|
1882 In Science
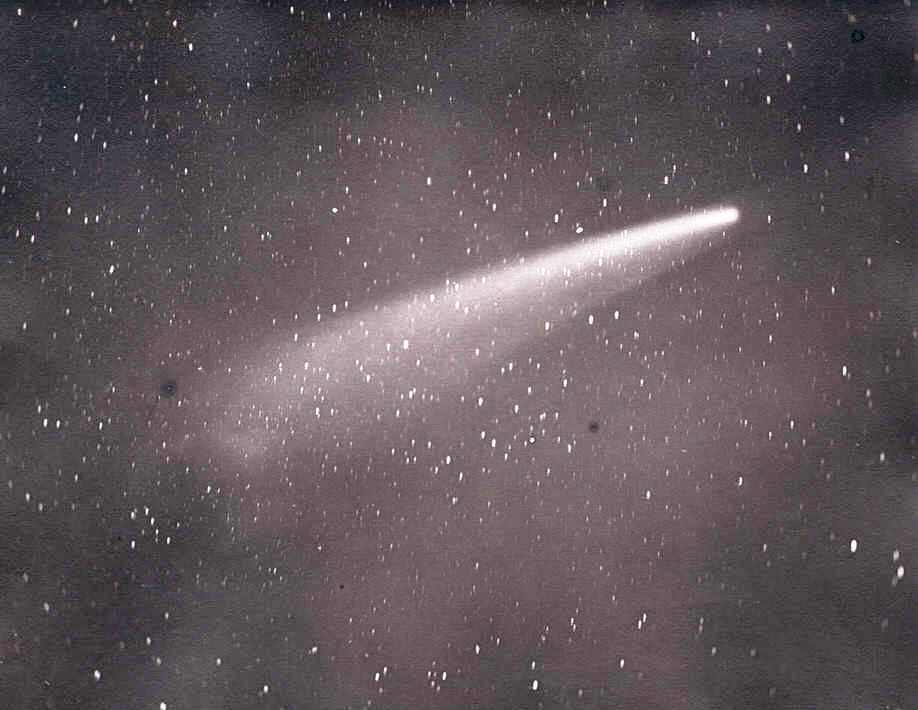
The year 1882 in science and technology involved some significant events, listed below. Astronomy * September – Great Comet of 1882 sighted. * December 6 – Transit of Venus, 1882. Biology * March 24 – Robert Koch announces his discovery of the bacterium responsible for tuberculosis, ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis''. * Élie Metchnikoff discovers phagocytosis. Chemistry * Italian physicist Luigi Palmieri detects helium on Earth for the first time through its D3 spectral line when he analyzes the lava of Mount Vesuvius. Earth sciences * Clarence Dutton's ''Tertiary History of the Grand Cañon District'' is published by the United States Geological Survey. Mathematics * June – German mathematician Ferdinand von Lindemann publishes proof that is a transcendental number and that squaring the circle is consequently impossible. * December – Swedish mathematician Gösta Mittag-Leffler establishes the journal ''Acta Mathematica''. * Felix Klein first desc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science
Science is a systematic endeavor that Scientific method, builds and organizes knowledge in the form of Testability, testable explanations and predictions about the universe. Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence for scientific reasoning is tens of thousands of years old. The earliest written records in the history of science come from Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia in around 3000 to 1200 Common Era, BCE. Their contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine entered and shaped Greek natural philosophy of classical antiquity, whereby formal attempts were made to provide explanations of events in the Universe, physical world based on natural causes. After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, knowledge of History of science in classical antiquity, Greek conceptions of the world deteriorated in Western Europe during the early centuries (400 to 1000 CE) of the Middle Ages, but was preserved in the Muslim world during the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mount Vesuvius
Mount Vesuvius ( ; it, Vesuvio ; nap, 'O Vesuvio , also or ; la, Vesuvius , also , or ) is a somma- stratovolcano located on the Gulf of Naples in Campania, Italy, about east of Naples and a short distance from the shore. It is one of several volcanoes forming the Campanian volcanic arc. Vesuvius consists of a large cone partially encircled by the steep rim of a summit caldera, resulting from the collapse of an earlier, much higher structure. The eruption of Mount Vesuvius in AD 79 destroyed the Roman cities of Pompeii, Herculaneum, Oplontis, Stabiae, and several other settlements. The eruption ejected a cloud of stones, ashes and volcanic gases to a height of , erupting molten rock and pulverized pumice at the rate of per second. More than 1,000 people are thought to have died in the eruption, though the exact toll is unknown. The only surviving eyewitness account of the event consists of two letters by Pliny the Younger to the historian Tacitus. Vesuvi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Beiersdorf
Paul Carl Beiersdorf (26 March 1836 – 17 December 1896) was a German pharmacist from Neuruppin, Brandenburg. He was founder of Beiersdorf AG in Hamburg. Life In 1880 he founded the Beiersdorf Company, a Hamburg pharmaceutical operation where he had close business ties to dermatologist Paul Gerson Unna. In 1882 Beiersdorf developed and patented a new type of medical plaster called ''Guttaperchapflastermulle'' (gutta-percha plaster gauze). The date of patent specification, 28 March 1882, is considered to be the founding date of Beiersdorf AG. In 1890 he sold the company to pharmacist Oscar Troplowitz Oscar Troplowitz (18 January 1863 – 27 April 1918) was a German pharmacist and entrepreneur. Troplowitz trained at Heidelberg University and in 1890 he purchased Beiersdorf AG, which at the time was a chemist's shop and laboratory in Hamburg ..., who retained the company's name of "Beiersdorf". Today, Beiersdorf AG is a multi-national corporation that is based in Hamburg, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Klein Bottle
