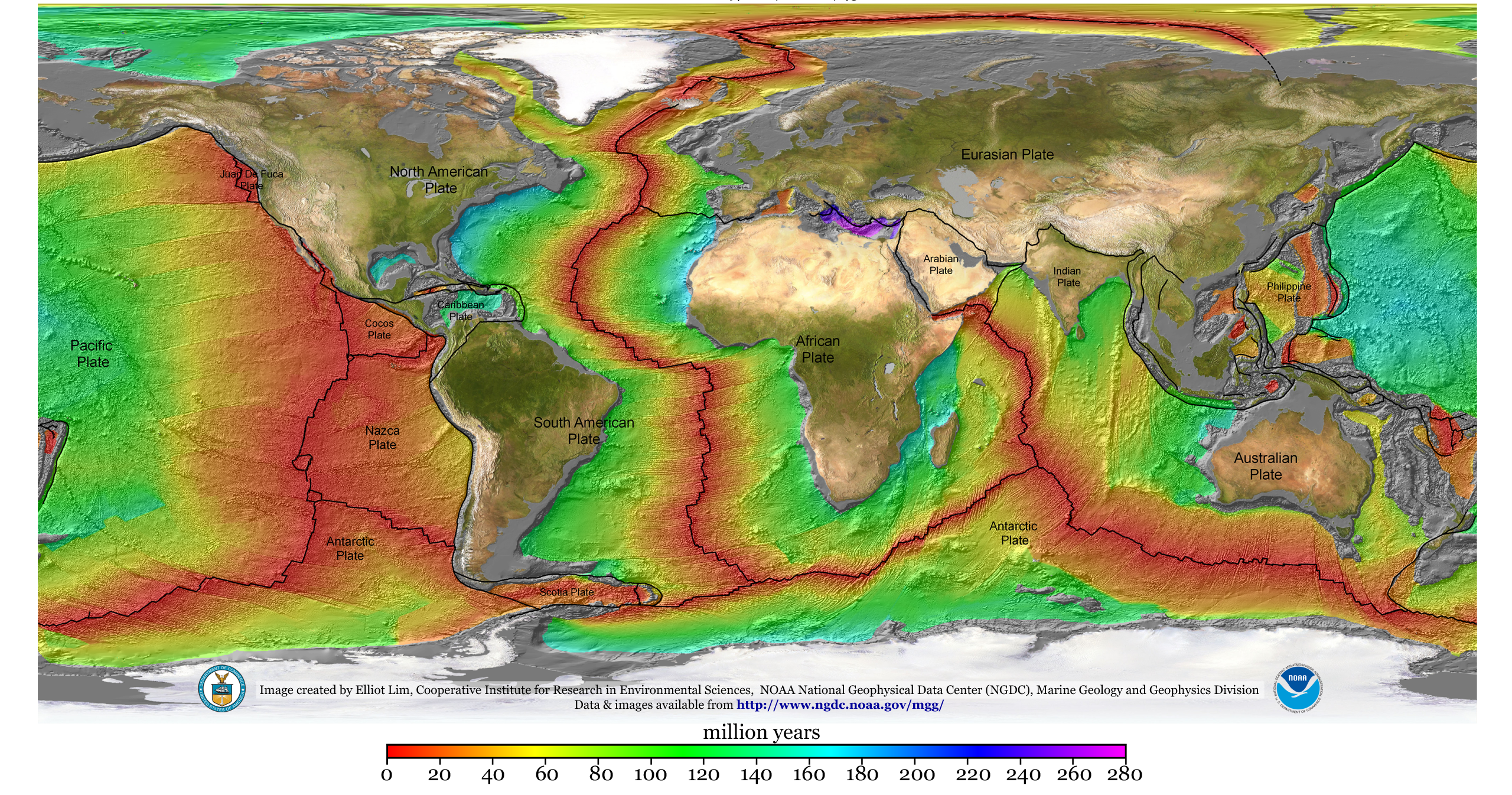
Plate Tectonics
Plate tectonics (from the la, label=Late Latin, tectonicus, from the grc, τεκτονικός, lit=pertaining to building) is the generally accepted scientific theory that considers the Earth's lithosphere to comprise a number of large tectonic plates which have been slowly moving since about 3.4 billion years ago. The model builds on the concept of ''continental drift'', an idea developed during the first decades of the 20th century. Plate tectonics came to be generally accepted by geoscientists after seafloor spreading was validated in the mid to late 1960s. Earth's lithosphere, which is the rigid outermost shell of the planet (the crust and upper mantle), is broken into seven or eight major plates (depending on how they are defined) and many minor plates or "platelets". Where the plates meet, their relative motion determines the type of plate boundary: '' convergent'', '' divergent'', or ''transform''. Earthquakes, volcanic activity, mountain-building, and oceanic tr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eurasian Plate
The Eurasian Plate is a tectonic plate that includes most of the continent of Eurasia (a landmass consisting of the traditional continents of Europe and Asia), with the notable exceptions of the Indian subcontinent, the Arabian subcontinent and the area east of the Chersky Range in eastern Siberia. It also includes oceanic crust extending westward to the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and northward to the Gakkel Ridge. The eastern edge is a boundary with the North American Plate to the north and a boundary with the Philippine Sea Plate to the south and possibly with the Okhotsk Plate and the Amurian Plate. The southern edge is a boundary with the African Plate to the west, the Arabian Plate in the middle and the Indo-Australian Plate to the east. The western edge is a divergent boundary with the North American Plate forming the northernmost part of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, which is straddled by Iceland. All volcanic eruptions in Iceland, such as the 1973 eruption of Eldfell, the 1783 eruptio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabian Plate
The Arabian Plate is a minor tectonic plate in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres. It is one of the three continental plates (along with the African and the Indian Plates) that have been moving northward in geological history and colliding with the Eurasian Plate. That is resulting in a mingling of plate pieces and mountain ranges extending in the west from the Pyrenees, crossing Southern Europe to Iran, forming the Alborz and the Zagros Mountains, to the Himalayas and ranges of Southeast Asia. Lexicology The ''Arabian Plate'' is a designation of the region, and it is also sometimes referred to as the ''Arab Plate''. Borders The Arabian Plate consists mostly of the Arabian Peninsula; it extends westward to the Sinai Peninsula and the Red Sea and northward to the Levant. The plate borders are: *East, with the Indian Plate, at the Owen Fracture Zone *South, with the African Plate to the west and the Somali Plate and the Indian Plate to the east *West, a left lateral fa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Suture Zone
In structural geology, a suture is a joining together along a major fault zone, of separate terranes, tectonic units that have different plate tectonic, metamorphic and paleogeographic histories. The suture is often represented on the surface by an orogen or mountain range. Overview In plate tectonics, sutures are the remains of subduction zones, and the terranes that are joined together are interpreted as fragments of different palaeocontinents or tectonic plates. Outcrops of sutures can vary in width from a few hundred meters to a couple of kilometers. They can be networks of mylonitic shear zones or brittle fault zones, but are usually both. Sutures are usually associated with igneous intrusions and tectonic lenses with varying kinds of lithologies from plutonic rocks to ophiolitic fragments. An example from Great Britain is the Iapetus Suture which, though now concealed beneath younger rocks, has been determined by geophysical means to run along a line roughly parallel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crocus Sativus2
''Crocus'' (; plural: crocuses or croci) is a genus of seasonal flowering plants in the family Iridaceae (iris family) comprising about 100 species of perennials growing from corms. They are low growing plants, whose flower stems remain underground, that bear relatively large white, yellow, orange or purple flowers and then become dormant after flowering. Many are cultivated for their flowers, appearing in autumn, winter, or spring. The flowers close at night and in overcast weather conditions. The crocus has been known throughout recorded history, mainly as the source of saffron. Saffron is obtained from the dried stigma of ''Crocus sativus'', an autumn-blooming species. It is valued as a spice and dyestuff, and is one of the most expensive spices in the world. Iran is the center of saffron production. Crocuses are native to woodland, scrub, and meadows from sea level to alpine tundra from the Mediterranean, through North Africa, central and southern Europe, the islands of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mercalli Intensity Scale
The Modified Mercalli intensity scale (MM, MMI, or MCS), developed from Giuseppe Mercalli's Mercalli intensity scale of 1902, is a seismic intensity scale used for measuring the intensity of shaking produced by an earthquake. It measures the effects of an earthquake at a given location, distinguished from the earthquake's inherent force or strength as measured by seismic magnitude scales (such as the "" magnitude usually reported for an earthquake). While shaking is caused by the seismic energy released by an earthquake, earthquakes differ in how much of their energy is radiated as seismic waves. Deeper earthquakes also have less interaction with the surface, and their energy is spread out across a larger volume. Shaking intensity is localized, generally diminishing with distance from the earthquake's epicenter, but can be amplified in sedimentary basins and certain kinds of unconsolidated soils. Intensity scales empirically categorize the intensity of shaking based on the effect ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Surface Wave Magnitude
The surface wave magnitude (M_s) scale is one of the magnitude scales used in seismology to describe the size of an earthquake. It is based on measurements of Rayleigh surface waves that travel along the uppermost layers of the Earth. This magnitude scale is related to the local magnitude scale proposed by Charles Francis Richter in 1935, with modifications from both Richter and Beno Gutenberg throughout the 1940s and 1950s. It is currently used in People's Republic of China as a national standard (GB 17740-1999) for categorising earthquakes. Recorded magnitudes of earthquakes through the mid 20th century, commonly attributed to Richter, could be either M_s or M_L. Definition The formula to calculate surface wave magnitude is: :M_s = \log_\left(\frac\right)_ + \sigma(\Delta)\,, where A is the maximum particle displacement in surface waves (vector sum of the two horizontal displacements) in μm, T is the corresponding period in s (usually 20 2 seconds), Δ is the epi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1979 Ghaenat Earthquakes
The 1979 Ghaenat earthquakes were a series of large earthquakes in Qaen County, Khorasan Province, northeast Iran, near the Afghanistan border. The first mainshock, known as the Korizan earthquake with a surface wave magnitude () of 6.6 and moment magnitude () of 6.8, struck on November 14, while the 7.1 or 7.2 Koli-Boniabad earthquake struck on November 27. The two mainshocks were assigned a maximum Modified Mercalli intensity of VIII (''Severe'') and X (''Extreme''), respectively. The earthquakes caused extensive damage throughout northeastern Iran, killing an estimated 297 to 440 people and left at least 279 injured. Tectonic setting Iran is situated within the Alpide belt, an active orogenic belt that spans the entire country. This tectonic environment is influenced by the oblique collision of the Arabian and Eurasian Plates at an estimated rate of 22 mm/yr. Iran itself is situated on the Eurasian Plate, where it hosts complex zones of faults, forming tectonic blocks within ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sistan
Sistān ( fa, سیستان), known in ancient times as Sakastān ( fa, سَكاستان, "the land of the Saka"), is a historical and geographical region in present-day Eastern Iran ( Sistan and Baluchestan Province) and Southern Afghanistan (Nimruz, Helmand, Kandahar). Largely desert, the region is bisected by the Helmand River, the largest river in Afghanistan, which empties into the Hamun Lake that forms part of the border between the two countries. Etymology Sistan derives its name from ''Sakastan'' ("the land of the Saka"). The Sakas were a Scythians, Scythian tribe which from the 2nd century BC to the 1st century migrated to the Iranian Plateau and Indus valley, where they carved a kingdom known as the Indo-Scythians, Indo-Scythian Kingdom. In the Bundahishn, a Zoroastrian scripture written in Middle Persian, Pahlavi, the province is called "Seyansih". After the Muslim conquest of Persia, Arab conquest of Iran, the province became known as Sijistan/Sistan. The more ancien ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |