|
1969 Atlantic Hurricane Season
The 1969 Atlantic hurricane season was the most active Atlantic hurricane season since the 1933 season, and was the final year of the most recent positive ("high-quality") Atlantic multidecadal oscillation (AMO) era. The hurricane season officially began on June 1, and lasted until November 30. The season had the highest number of systems reach hurricane status – twelve – in a single season, until that record was surpassed in 2005. The season was above-average despite an El Niño, which typically suppresses activity in the Atlantic Ocean, while increasing tropical cyclone activity in the Pacific Ocean. Activity began with a tropical depression that caused extensive flooding in Cuba and Jamaica in early June. On July 25, Tropical Storm Anna developed, the first named storm of the season. Later in the season, Tropical Depression Twenty-Nine caused severe local flooding in the Florida Panhandle and southwestern Georgia in September. The most significant storm of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
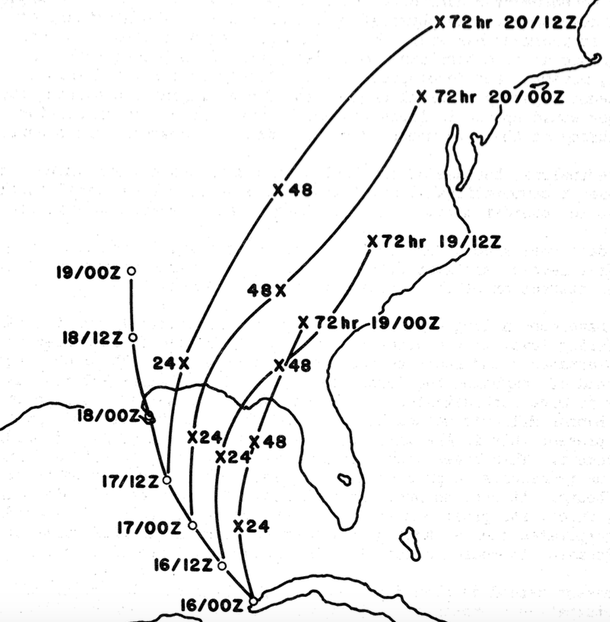
Hurricane Camille
Hurricane Camille was the second most intense tropical cyclone on record to strike the United States, behind the 1935 Labor Day hurricane. The most intense storm of the 1969 Atlantic hurricane season, Camille originated as a tropical depression on August 14, south of Cuba, from a long-tracked tropical wave. Located in a favorable environment for strengthening, the storm quickly intensified into a Category 2 hurricane before striking the western part of Cuba on August 15. Emerging into the Gulf of Mexico, Camille underwent another period of rapid intensification and became a Category 5 hurricane the next day as it moved northward towards the Louisiana–Mississippi region. Despite weakening slightly on August 17, the hurricane quickly re-intensified back into a Category 5 hurricane before it made landfall a half-hour before midnight in Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. At peak intensity, the hurricane had peak 1-minute sustained winds of 175 mph (280 km/h) and a mi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mississippi
Mississippi () is a state in the Southeastern region of the United States, bordered to the north by Tennessee; to the east by Alabama; to the south by the Gulf of Mexico; to the southwest by Louisiana; and to the northwest by Arkansas. Mississippi's western boundary is largely defined by the Mississippi River. Mississippi is the 32nd largest and 35th-most populous of the 50 U.S. states and has the lowest per-capita income in the United States. Jackson is both the state's capital and largest city. Greater Jackson is the state's most populous metropolitan area, with a population of 591,978 in 2020. On December 10, 1817, Mississippi became the 20th state admitted to the Union. By 1860, Mississippi was the nation's top cotton-producing state and slaves accounted for 55% of the state population. Mississippi declared its secession from the Union on January 9, 1861, and was one of the seven original Confederate States, which constituted the largest slaveholding states in t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Debbie (1969)
Hurricane Debbie was an intense and long-lived hurricane that formed during August 1969. The fifth tropical cyclone, fourth named storm, third hurricane and second major hurricane of the 1969 Atlantic hurricane season, Debbie formed on August 14 in the southern Atlantic Ocean and took a general northwesterly path until turning northward into the central Atlantic. The storm was characterized by numerous fluctuations in intensity, but it still reached winds corresponding to Category 3 status on the Saffir–Simpson scale. The hurricane bypassed the island of Bermuda to the southeast on August 22, before ultimately brushing southeastern Newfoundland with strong winds. It dissipated over the cold waters east of Greenland. Although Debbie had little effect on land, it was extensively researched and was subject to a weather modification experiment by Project Stormfury, in which it was seeded with silver iodide. Meteorological history A disturbance associated with a tropical ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Costa Rica
Costa Rica (, ; ; literally "Rich Coast"), officially the Republic of Costa Rica ( es, República de Costa Rica), is a country in the Central American region of North America, bordered by Nicaragua to the north, the Caribbean Sea to the northeast, Panama to the southeast, the Pacific Ocean to the southwest, and Maritime boundary, maritime border with Ecuador to the south of Cocos Island. It has a population of around five million in a land area of . An estimated 333,980 people live in the capital and largest city, San José, Costa Rica, San José, with around two million people in the surrounding metropolitan area. The sovereign state is a Unitary state, unitary Presidential system, presidential Constitution of Costa Rica, constitutional republic. It has a long-standing and stable democracy and a highly educated workforce. The country spends roughly 6.9% of its budget (2016) on education, compared to a global average of 4.4%. Its economy, once heavily dependent on agricultu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Panama
Panama ( , ; es, link=no, Panamá ), officially the Republic of Panama ( es, República de Panamá), is a transcontinental country spanning the southern part of North America and the northern part of South America. It is bordered by Costa Rica to the west, Colombia to the southeast, the Caribbean Sea to the north, and the Pacific Ocean to the south. Its capital and largest city is Panama City, whose metropolitan area is home to nearly half the country's million people. Panama was inhabited by indigenous tribes before Spanish colonists arrived in the 16th century. It broke away from Spain in 1821 and joined the Republic of Gran Colombia, a union of Nueva Granada, Ecuador, and Venezuela. After Gran Colombia dissolved in 1831, Panama and Nueva Granada eventually became the Republic of Colombia. With the backing of the United States, Panama seceded from Colombia in 1903, allowing the construction of the Panama Canal to be completed by the United States Army Corps of En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Martha
Hurricane Martha was the only known tropical cyclone to make landfall in Panama. The eighteenth named storm and twelfth hurricane of the 1969 Atlantic hurricane season, Martha developed in the southwestern Caribbean Sea on November 21. Initially, the storm developed with sustained winds of , skipping tropical depression status. It remained stationary and quickly intensified into a hurricane. Martha attained maximum sustained winds of on November 22. Subsequently, Martha weakened and drifted southward. On November 24, Martha made landfall in Veraguas Province, Panama, as a strong tropical storm. The system weakened to a tropical depression and dissipated over land on November 25. Because the storm weakened prior to landfall, strong winds were not expected or reported in the impacted countries. In Panama, more than of precipitation may have fallen in some areas. Agricultural land was flooded in Almirante, Bocas del Toro and streets became inundated in low-lyin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Inga (1969)
Hurricane Inga is the third longest-lived Atlantic hurricane on record. The 11th tropical cyclone and 9th named storm of the 1969 Atlantic hurricane season, Inga developed on September 20 in the central Atlantic and tracked westward. After attaining tropical storm status, the system deteriorated into a depression, but once again intensified several days later. The storm eventually peaked in strength on October 5, with winds corresponding to Category 2 on the modern-day Saffir–Simpson hurricane scale. Throughout its path, Inga underwent several changes in direction and oscillations in strength, before dissipating on October 15, 25 days after it formed. Despite its duration, Inga caused little damage, and mostly remained over open waters. Meteorological history On September 20, a tropical disturbance in the Atlantic Ocean developed into a tropical depression. On the next morning, the National Hurricane Center reported that the system became a tropical storm while centered about ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central America
Central America ( es, América Central or ) is a subregion of the Americas. Its boundaries are defined as bordering the United States to the north, Colombia to the south, the Caribbean Sea to the east, and the Pacific Ocean to the west. Central America consists of eight countries: Belize, Costa Rica, El Salvador, Guatemala, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, and Panama. Within Central America is the Mesoamerican biodiversity hotspot, which extends from northern Guatemala to central Panama. Due to the presence of several active geologic faults and the Central America Volcanic Arc, there is a high amount of seismic activity in the region, such as volcanic eruptions and earthquakes which has resulted in death, injury, and property damage. In the pre-Columbian era, Central America was inhabited by the indigenous peoples of Mesoamerica to the north and west and the Isthmo-Colombian peoples to the south and east. Following the Spanish expedition of Christopher Columbus' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Francelia
Hurricane Francelia was the deadliest hurricane of the 1969 Atlantic hurricane season after causing significant flooding to Central America, especially Belize and Guatemala. The sixth named storm and fourth hurricane of the season, Francelia developed from a tropical wave in the southeastern Caribbean Sea on August 29. It moved west-northwestward and strengthened into a tropical storm on the following day. On September 1, Francelia reached hurricane status, shortly before re-curving west-southwest. While approaching Central America, the storm intensified and peaked as a 100 mph (155 km/h) Category 2 hurricane on September 2. Francelia weakened slightly before making landfall near Punta Gorda, Belize (then British Honduras) late on September 3. The storm quickly weakened inland and dissipated by the following day. During its early stages, Francelia brought gusty winds and light rainfall to several islands in the Caribbean Sea. While remaining near ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1972 Atlantic Hurricane Season
The 1972 Atlantic hurricane season was a significantly below average season, having only seven named storms, four fully tropical storms (the fewest since 1930) and three subtropical storms. It officially began on June 1, 1972, and lasted until November 30, 1972. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the Atlantic basin. The first storm, Subtropical Storm Alpha, developed on May 23 off the Southeast United States and struck Florida, causing minor damage and two fatalities. Although several other tropical depressions developed, only Tropical Depression Five is known to have affected land. The most significant storm of the season was Hurricane Agnes, which at the time was the costliest United States hurricane, until Frederic in 1979. After brushing the western tip of Cuba, the hurricane made landfall on the Florida Panhandle. It caused at least $2.1 billion (1972 USD) in damage and 137 fatalitie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hurricane Agnes
Hurricane Agnes in 1972 was the costliest hurricane to hit the United States at the time, causing an estimated $2.1 billion in damage. The hurricane's death toll was 128. The effects of Agnes were widespread, from the Caribbean to Canada, with much of the east coast of the United States affected. Damage was heaviest in Pennsylvania, where Agnes was the state's wettest tropical cyclone. Due to the significant effects, the name ''Agnes'' was retired in the spring of 1973. Agnes was the second tropical cyclone and first named storm of the 1972 Atlantic hurricane season. It developed as a tropical depression on June 14 from the interaction of a polar front and an upper trough over the Yucatán Peninsula. The storm emerged into the western Caribbean Sea on June 15, and strengthened into Tropical Storm Agnes the next day. Thereafter, Agnes slowly curved northward and passed just west of Cuba on June 17. Early on June 18, the storm intensified enough to be u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Dollars
The United States dollar ( symbol: $; code: USD; also abbreviated US$ or U.S. Dollar, to distinguish it from other dollar-denominated currencies; referred to as the dollar, U.S. dollar, American dollar, or colloquially buck) is the official currency of the United States and several other countries. The Coinage Act of 1792 introduced the U.S. dollar at par with the Spanish silver dollar, divided it into 100 cents, and authorized the minting of coins denominated in dollars and cents. U.S. banknotes are issued in the form of Federal Reserve Notes, popularly called greenbacks due to their predominantly green color. The monetary policy of the United States is conducted by the Federal Reserve System, which acts as the nation's central bank. The U.S. dollar was originally defined under a bimetallic standard of (0.7735 troy ounces) fine silver or, from 1837, fine gold, or $20.67 per troy ounce. The Gold Standard Act of 1900 linked the dollar solely to gold. From 1934, its e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)