In topology, a branch of mathematics, the Klein bottle () is an example of a non-orientable surface; it is a two-dimensional manifold against which a system for determining a normal vector cannot be consistently defined. Informally, it is a one-sided surface which, if traveled upon, could be followed back to the point of origin while flipping the traveler upside down. Other related non-orientable objects include the Möbius strip and the real projective plane. While a Möbius strip is a surface with boundary, a Klein bottle has no boundary. For comparison, a sphere is an orientable surface with no boundary. The concept of a Klein bottle was first described in 1882 by the German mathematician Felix Klein. Construction The following square is a fundamental polygon of the Klein bottle. The idea is to 'glue' together the corresponding red and blue edges with the arrows matching, as in the diagrams below. Note that this is an "abstract" gluing in the sense that trying to rea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Felix Klein
Christian Felix Klein (; 25 April 1849 – 22 June 1925) was a German mathematician and mathematics educator, known for his work with group theory, complex analysis, non-Euclidean geometry, and on the associations between geometry and group theory. His 1872 Erlangen program, classifying geometries by their basic symmetry groups, was an influential synthesis of much of the mathematics of the time. Life Felix Klein was born on 25 April 1849 in Düsseldorf, to Prussian parents. His father, Caspar Klein (1809–1889), was a Prussian government official's secretary stationed in the Rhine Province. His mother was Sophie Elise Klein (1819–1890, née Kayser). He attended the Gymnasium in Düsseldorf, then studied mathematics and physics at the University of Bonn, 1865–1866, intending to become a physicist. At that time, Julius Plücker had Bonn's professorship of mathematics and experimental physics, but by the time Klein became his assistant, in 1866, Plücker's interes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Acta Mathematica
''Acta Mathematica'' is a peer-reviewed open-access scientific journal covering research in all fields of mathematics. According to Cédric Villani, this journal is "considered by many to be the most prestigious of all mathematical research journals".. According to the ''Journal Citation Reports'', the journal has a 2020 impact factor of 4.273, ranking it 5th out of 330 journals in the category "Mathematics". Publication history The journal was established by Gösta Mittag-Leffler in 1882 and is published by Institut Mittag-Leffler, a research institute for mathematics belonging to the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences. The journal was printed and distributed by Springer from 2006 to 2016. Since 2017, Acta Mathematica has been published electronically and in print by International Press. Its electronic version is open access without publishing fees. Poincaré episode The journal's "most famous episode" (according to Villani) concerns Henri Poincaré, who won a prize offered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
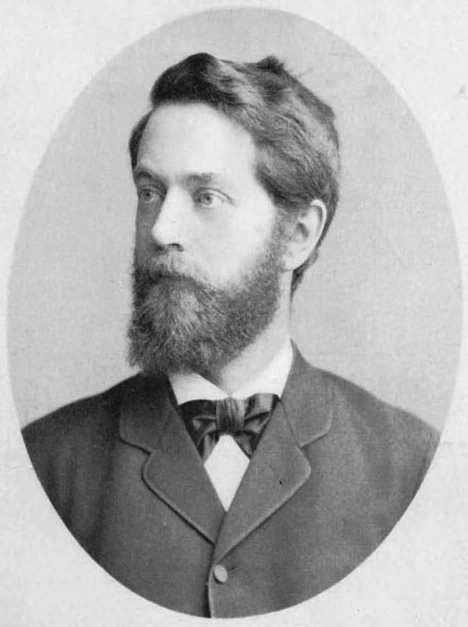
Gösta Mittag-Leffler
Magnus Gustaf "Gösta" Mittag-Leffler (16 March 1846 – 7 July 1927) was a Swedish mathematician. His mathematical contributions are connected chiefly with the theory of functions, which today is called complex analysis. Biography Mittag-Leffler was born in Stockholm, son of the school principal John Olof Leffler and Gustava Wilhelmina Mittag; he later added his mother's maiden name to his paternal surname. His sister was the writer Anne Charlotte Leffler. He matriculated at Uppsala University in 1865, completed his PhD in 1872 and became docent at the university the same year. He was also curator (chairman) of the Stockholms nation (1872–1873). He next traveled to Paris, Göttingen and Berlin, studying under Weierstrass in the latter place. During this period he edited a weekly newspaper, '' Ny Illustrerad Tidning'', which was based in Stockholm. He then took up a position as professor of mathematics (as successor to Lorenz Lindelöf) at the University of Helsinki from 187 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedes
Swedes ( sv, svenskar) are a North Germanic ethnic group native to the Nordic region, primarily their nation state of Sweden, who share a common ancestry, culture, history and language. They mostly inhabit Sweden and the other Nordic countries, in particular Finland where they are an officially recognized minority, with a substantial diaspora in other countries, especially the United States. Etymology The English term "Swede" has been attested in English since the late 16th century and is of Middle Dutch or Middle Low German origin. In Swedish, the term is ''svensk'', which is from the name of ''svear'' (or Swedes), the people who inhabited Svealand in eastern central Sweden, and were listed as ''Suiones'' in Tacitus' history ''Germania'' from the first century AD. The term is believed to have been derived from the Proto-Indo-European reflexive pronominal root, , as the Latin ''suus''. The word must have meant "one's own (tribesmen)". The same root and original meanin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematische Annalen
''Mathematische Annalen'' (abbreviated as ''Math. Ann.'' or, formerly, ''Math. Annal.'') is a German mathematical research journal founded in 1868 by Alfred Clebsch and Carl Neumann. Subsequent managing editors were Felix Klein, David Hilbert, Otto Blumenthal, Erich Hecke, Heinrich Behnke, Hans Grauert, Heinz Bauer, Herbert Amann, Jean-Pierre Bourguignon, Wolfgang Lück, and Nigel Hitchin. Currently, the managing editor of Mathematische Annalen is Thomas Schick. Volumes 1–80 (1869–1919) were published by Teubner. Since 1920 (vol. 81), the journal has been published by Springer. In the late 1920s, under the editorship of Hilbert, the journal became embroiled in controversy over the participation of L. E. J. Brouwer on its editorial board, a spillover from the foundational Brouwer–Hilbert controversy. Between 1945 and 1947 the journal briefly ceased publication. References External links''Mathematische Annalen''homepage at Springer Springer or springers may refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Squaring The Circle
Squaring the circle is a problem in geometry first proposed in Greek mathematics. It is the challenge of constructing a square with the area of a circle by using only a finite number of steps with a compass and straightedge. The difficulty of the problem raised the question of whether specified axioms of Euclidean geometry concerning the existence of lines and circles implied the existence of such a square. In 1882, the task was proven to be impossible, as a consequence of the Lindemann–Weierstrass theorem, which proves that pi (\pi) is a transcendental number. That is, \pi is not the root of any polynomial with rational coefficients. It had been known for decades that the construction would be impossible if \pi were transcendental, but that fact was not proven until 1882. Approximate constructions with any given non-perfect accuracy exist, and many such constructions have been found. Despite the proof that it is impossible, attempts to square the circle have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcendental Number
In mathematics, a transcendental number is a number that is not algebraic—that is, not the root of a non-zero polynomial of finite degree with rational coefficients. The best known transcendental numbers are and . Though only a few classes of transcendental numbers are known—partly because it can be extremely difficult to show that a given number is transcendental—transcendental numbers are not rare. Indeed, almost all real and complex numbers are transcendental, since the algebraic numbers comprise a countable set, while the set of real numbers and the set of complex numbers are both uncountable sets, and therefore larger than any countable set. All transcendental real numbers (also known as real transcendental numbers or transcendental irrational numbers) are irrational numbers, since all rational numbers are algebraic. The converse is not true: not all irrational numbers are transcendental. Hence, the set of real numbers consists of non-overlapping rational, alg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ferdinand Von Lindemann
Carl Louis Ferdinand von Lindemann (12 April 1852 – 6 March 1939) was a German mathematician, noted for his proof, published in 1882, that (pi) is a transcendental number, meaning it is not a root of any polynomial with rational coefficients. Life and education Lindemann was born in Hanover, the capital of the Kingdom of Hanover. His father, Ferdinand Lindemann, taught modern languages at a Gymnasium in Hanover. His mother, Emilie Crusius, was the daughter of the Gymnasium's headmaster. The family later moved to Schwerin, where young Ferdinand attended school. He studied mathematics at Göttingen, Erlangen, and Munich. At Erlangen he received a doctorate, supervised by Felix Klein, on non-Euclidean geometry. Lindemann subsequently taught in Würzburg and at the University of Freiburg. During his time in Freiburg, Lindemann devised his proof that is a transcendental number (see Lindemann–Weierstrass theorem). After his time in Freiburg, Lindemann tra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |